D882 Transistor Explained with Practical Applications
The D882 transistor is a widely used component in electronics, valued for its flexibility and dependable performance. It's a type of bipolar junction transistor (BJT) that’s suitable for both amplifying signals and switching. This article will guide you through the features, operating principles, and practical applications of the D882, making it easy to understand how it works and where you can use it effectively.Catalog
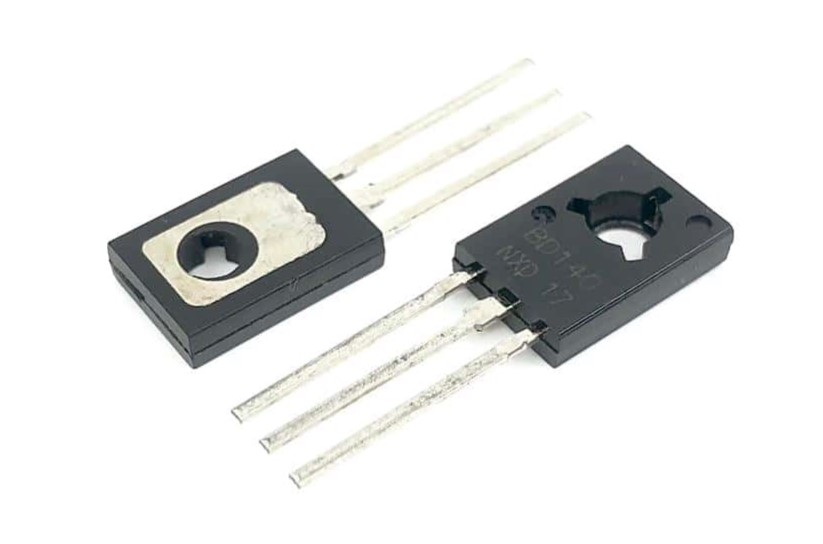

Overview of the D882 Transistor
The D882 transistor is widely used in various electronic circuits due to its reliability and efficiency. This bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is well-suited for both switching and amplification tasks, efficiently managing current flow and making it a core component in many modern electronic systems.
The development of the D882 transistor is rooted in the progress made in semiconductor technology during the mid-20th century. Early transistors set the groundwork for devices like the D882, and with ongoing advancements in materials and production techniques, transistors became more reliable and higher performing. This evolution made them a staple in many electronic applications, ranging from consumer electronics to more specialized industrial devices.
The D882 transistor stands out for its ability to handle high collector currents and maintain commendable voltage ratings, making it versatile for a range of uses. Its key specifications include a collector-emitter voltage of 30V, a collector current of 3A, and a power dissipation rating of 1W. These characteristics allow it to handle a variety of loads, from small signals to larger power demands.
In practical applications, you’ll find the D882 transistor in power regulation circuits, motor controllers, and audio amplifiers. Its capacity to amplify weak signals makes it ideal for audio and radio frequency (RF) applications, while its ability to handle high current loads is beneficial for managing power in circuits. The D882 is known for its durability, performing reliably even in challenging conditions, making it a preferred choice for both consumer electronics and more demanding industrial uses.
Key Specifications
| Specification | Details |
| Part Number | D882 |
| Type | NPN (Negative-Positive-Negative) bipolar junction transistor |
| Package Type | TO-126, TO-251, TO-220, or similar through-hole package |
| Collector-Base Voltage (VCBO) | Typically around 40V to 60V |
| Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO) | Typically around 30V to 40V |
| Emitter-Base Voltage (VEBO) | Typically around 5V to 7V |
| Collector Current (IC) | Maximum continuous collector current, often in the range of 2A to 3A |
| Base Current (IB) | Maximum continuous base current, usually a few mA |
| Power Dissipation (PD) | Maximum power dissipation, generally in the range of 1W to 2W |
| Transition Frequency (fT) | Frequency at which the transistor's current gain (hFE) falls to unity, often in the range of a few hundred megahertz |
Operational Principles of the D882 Transistor
Structure and Function
You’ll find that Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs), like the D882, are made up of three semiconductor layers: the emitter, base, and collector. The way these layers interact greatly affects how the transistor performs. The operation of a BJT is controlled by the interaction between a small current flowing through the base-emitter junction (IB) and a much larger current flowing through the collector-emitter junction (IC). By applying a specific voltage to the base-emitter junction, you can control the overall current flow through the transistor, allowing the BJT to regulate current and amplify signals that are applied to the base-emitter junction.
Operating States
The D882 transistor can function in different states, each suitable for particular applications.
In saturation mode, the transistor is fully on, permitting maximum current flow between the collector and emitter. This mode is useful for applications that need high current conduction with minimal resistance, like power switching circuits. Keeping the transistor in saturation reduces power loss and overheating, ensuring that the system continues to run smoothly.
In cutoff mode, the transistor is fully off, meaning only a small amount of current can pass through the collector-emitter path. This state is beneficial for digital logic circuits, where a precise off-state is needed to represent binary information accurately.
When the transistor is in active mode, it acts as an amplifier. By carefully adjusting the base current, you can produce a much larger collector current. This mode is useful for analog signal processing, such as in audio amplifiers, where it’s essential to maintain the clarity of audio signals without introducing distortion.
Thermal Management and Reliability
Temperature changes can impact how the D882 transistor operates. High-power applications often need good thermal management to keep the transistor stable. Using heat sinks or active cooling systems can prevent issues caused by excessive heat, which is especially necessary in high-frequency circuits to avoid problems like thermal runaway and ensure long-term performance.
Practical Implications and Optimization
Knowing how the D882 transistor operates helps you make the most of it in practical applications.
For consistent performance, ensure the transistor is properly biased. Using voltage dividers or active bias circuits can stabilize the operating point and minimize issues caused by changes in temperature or supply voltage. In switching circuits, you can enhance efficiency by reducing the rise and fall times through well-thought-out circuit designs. This can be achieved by using techniques like snubber circuits or driving transistors with low-impedance sources.
If you’re using the D882 transistor for amplification, keep it in its active region to maintain linearity and prevent distortion. Select components and lay out your circuit carefully to achieve the best performance and reliable output, avoiding extremes like saturation or cutoff that could introduce errors in the signal.
Significance in Electronic Circuits
The D882 transistor plays an essential role in various electronic circuits, especially for tasks like amplifying signals and switching. Its ability to boost audio signals significantly impacts the performance of audio devices, making it an ideal component in sound systems, audio amplifiers, and equalizers. With the help of the D882, you can achieve consistent sound quality in both consumer and professional audio equipment.
This transistor is widely used for its signal amplification capabilities. In audio equalizers, for example, it enhances and balances different frequencies, which results in clearer and richer audio output. It’s also used in sound systems where it amplifies weak signals to drive speakers, ensuring that the sound produced is both powerful and clear.
Besides amplification, the D882 excels as a switch in electronic circuits. It manages current flow using control signals, making it a reliable choice for high-power circuits in applications like voltage regulators, LED lights, and motor controllers. Its precise control over current flow is especially beneficial in contexts that require stable performance, such as automotive systems where maintaining consistent motor control is key to reliability.
Integrating the D882 into your designs means you need to be familiar with its specific properties and behaviors. Electronics enthusiasts often test and refine these components to ensure they meet the requirements of each application. Understanding how to choose the right transistor for your circuit ensures it can handle the required current and voltage levels without compromising the circuit’s overall integrity.
Practical Applications of the D882 Transistor
The D882 transistor is widely used across various circuits, showcasing its adaptability and reliable performance. Below are some specific applications that demonstrate its capabilities.
Amplification Circuits
You can use the D882 transistor in amplification circuits, where it effectively increases low-power audio signals to levels that can drive speakers or headphones. Its high gain and low noise performance make it suitable for low to medium power uses. This is why you’ll often find it in consumer electronics where sound quality and clear signal transmission matter most.
Switching Circuits
The D882 transistor performs well in switching circuits, where it handles significant power loads controlled by smaller input signals. This makes it ideal for applications like relay drivers, motor control systems, and LED drivers. Its fast response time and dependable operation ensure smooth device functionality, making it useful in automation and control systems.
Voltage Regulation
In voltage regulation circuits, the D882 transistor helps keep voltage levels stable, providing a steady power supply to delicate components. By carefully controlling the base current, it maintains a consistent output voltage, which is necessary for the durability and performance of electronic devices. This is especially useful in precision equipment where voltage consistency is needed to avoid malfunction.
Inverter Circuits
The D882 transistor plays a role in inverter circuits, where it converts DC input into an AC output waveform. This application is common in solar power systems and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), where efficient and reliable power conversion is needed to maintain a continuous power supply. Its effectiveness in this area contributes to better energy utilization, which supports advancements in renewable energy solutions.
Oscillator Circuits
The D882 transistor is often used in oscillator circuits to generate periodic signals needed for clocks, signal generators, and frequency synthesizers. It produces stable and precise signals at various frequencies, making it valuable in telecommunications and timing devices where synchronization is required.
Pulse Generator Circuits
In pulse generator circuits, the D882 transistor creates accurate pulses necessary for timing circuits, pulse width modulation (PWM) controls, and digital communication systems. Its precision ensures that timing and signaling tasks are executed correctly, thereby improving the performance of digital systems.
Voltage Amplification
The D882 transistor is effective in voltage amplification, where it amplifies small variations in input voltage. This is widely used in sensor and instrumentation signal conditioning. Its capability to capture and amplify even the smallest changes without much distortion supports applications like scientific and medical instrumentation, where accurate signal representation is required.
These various applications show the D882 transistor’s versatility in ensuring reliable performance in numerous electronic systems.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
You can benefit from this component’s high gain when amplifying small input signals to reach your desired output levels. For example, in audio equipment, amplifying minimal input helps maintain sound quality.
The low cost of this component makes it a budget-friendly choice for many electronic devices. This is particularly helpful in large-scale production projects where keeping expenses low is necessary.
Due to its wide availability, you can easily find this component from various suppliers. This makes it convenient for large-scale projects since you won't have to worry about procurement issues. Consistent availability supports projects that require standardized components.
Its versatility allows it to be used in various applications, such as oscillators, switches, voltage regulators, and amplifiers. For instance, in communication equipment, its flexible design enables multiple functionalities to be integrated into compact devices, enhancing system performance.
The compact size of this component is ideal for fitting into small devices or complex circuits. This makes it suitable for wearable technology and portable gadgets, where every bit of space matters.
Disadvantages
One limitation of this component is its limited power handling. It may not perform well in high-power applications like industrial machinery, where components need to handle larger electrical loads without breaking down.
Heat dissipation can also be a challenge. Managing heat effectively is necessary to prevent the component from overheating, which can lead to failures. Adding heat sinks or active cooling solutions can help keep the temperature under control.
Adhering to specific voltage and current ratings is required to avoid damage. If these limits are exceeded, it could result in failure or reduced performance.
Speed limitations make this component unsuitable for very fast switching tasks. High-frequency applications, such as gigahertz-range data processing, require faster components to ensure smooth operation.
The component’s environmental sensitivity means it can be affected by factors like moisture, temperature changes, and electromagnetic interference. Using protective coatings, shielding, or designing for stable environments can reduce these effects and improve reliability.
Balancing these advantages and disadvantages helps you get the best performance and reliability for your application.
Practical Considerations
To get the best performance and reliability from the D882 transistor, it's essential to think about a few practical factors:
Proper Biasing and Configuration
When using the D882 transistor, making sure it's correctly biased and configured is necessary for it to work as expected. Proper biasing means applying the right voltages and currents to the transistor's terminals to get the desired amplification or switching behavior. You might need to use resistors or fixed bias techniques to set stable operating points. Through practical application, careful design and calibration can help improve efficiency and control over the device’s electronic properties.
Thermal Management
Managing heat effectively is very necessary, especially in high-current applications where overheating can become a concern. Using heat sinks, ensuring good airflow, and choosing packaging materials with good thermal conductivity are strategies that can help reduce excess heat. In real-world applications, the lifespan and reliability of the transistor depend a lot on how well you apply these thermal management techniques.
Component Selection Guidelines
Choosing the right components that match the D882 transistor’s specifications and the needs of your application is also very important. You should consider voltage ratings, power handling abilities, and tolerance levels. Using resistors, capacitors, and other components that can handle various conditions helps maintain the stability and efficiency of the circuit.
Conclusion
To sum up, the D882 transistor is a versatile and reliable component for many electronic projects. Whether you’re amplifying audio signals or controlling power in circuits, its straightforward operation and high performance make it a solid choice. With a good grasp of its properties and practical tips on usage, you can confidently integrate the D882 into your designs for optimal results.
About us
ALLELCO LIMITED
Read more
Quick inquiry
Please send an inquiry, we will respond immediately.

RS232 vs RS485 Explained: Which Communication Protocol to Choose
on October 10th
DRV8825 vs A4988 Comparison Guide
on October 9th
Popular Posts
-
What is GND in the circuit?
on January 1th 2860
-

RJ-45 Connector Guide: RJ-45 Connector Color Codes, Wiring Schemes, R-J45 Applications, RJ-45 Datasheets
on January 1th 2437
-

Fiber Connector Types: SC Vs LC And LC Vs MTP
on January 1th 2039
-
Understanding Power Supply Voltages in Electronics VCC, VDD, VEE, VSS, and GND
on November 6th 1796
-

Comparison Between DB9 and RS232
on January 1th 1740
-

What Is An LR44 Battery?
Electricity, that ubiquitous force, quietly permeates every aspect of our daily lives, from trivial gadgets to life-threatening medical equipment, it plays a silent role. However, truly grasping this energy, especially how to store and efficiently output it, is no easy task. It is against this background that this article will focus on a type of coin cell battery that may seem insignificant on the...on January 1th 1692
-
Understanding the Fundamentals:Inductance Resistance, andCapacitance
In the intricate dance of electrical engineering, a trio of fundamental elements takes center stage: inductance, resistance, and capacitance. Each bears unique traits that dictate the dynamic rhythms of electronic circuits. Here, we embark on a journey to decipher the complexities of these components, to uncover their distinct roles and practical uses within the vast electrical orchestra. Inductan...on January 1th 1632
-

CR2430 Battery Comprehensive Guide: Specifications, Applications and Comparison to CR2032 Batteries
What is CR2430 battery ?Benefits of CR2430 BatteriesNormCR2430 Battery ApplicationsCR2430 EquivalentCR2430 VS CR2032Battery CR2430 SizeWhat to look for when buying the CR2430 and equivalentsData Sheet PDFFrequently Asked Questions Batteries are the heart of small electronic devices. Among the many types available, coin cells play a crucial role, commonly found in calculators, remote controls, and ...on January 1th 1504
-
What Is RF and Why Do We Use It?
Radio Frequency (RF) technology is a key part of modern wireless communication, enabling data transmission over long distances without physical connections. This article delves into the basics of RF, explaining how electromagnetic radiation (EMR) makes RF communication possible. We will explore the principles of EMR, the creation and control of RF signals, and their wide-ranging uses. The article ...on January 1th 1482
-

CR2450 vs CR2032: Can The Battery Be Used Instead?
Lithium manganese batteries do have some similarities with other lithium batteries. High energy density and long service life are the characteristics they have in common. This kind of battery has won the trust and favor of many consumers because of its unique safety. Expensive tech gadgets? Small appliances in our homes? Look around and you'll see them everywhere. Among these many lithium-manganes...on January 1th 1476

















































