HomeBlogRJ-45 Connector Guide: RJ-45 Connector Color Codes, Wiring Schemes, R-J45 Applications, RJ-45 Datasheets
RJ-45 Connector Guide: RJ-45 Connector Color Codes, Wiring Schemes, R-J45 Applications, RJ-45 Datasheets
Originally designed for telephone lines, the RJ-45 has adapted and evolved with the changing needs of the times and is a vital hub for the modern Internet. In this article we will explore the RJ-45 connector. The article covers not only the definition of RJ-45, but also the various types of RJ-45 cables as well as the various wiring schemes that apply to RJ-45 connectors.
What is an RJ45 Connector?

Common Crystal Connectors
The RJ-45 connector, also known as registered jack-45, is a widely used networking cable standard in Ethernet systems. This cable is equipped with four pairs of twisted-pair wires used for high-speed data transmission. Originally the RJ-45 was designed for telephone line connections, but is now widely used in a variety of network connection scenarios. In the construction of a local area network (LAN), the RJ-45 connector becomes the key connection point between nodes, so the term "RJ45" is commonly used to refer to those network jacks and interfaces that establish an Ethernet connection.
Cable Categories
Network cables equipped with RJ-45 connectors come in various types, each defined by its unique characteristics and capacity for data transmission. Below are some prevalent RJ-45 cable categories:
1. CAT5: As one of the initial variants of Ethernet cables, Category 5 (CAT 5) supports data transmission speeds up to 100 Mbps over distances up to 100 meters. It is constructed with four pairs of twisted-wire conductors.
2. CAT 5e: Serving as an enhancement of the CAT 5, Category 5e (CAT 5e) delivers improved performance. Capable of data rates up to 1 Gbps, it maintains effective transmission over distances up to 100 meters, utilizing four pairs of twisted-wire conductors like its predecessor.
3. CAT 6: Offering a leap in throughput and reliability, Category 6 (CAT 6), when compared to CAT 6e, accommodates speeds up to 10 Gbps for up to 55 meters. CAT 6 cables are equipped with four pairs of twisted-wire conductors, featuring enhanced shielding against interference.
4. CAT 6a: As an advanced version of CAT 6, Category 6a (CAT 6a) extends both the throughput and range. It supports data transmission speeds as high as 10 Gbps up to distances of 100 meters and uses four pairs of twisted-wire conductors with more effective shielding mechanisms.
5. CAT 7: Category 7 (CAT 7) is a more recent standard, excelling in both performance and reliability. This category can handle speeds up to 10 Gbps and covers distances up to 100 meters. CAT 7 cables consist of four pairs of twisted-wire conductors with tighter shielding to significantly reduce interference.
Twisted Pair
Consisting of two conductors intricately twisted in pairs, twisted pair cables are an important part of various data networks. The following are the key features of twisted pair cables.
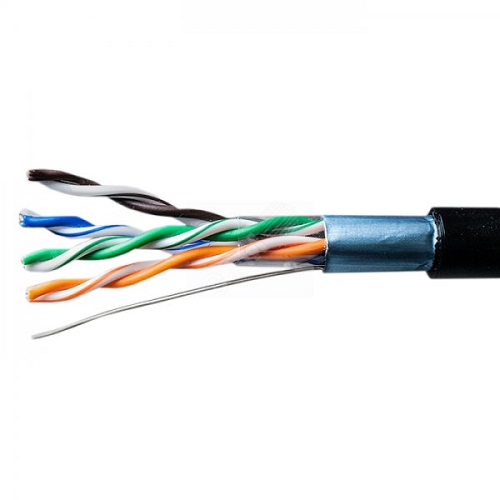
unshielded twisted pair
Superior Interference Capability: The greatest advantage of twisted pair cables is their ability to suppress electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk, thus ensuring clarity and stability of transmissions.
Cables come in many varieties: from the most basic Cat5 to the more complex Cat6a, each classification has different specifications, including bandwidth capacity, data transmission span and more. Advanced cables such as Cat6 and Cat6a are designed for demanding network environments, ensuring increased operational efficiency while accelerating data transfer.
Conductor materials and ingenious designs: The conductors in these cables are typically forged from copper or aluminum, providing a subtle insulation in the form of rings. This not only prevents short circuits in the line, but also eliminates possible interference from neighboring conductors.
Fine Pin Arrangement: Each pair of wires inside the cable is carefully arranged side-by-side to harmonize with the precise pin configuration of the RJ-45 connector. This meticulous alignment is key to ensuring that the cable transmits data seamlessly.
Together, these unique attributes give twisted pair cables an enviable position in networking. Known for its robust performance, adaptability and ability to reduce signal interference in Ethernet-centric networks, twisted pair cables often rendezvous with RJ-45 connectors as the cornerstone of connectivity. They cover a wide range of network devices, including computers, routers and switches, thus providing direction for network operations characterized by smoothness and uninterrupted efficacy.
RJ45 Connector Pin Assignment
The RJ45 connector is a typical interface commonly used in network cabling and is generally used to facilitate the connection of network cards to Category 10Base-T and 100Base-TX network cable hubs. As a practical standard for interconnecting network cables, the RJ45 is available in a modular configuration consisting of 8 positions and 8 pins.
In the realm of NIC cabling, the first and second pairs assume responsibility for signal transmission, while the third and sixth pairs assume the designated role of signal reception. Notably, the remaining two pairs are dormant in standard cable configurations. Crossover cables, on the other hand, are responsible for direct communication between devices, coordinating exchanges between senders and receivers.
RJ-45 cables consist of four pairs of wires, each comprising one solid color wire and one striped wire of the same color. There are two predominant wiring standards for RJ-45: T-568A and T-568B. Although the cable includes four pairs of wires, only two pairs are commonly used in 10BaseT/100BaseT Ethernet, specifically the orange and green pairs. The remaining blue and brown pairs can be used for additional Ethernet lines or telephone connections. These two wiring standards are utilized to create crossover cables (one end with T-568A and the other with T-568B) or standard cables (both ends using T-568B or T-568A). Below are the detailed pin configurations for these two wiring standards.
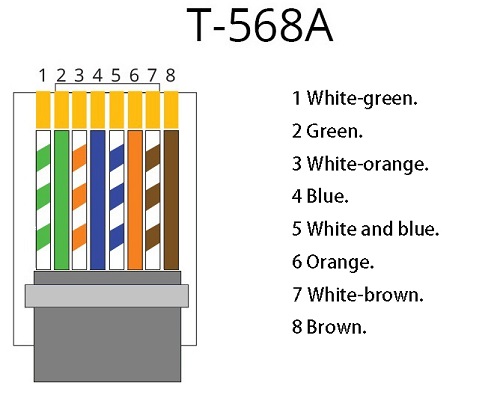
T-568A
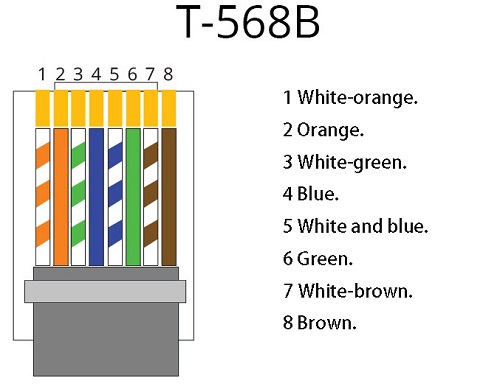
T-568B
RJ-45 Crimping Schemes
There are two main crimping schemes for RJ-45:
8-Core, 4-Pair: This scheme is used for connecting one computer to another. It allows you to directly connect two computers to a network. In a local network, it's not possible to use more than two computers with this scheme!
4-Core, 2-Pair: This scheme is used for connections from a computer to a network switch.
8-core, 4-pair pinout
1. Unwrap the pairs and arrange the wires in the following order (top to bottom):
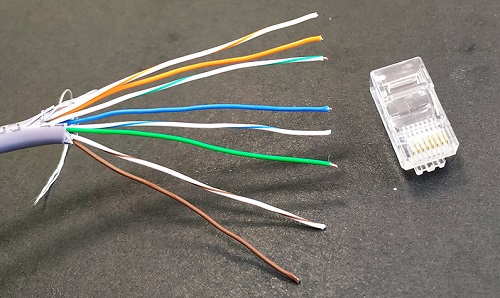
2. Align the wires exactly on a flat surface and cut off the excess length of the pair so that the outer insulation does not exceed 1 cm.
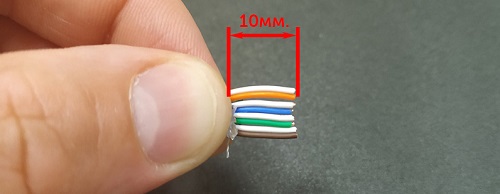
3. Hold the wires in your left hand so that the white-orange wires are further away from you and the brown wires are closer to you. Check the order of the wires according to the diagram in step one.

4.Using the clamps at the bottom pick up the 8P8C connector with your right hand and insert the wires into the connector so that each wire falls into a separate cell. There are 8 cells there.
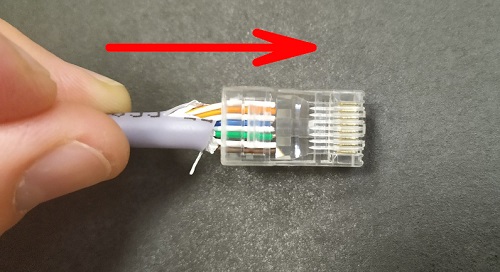
5. Double check the correct position of the wires as described in step 1
6. Insert the connector into the crimping pliers. Crimp the wires in completely so that all wires are deeper than the teeth of the connector contacts. and carefully clamp the jaws.
7.Repeat the same operation for the other end of the wire. Follow the same pattern.
4-core, 2-pair pin arrangement
1. Prepare the twisted pair for crimping by preparing the following scheme for crimping the twisted pair.
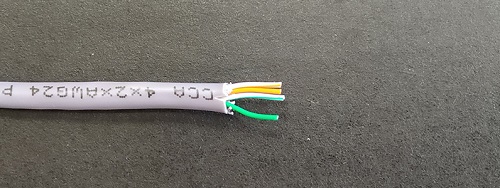
2. Your wires may be different colors. Then you need to understand some logic. We alternate:
- white-[color-1].
- [color-1]; 3. white-[color-1].
- white-[color-2].
- no wires.
- no-wire.
- [color-2].
- no-wire.
- no wires.
- The main thing is that the scheme should be the same at both ends from the first to the eighth contact.
3. Hold the wire in your left hand so that the white-orange wire is further away from you and the brown wire is closer to you. Check the order of the wires against the diagram in Step 2.
4. Hold the same 8P8C connector in your right hand so that the clip is on the bottom.
5. We have a connector for 8 pins, so we leave 4, 5, 7 and 8 blank. Plug the wires into the 2 sockets according to the diagrams in steps 1, 2, 3 and 6.

6. Check the correct position of the wires.
7. Insert connector into crimping pliers. Crimp wires in completely so that all wires are further than the teeth of the connector contacts.Clamp thoroughly on the jaws.
8.Repeat the same operation for the other end of the wire.
Applications of RJ-45
RJ-45 is used in a wide variety of applications that require data transmission and network connectivity. The following are some of the major applications of RJ-45:

1. Computer networks: RJ-45 cables serve as the linchpin in computer networks, seamlessly interlinking an array of devices including computers, servers, routers, and switches within the realms of both local area networks (LANs) and wide area networks (WANs).
2. Internet Connectivity Solutions: In the realm of Internet Connectivity Solutions, RJ-45 cables emerge as the conduit for establishing the digital highway. They form the pivotal link, connecting computers and assorted digital contrivances to the modems and routers, playing a pivotal role in channeling signals from Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to end-user devices.
3. Telecommunication Infrastructure: plays an important role in connecting IP phones to various VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) devices. This utilization provides an efficient channel for transmitting voice data across complex networks.
4. Multimedia Transmission: Exhibiting prowess in the domain of Multimedia Transmission, RJ-45 cables showcase their adeptness in transmitting audio and video signals. This is particularly pronounced in specialized systems employing Ethernet-based HDMI or relying on IP technology for the seamless transmission of audio and video data.
5. Security and Surveillance Systems: Within the realm of Security and Surveillance Systems, RJ-45 cables stand sentinel, ensuring the uninterrupted and steadfast transmission of data. This fortification of connectivity plays a crucial role in bolstering security and access control measures.
6. Home Network Efficiency: At the heart of Home Network Efficiency lies the indispensability of RJ-45 cables. They act as the conduit for establishing a harmonious home network, interconnecting an assortment of devices ranging from computers and printers to gaming consoles and media players. This interconnectivity facilitates the facile sharing of data and access to communal resources.
7. Industrial Network Management: Within industrial spheres, RJ-45 cables carve a niche for themselves in the tapestry of Industrial Network Management. Their application spans a broad spectrum, from industrial networking to device connectivity, fostering the exchange of critical data. This plays a pivotal role in the effective monitoring and control of engineering operations in realms such as automation, manufacturing, and control.
RJ45 vs RJ11
RJ45 connectors are typically used with Cat5 and Cat6 cables, while RJ11 is used exclusively with telephone lines, switches, and cables. In copper cable networks, PCs, routers, and other devices can all utilize RJ45 connections. RJ11 connections on switches usually have two sockets for two-line telephone systems.
|
|
RJ11 |
RJ45 |
|
Configuration |
6P4C (6 positions, 4 connectors) |
8P8C (8 positions, 8 connectors) |
|
Shape and Size |
Compact, square-shaped |
Longer, more rectangular |
|
Bandwidth |
RJ11 connectors can support about 24Mbps |
RJ45 connectors can support 10Gbps over Ethernet. |
|
Usage |
Phones, ADSL lines, modem cables. RJ11 is mostly used for
voice applications. |
Computer networking. RJ45 is typically used in Ethernets or
connecting cable modems with Wi-Fi routers. |
Dimensions of RJ-45
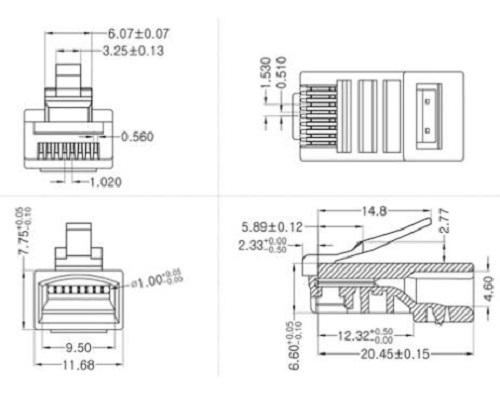
RJ-45 Datasheet
Download HellermannTyton RJ45FC6AS12 datasheets and manufacturer's documentation.
Conclusion
Through an in-depth analysis of RJ45 connectors and various categories of network cables, we can discern the significance of these technological components in modern communication networks. RJ45 is more than just a connector; it is key to achieving high-speed and efficient data transmission. From Cat5 to Cat7, each advancement in cable technology marks a significant stride in network technology, ensuring connectivity and seamless communication in the digital era. Whether in home networks, corporate settings, or industrial applications, RJ45 and its related cable categories ensure stable and secure information flow. As network technology continues to evolve, the design of RJ45 and twisted pair cables will also progress to support the growing demands for data transmission. And we, as users of the digital world, will continue to enjoy the convenience of connectivity and communication brought about by these seemingly ordinary but crucial technologies.
FAQ
What is the color code for RJ45?
The two most popular pinouts are T568A and T568B. The T568B is used in the United States for twisted-pair structured cabling. The four wires it has each pair being a different color.
What is the difference between RJ11 and RG45?
RJ11 and RJ45 are plastic connectors for communication cables that look very similar. However, RJ45 is used for Ethernet cables like Cat5 and Cat5e, while RJ11 is specifically for telephone lines. The abbreviation "RJ" means registered jack. RJ11 is often referred to as a phone jack.
What does 45 mean in RJ45?
It refers to a type of modular plug normally used at the end of Ethernet patch cables, and when attached at the end of an Ethernet cable it is called a RJ45 8P8C plug. RJ stands for registered jack while the “45” refers to the listing number.
Is RJ45 same as Ethernet?
Ethernet cables come with RJ45 connectors on both ends. Because of this, an Ethernet cable is sometimes designated as an RJ45 cable. These cables are often used to connect computers onto Ethernet networks. The RJ45 connector resembles a six-pin RJ11 connector, though the 45 is slightly wider.