on April 25th
464
1.5V Battery —— How Much Do You Know?
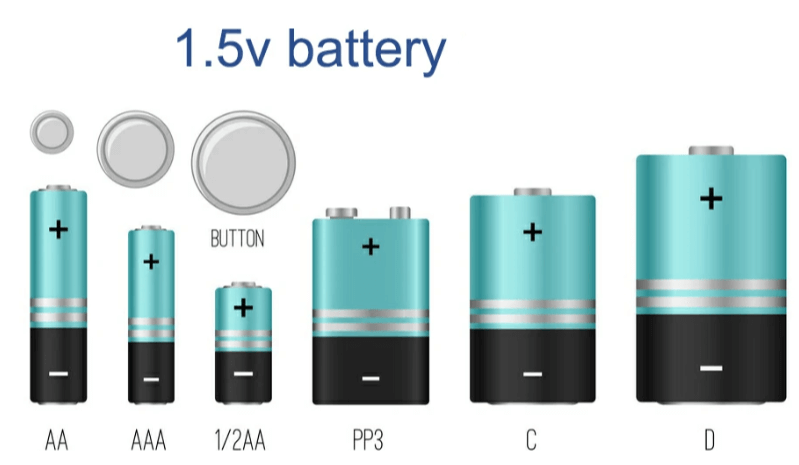
Exploring the dynamics of 1.5V batteries reveals not only their critical role in powering a diverse array of devices but also their rich historical and technological context. These batteries, which come in various forms such as AA, AAA, C, and D cells, have become indispensable in both everyday and specialized applications. Originating from the pioneering carbon-zinc cells that established 1.5 volts as a standard voltage, these batteries have evolved to meet the growing and changing demands of modern electronics. This discussion delves deep into the nuances of 1.5V battery technology, including the distinct types like alkaline and lithium, their respective chemistries, and the implications of these differences on their application and performance. Understanding these batteries' underlying principles and functionalities not only enhances our appreciation of their role in current technologies but also informs our choices in various applications, from household electronics to emergency equipment.
Catalog
Figure 1: 1.5V Battery
A 1.5V battery, commonly found in AA, AAA, C, and D cell forms, serves as a staple power source in a myriad of household devices. The origins of this voltage standard trace back to the development of the first carbon-zinc cells, which were revolutionary in providing a reliable 1.5 volts, thus setting the groundwork for the battery technology prevalent today. This voltage rating is an important reference because it matches well with the operational requirements of many electronic devices, allowing for optimal performance without risking damage from excessive power supply.
Exploring further into the types and functionalities of 1.5V batteries, we encounter two primary categories: alkaline and lithium. Alkaline batteries are distinguished by their higher energy capacity, making them suitable for powering devices with significant energy demands. The chemistry behind these batteries involves a reaction between zinc and manganese dioxide, facilitated by an alkaline electrolyte, typically potassium hydroxide. This reaction is highly efficient in terms of energy density, translating into longer battery life and reliability for consumer electronics such as digital cameras and children's toys, which require sustained power delivery to function optimally.
On the other spectrum are lithium 1.5V batteries, known for their exceptional durability and power density. These characteristics are primarily due to lithium's inherent properties, such as its lightweight and high electrochemical potential, which provide a greater energy output per weight compared to other battery types. Consequently, lithium 1.5V batteries are perfectly suited for both high-drain applications, including advanced digital cameras that consume a lot of power quickly, and low-drain applications, such as smoke detectors, which require a steady energy supply over extended periods. Remarkably, these batteries maintain their charge for up to nine years when stored, a feature that stands out, particularly in emergency or infrequent use scenarios.
Focusing on alkaline batteries, their near ubiquity in low-power consumer electronics can be attributed to their cost-effectiveness and the convenience they offer. Devices like wall clocks, remote controls, and small flashlights typically do not require intensive power consumption, which makes the energy output of AA alkaline batteries ideal. Their widespread availability and economic value also ensure that they are a go-to choice for many households, balancing performance and affordability.
However, it is crucial to note the non-rechargeable nature of standard 1.5V batteries, a fact that must be emphasized to prevent unsafe practices. Unlike rechargeable batteries that are designed to withstand multiple charging cycles without significant degradation, attempting to recharge a standard alkaline or lithium 1.5V battery can lead to chemical leakage or even explosions due to the unstable buildup of gases within the sealed unit. Therefore, proper disposal practices must be adhered to, ensuring these batteries are responsibly recycled or disposed of by local environmental standards to avoid harming both human health and the environment.
|
Name
|
Shape
|
Volts
|
|
AA
|
Cylinder L 50 mm, D 14.2 mm
|
1.5
|
|
AAA
|
Cylinder L 44.5 mm, D 10.5 mm
|
1.5
|
|
AAAA
|
Cylinder L 42 mm, D 8 mm
|
1.5
|
|
C
|
Cylinder L 46 mm, D 26 mm
|
1.5
|
|
D
|
Cylinder L 58 mm, D 33 mm
|
1.5
|
Chart
1: the Sizes of 1.5V Batteries
1.5V batteries come in various sizes and types, primarily classified into button and cylindrical categories. These batteries are integral to numerous portable devices, thanks to their versatility.
Figure 2: Battery Structure Internal Diagram
Button batteries are compact and lightweight, making them ideal for devices like watches, calculators, and certain medical equipment that require minimal space and weight. In contrast, cylindrical batteries, due to their larger size and capacity, are better suited for devices that need continuous power supply, such as flashlights, remote controls, and children's toys.
Let's delve into the details of button batteries. These are specified by their diameter and thickness. For instance, a battery with a diameter of 6.8 mm and a thickness of 2.1 mm can be found in both silver oxide and alkaline chemical compositions. Silver oxide batteries, such as the SR621 and SR60, are preferred for high-precision devices due to their stable voltage and longevity. On the other hand, alkaline batteries like the LR621 and AG1, which are cheaper, cater to devices where batteries are infrequently changed.
Looking at larger button batteries, the SR1130 series, measuring 11.6 mm in diameter and 3.1 mm in thickness, is also popular in watches and small electronic devices. These batteries provide a reliable and prolonged power supply, ensuring uninterrupted operation of the devices.
Figure 3: AA&AAA&AAAA Battery
Moving on to cylindrical batteries, the standardized sizes include but are not limited to AAA, AA, C, and D. For example, the AA battery measures 14.5 x 50.5 mm and is one of the most commonly used batteries, powering devices requiring moderate amounts of energy like remote controls and wireless mice.
Figure 4: C&D Battery
The larger D-size batteries, measuring 34.2 x 61.5 mm, are typically used in devices with higher energy consumption, such as motorized children's toys and portable speakers. Their larger size allows for a greater storage of energy, providing extended usage periods.
Each of these batteries is designed to fit specific device requirements, ensuring that whether it is a high-drain toy or a low-drain watch, the battery not only fits perfectly but also meets the energy demands efficiently. Careful matching of battery type to device not only ensures optimal performance and longevity but also increases user satisfaction and device reliability.
|
Name
|
Other Names
|
|
AA
|
R6, R06, MN1500, MX1500, PC1500, AM3, UM3, UM-3, HP7, 15AC,
15A, E91, EN91, 815, AL-AA, ALAA, 7524, HR6, HR06, LR06, LR6, X91, PC1501,
Mignon, Penlight, Double A, 2AA
|
|
AAA
|
LR03, LR3, LR03X, R03, R3, MN2400, MX2400, PC2400, AM4, UM4,
UM-4, HP16, 24AC, 24A, 24G, EN92, E92, 824, ALAAA, AL-AAA, 7526, 4003, K3A,
Micro, Microlight, Potlood, Penlight, Triple A, 3AAA
|
|
AAAA
|
LR61, 25A , MN2500, MX2500, E96, EN96, GP25A, LR8D425, 4061,
K4A, Quadruple A, Quad A, 4AAAA
|
|
C
|
LR14, R14, UM2, UM-2, MN1400, MX1400, PC1400, 14AC, 14A, E93,
EN93, 814, ALC, AL-C, 7522, AM2, HP11, Baby, Mignon
|
|
D
|
LR20, R20, R20MA, R20P, MN1300, MX1300, PC1300, UM1, UM-1,
SUM-1, AM1, 13AC, 13A, E95, EN95, 813, AL-D, 1250, 7520, HP2, HR20, Mono,
Goliath
|
Chart
2: Other Names for 1.5V Batteries
1.5V batteries are available in a variety of chemical compositions, each with specific characteristics and applications.
Zinc-Carbon Batteries
Zinc-carbon batteries, among the oldest types of non-rechargeable batteries, generally provide a nominal voltage of 1.5V. Their cutoff voltage typically ranges from 0.8 to 1.0V depending on the device in use. These batteries employ ammonium chloride as their standard electrolyte, with zinc chloride often used in the 'heavy-duty' variants. They are commonly found in cylindrical forms for 1.5V applications and are also used in batteries arranged in series to achieve higher voltages such as 4.5V, 6V, and 9V. Although zinc-carbon batteries are inexpensive and reliable, they are prone to leakage even without use, have a shorter storage life, and typically offer lower capacity and quicker voltage decline compared to alkaline batteries.
Figure 5: Zinc-Carbon Battery
Alkaline Batteries
Alkaline batteries, typically non-rechargeable and using a zinc-manganese dioxide chemistry with potassium hydroxide or a similar electrolyte, also maintain a nominal voltage of 1.5V, with a cutoff voltage between 0.9 and 1.0V. They have a longer shelf life, higher capacity, and greater energy density than zinc-carbon batteries and are less prone to leakage. Alkaline batteries are versatile, and used in both cylindrical and button cell formats. Despite their many benefits, the voltage of alkaline batteries also drops significantly as they discharge.
Figure 6: Alkaline Battery
Silver Oxide Batteries
Silver oxide batteries, another non-rechargeable option, typically offer a nominal voltage of 1.55V and a cutoff voltage of around 1.2V. These batteries maintain a very stable voltage output throughout their discharge cycle, making them ideal for powering sensitive instruments and devices. Silver oxide batteries offer longer shelf life and higher capacity without the leakage issues common with alkaline batteries. However, they are more expensive and primarily used in button cell applications.
Figure 7: Silver Oxide Battery
Zinc Air Batteries
Zinc air batteries are non-rechargeable with a nominal voltage typically between 1.4 to 1.45V and a cutoff voltage of about 1.05 to 1.1V. They offer significantly higher capacity compared to both alkaline and silver oxide batteries. One drawback is that their wet electrolyte can dry out over time, leading to battery failure regardless of discharge state. These batteries are primarily used in hearing aids; they are activated by removing a protective foil that allows air into the cell. Once activated, these batteries become operational within minutes. The lifespan of zinc air batteries can vary depending on local temperature and humidity conditions but can last unactivated for about three to four years.
Figure 8: Zinc Air Battery
Mercury Oxide Batteries
Mercury oxide batteries, which are no longer in use due to environmental concerns, had a nominal voltage of 1.35V and a cutoff voltage of 1.1V. They were favored for various sensitive instruments because of their stable voltage output but have been phased out due to their mercury content.
Each type of 1.5V battery offers distinct advantages and limitations, influencing their suitability for different devices and applications. Users choose based on factors such as device requirements, expected lifespan, environmental conditions, and budget.
|
Chemistry
|
Common Name
|
Rechargeable
|
Typical Capacity (mAh)
|
Voltage (V)
|
Chemistry
|
|
Zinc Carbon
|
R6, 15D
|
No
|
600 - 1600
|
1.5
|
Zinc Carbon
|
|
Alkaline
|
LR6, 15A
|
No (Mostly No)
|
1800 - 2700
|
1.5
|
Alkaline
|
|
Li-FeS2
|
FR6, 15LF
|
No
|
2700 - 3300
|
1.5 (1.8 max)
|
Li-FeS2
|
|
Lithium
|
-
|
Yes
|
1000-2000+
|
1.5
|
Lithium
|
|
NiCd
|
KR6, 1.2K2
|
Yes
|
600 - 1200
|
1.2
|
NiCd
|
|
NiMH
|
HR6, 1.2H2
|
Yes
|
700 - 2800
|
1.2
|
NiMH
|
|
NiOOH
|
-
|
No
|
2200 - 2700
|
1.5 (1.7 max)
|
NiOOH
|
|
NiZn
|
ZR6
|
Yes
|
1500 - 1800
|
1.6 - 1.65
|
NiZn
|
Chart
3: 1.5V Batteries of Different Chemistries
Lithium 1.5V batteries stand out for their capacity to power devices that consume a lot of energy quickly. Their most notable feature is that they do not leak and can function in devices for many years without needing a replacement, making them ideal for important applications such as digital cameras and smoke detectors. To ensure a device operates at its best, it's crucial to choose a battery whose capacity and power output match the device’s specifications. The long-term reliability of lithium batteries means they don’t require frequent changes, which is a significant advantage for users.
On the other hand, alkaline 1.5V batteries are the go-to choice for more common, everyday devices like TV remotes and children's toys. These batteries are also often used to power wall clocks, and cordless phones, and provide backup lighting with small flashlights. In the kitchen, various small appliances and beauty gadgets rely on AA batteries, as do portable audio-visual devices. Keeping a supply of these batteries at home ensures that daily-used devices always have power.
AA batteries are especially popular due to their versatility. They are broadly used in devices ranging from thermometers and pagers to cordless phones and are sometimes used in clocks that require only a minimal amount of power to operate.
AAA batteries, which are slightly less common than AA, are frequently used in a variety of devices including toys, thermometers, TV remotes, kitchen timers, graphic calculators, and bathroom scales. These batteries are ideal for devices that require less energy, making the smaller AAA size perfect for such applications.
Although not as widely used, AAAA batteries deliver powerful performance for their compact size. These slender batteries are essential for small devices that need a compact but strong power source, such as LED penlights, laser pointers, glucometers, hearing aid remotes, and digital styluses.
C batteries are designed for devices that use more power and may need batteries replaced more often. They are typically used in toys, flashlights, and radios, and are also found in automatic soap dispensers. Moreover, you can find these batteries in restrooms with battery-powered flushing sensors, highlighting their versatility.
D batteries are reserved for devices that need power for extended periods. These large batteries are ideal for powering large flashlights, audio equipment, and hands-free soap or paper towel dispensers, especially for heavy-duty applications like sensor faucets or air freshener systems. In these applications, whether the battery can provide long-lasting power is the primary consideration when people buy batteries.
The distinction between 1.5V and 3.7V batteries primarily hinges on their voltage levels and the devices they are designed to power, influenced significantly by their chemical composition, voltage characteristics, and rechargeability.
Voltage Levels and Device Compatibility
1.5V batteries are geared towards a broader range of less power-intensive devices found around the home, such as remote controls, flashlights, and digital cameras. These batteries are available in both disposable and rechargeable forms, including alkaline, zinc-carbon, and silver oxide types. Alkaline batteries are particularly favored for general use due to their longevity and reliable power output. For devices requiring precise voltage regulation, like watches and calculators, silver oxide batteries are preferred because of their stable output.
Conversely, 3.7V batteries typically support high-drain devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops. These devices require a robust power supply due to their energy-intensive functions. Batteries like lithium-ion or lithium-polymer that support these devices start with a nominal voltage of 3.7V but can peak up to 4.2V when fully charged, then slowly decrease as the battery depletes.
Chemical Composition and Performance
The variety of chemical compositions in 1.5V batteries allows them to serve a wider array of everyday devices. Alkaline batteries are common and provide dependable performance for regular use. Zinc-carbon batteries are more economical but offer lower performance, making them suitable for less demanding applications. Some 1.5V batteries are also available in lithium variants, which, though less common, offer rechargeability with greater energy density, giving them an edge over other types.
On the other hand, the chemical makeup of 3.7V batteries typically involves sophisticated lithium-based technologies—lithium cobalt oxide, lithium iron phosphate, or lithium polymer. These materials are chosen for their ability to hold a high energy density, which translates into longer battery life and consistent power delivery throughout the battery's life. This consistency helps maintain the performance of the equipment it powers.
Rechargeability and Sustainability
1.5V batteries include both disposable and rechargeable options. The disposable types are convenient and widely used, available in multiple capacities to suit various needs. Rechargeable 1.5V lithium-ion batteries, although not as widespread, offer a sustainable alternative by minimizing waste and providing extended usability compared to their single-use counterparts.
In contrast, one of the significant advantages of 3.7V batteries is their rechargeability. Designed to endure multiple charge and discharge cycles, these batteries are both cost-effective and environmentally friendly over their lifecycle. Maintaining these batteries requires proper chargers that can accommodate their specific needs and maximize their lifespan without degrading their capacity.
Replacing a 1.5V battery with a 1.2V battery in your devices requires careful thought due to the significant differences in voltage and the effects these differences can have on device functionality.
The most noticeable difference between 1.2V and 1.5V batteries is their voltage output. A 1.2V battery outputs less voltage than a 1.5V battery. This lower voltage can substantially affect how well devices designed for 1.5V perform. For instance, devices calibrated for a 1.5V input might not only work less efficiently but might also fail to function correctly if the voltage supplied does not meet their designed specifications.
Using a 1.2V battery in place of a 1.5V battery reduces the voltage available to the device, which directly impacts its power output. This reduction can particularly affect devices reliant on a higher voltage for optimal functionality, such as high-power electronic equipment or certain motor types. The consequences might include slower performance, diminished effectiveness, or even an inability to perform necessary functions, especially in scenarios where consistent and reliable energy input is important.
Many electronic devices come with specific voltage needs that are integral to their operation. These requirements are generally set based on the device's design and the intended reliability and safety standards. If a device is specifically designed to operate with a 1.5V battery, using a 1.2V battery instead can result in suboptimal performance and potentially compromise the device's stability and lifespan.
1.5V batteries represent a cornerstone of modern portable power, characterized by a blend of reliability, versatility, and innovation. As we've explored, these batteries are not just uniform sources of energy but are distinguished by significant variations in chemistry, capacity, and design tailored to specific needs and devices. From the robust, high-density output of lithium variants ideal for power-intensive applications to the dependable and economical alkaline types suitable for everyday gadgets, 1.5V batteries encapsulate a fascinating spectrum of electrochemical technology. Their widespread implementation across devices that mark our daily lives—from remote controls and toys to critical smoke detectors and medical devices—underscores their importance. Furthermore, the evolution and optimization of these batteries continue to be driven by both technological advancements and increasing environmental awareness, pointing toward a future where power storage is not only more efficient but also more sustainable. As we move forward, the continuous refinement and adaptation of battery technologies will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in powering not just individual devices but the broader infrastructure of portable and wearable technology.
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
1. How long can a 1.5V battery be used?
The duration a 1.5V battery can last depends on its type (alkaline, lithium, etc.), its capacity, and the power demands of the device it powers. Typically, an alkaline AA or AAA battery might last between a few weeks to several months in low to moderate-use devices like remotes and clocks. For high-drain devices like digital cameras, usage might be considerably shorter.
2. Can I use AA batteries instead of 1.5 V batteries?
Yes, you can use AA batteries as replacements if the device calls for 1.5V batteries, assuming the AA battery is also rated at 1.5V. AA simply refers to the size and form factor of the battery and is commonly available with a 1.5V rating.
3. Are AAA batteries always 1.5 V?
Typically, AAA batteries are indeed 1.5V. They are designed to provide a standard voltage that is suitable for a wide range of devices. However, rechargeable AAA batteries usually have a lower voltage of about 1.2V.
4. Is the 1.5 V battery size C or D?
A 1.5V battery can be either size C or D among others. Both C and D batteries can provide 1.5 volts of power; the difference between them lies in their size and capacity (mAh), with D batteries being larger and typically having a higher capacity than C batteries.
5. Can rechargeable batteries be 1.5 V?
Yes, rechargeable batteries can be rated at 1.5V. However, most common rechargeable AA and AAA batteries are typically rated slightly lower at around 1.2V due to the chemistry used (usually NiMH - Nickel-Metal Hydride). There are newer technologies, such as NiZn (Nickel-Zinc) rechargeable batteries, which can provide a closer output to 1.5V.
Share: