RS232 vs RS485 Explained: Which Communication Protocol to Choose
When comparing RS232 and RS485, it's important to understand the unique strengths of each communication protocol. Both have been around for decades and remain relevant in many industries due to their reliability and simplicity. In this article, you'll learn about the basic features of RS232 and RS485, their advantages and limitations, and how to choose the right one for your specific needs.Catalog
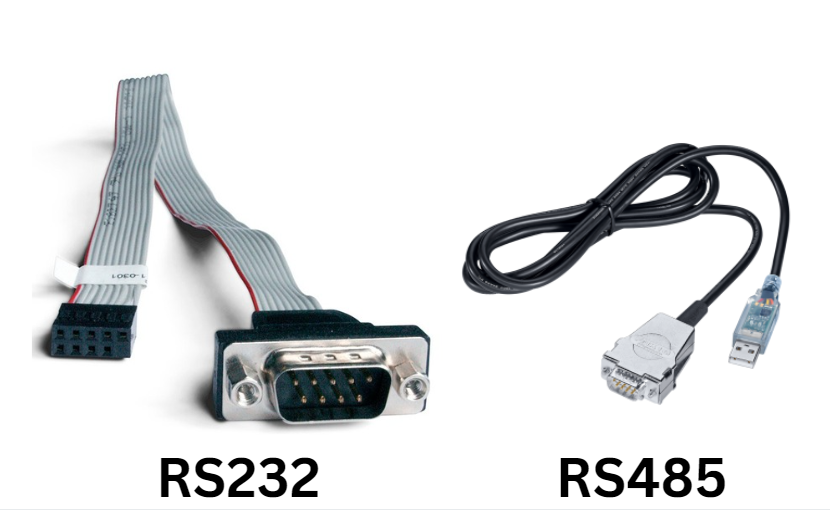

RS232 vs. RS485
The comparison between RS232 and RS485 has been ongoing for years, yet both remain widely used today. Although these protocols were developed over fifty years ago, they are still chosen for their reliability and specific uses.
RS232, introduced in the 1960s, is commonly used for point-to-point communication. You often find it in computer serial ports, making it easy to connect devices like computers and modems for straightforward data exchange. Its simplicity is why it’s still a preferred choice for basic data transfers and troubleshooting.
RS485, on the other hand, is better for handling longer distances and connecting multiple devices on the same network. This makes it ideal for industrial settings. It also performs well in areas with high electromagnetic interference, ensuring stable communication even in harsh environments.
RS232 is usually used where two devices need direct communication without complex setup. It works well in quieter environments, making it suitable for simple embedded systems. RS485 is more suitable for connecting multiple devices over a single network, like in factory floors or building automation, where its resistance to noise and stable signal over longer distances make it a reliable option.
Understanding RS232

RS232, also known as TIA/EIA-232, is a widely used serial communication standard that has served as a backbone for data transfer between devices for decades. It defines how information is exchanged between equipment like computer terminals and modems, ensuring reliable communication across different devices.
Introduced by the Electronic Industries Association (EIA) in 1960, RS232 was originally designed to connect teletypewriters and modems. Despite the arrival of newer technologies, it has stood the test of time due to its reliability and simplicity, making it a trusted choice in many specialized and industrial applications.
The RS232 standard works with voltage levels ranging from -15 to +15 volts and supports data transmission over distances up to 50 feet at speeds up to 20 Kbps. It uses separate signals for sending and receiving data—known as TXD (Transmit Data) and RXD (Receive Data)—which helps reduce electrical interference and ensures stable communication.
You’ll often find RS232 used in settings that require consistent and precise data exchange. For instance, it’s commonly used to connect laboratory instruments to data systems for accurate control and monitoring. In industrial automation, RS232 helps establish reliable communication between machines and control units, ensuring efficient data flow even in complex environments.
While RS232 does have its limitations in terms of speed and distance, it remains adaptable to modern requirements. Many users turn to RS232-to-USB converters to connect older devices to newer computer systems, maintaining compatibility without sacrificing the benefits of the standard.
Although technologies like USB, Ethernet, and wireless protocols are more common in everyday use, RS232 still holds a unique place in certain fields. Its continued presence in many devices today shows that RS232 remains a dependable option when straightforward and stable communication is needed.
What is RS485?

RS485, also known as EIA-485, is a widely used serial interface, especially in industrial applications. It stands out from RS232 by supporting multiple devices on a single network using a multi-point topology. This allows for a more flexible and cost-effective system setup, as multiple transmitters and receivers can communicate over the same network, reducing the need for extensive cabling.
One of RS485’s key features is its use of differential signals, which helps minimize electrical interference, a common issue in industrial environments. This ensures stable and reliable data transmission, even over long distances. Its robustness and ability to maintain communication integrity make it ideal for connecting various devices in industrial automation and control systems.
RS485 can operate in two modes: half-duplex and full-duplex. In half-duplex mode, it uses a two-wire connection, where data is transmitted and received alternately. This setup is suitable for simpler communication needs, where direct point-to-point data exchange is sufficient. In contrast, full-duplex mode employs a four-wire connection, allowing for simultaneous data transmission and reception. This configuration is preferred for applications that require continuous, two-way communication, such as in monitoring and control systems.
Due to its versatility and reliability, RS485 is commonly found in industrial automation, building management systems, and process control. Its ability to function effectively in noisy environments makes it a go-to choice for ensuring stable and error-free communication. Depending on the application’s specific needs, choosing between half-duplex or full-duplex modes is crucial for optimal performance.
RS232 vs. RS485: Specifications
| Specification | RS232 | RS485 |
| Voltage System | Voltage level-based | Differential |
| Total Drivers and Receivers on One Line | 1 Driver, 1 Receiver | 32 Drivers, 32 Receivers (One Driver active at a time) |
| Line Configuration | Point-to-point | Multidrop |
| Maximum Operational Distance | 15M / 50FT | 1,200M / 3000FT |
| Maximum Data Transmission Rate | 1 MBit/s | 10 MBit/s |
| Duplex Mode | Full Duplex | Half Duplex or Full Duplex |
| Maximum Driver Output Voltage | +/-25V | -7V to +12V |
| Receiver Input Resistance | 3 to 7 kΩ | 12 kΩ |
| Receiver Input Voltage Range | +/-15V | -7V to +12V |
| Receiver Sensitivity | +/-3V | ±200mV |
RS232 vs. RS485: Distinctions in Operational Distance
One key difference between RS232 and RS485 is the distance each protocol can cover effectively. RS232 generally works well up to 50 feet. Extending this range may compromise data speed and reliability, though reducing the baud rate can sometimes help extend its reach. However, practical limitations often make RS232 less suitable for applications requiring longer distances.
On the other hand, RS485 can transmit data over distances of up to 4,000 feet, making it ideal for environments where long-distance communication is necessary. This extended range allows RS485 to be used in a wider variety of scenarios, particularly where devices need to be connected over significant distances.
Another distinction is in their communication topologies. RS232 is limited to a point-to-point connection, meaning it can only link two devices directly. This restriction can be a drawback in more complex systems that require interactions among multiple devices.
In contrast, RS485 supports a multidrop topology, enabling several devices to share the same communication bus. This capability makes RS485 more scalable and flexible, accommodating larger and more interconnected networks.
The choice between RS232 and RS485 often comes down to your specific application needs, such as the required communication distance and network complexity. RS485 is commonly preferred in industrial settings because its long range and multidrop capability facilitate efficient communication across large systems. Additionally, RS485 is more resistant to electromagnetic interference, ensuring stable data transfer even in environments with high electrical noise.
RS232 vs. RS485: Differences in Electrical Noise and Ground Potential Resistance
RS232 uses specific voltage levels for data transmission, which makes it more sensitive to electrical noise. In environments with high electromagnetic interference (EMI), such as industrial settings with heavy machinery, this sensitivity can lead to data corruption, raising concerns about communication reliability.
Another limitation of RS232 is its inability to manage variations in ground potential. Devices connected to different ground levels can create ground loops, which introduce noise and errors during data transmission. This issue is especially problematic over longer distances. In large facilities or building complexes where devices might not share the same power circuits, variations in ground potential can disrupt communication.
In contrast, RS485 uses differential voltage signaling, which significantly improves its resistance to electrical noise. By using two wires for each signal, any external noise introduced affects both wires equally, allowing the receiver to cancel out the interference. This makes RS485 an excellent choice for industrial and commercial settings where reliable data transmission is needed, even in high-noise environments.
RS485’s ability to handle longer distances with minimal voltage drop is another advantage. Its higher voltage levels and differential signaling allow it to transmit data over extended distances without losing signal quality. This makes RS485 suitable for applications like traffic control systems and utility meters, where devices are often positioned far from central monitoring stations.
Choosing between RS232 and RS485 often depends on the environment and required transmission distance. RS232’s susceptibility to noise and ground potential differences makes it better suited for short-range, controlled settings. Meanwhile, RS485’s noise resistance and stability over long distances make it a preferred option for more challenging conditions.
The differential signaling method used by RS485 not only minimizes noise interference but also supports longer transmission distances, making it a reliable choice for complex infrastructures and demanding environments.
RS232 vs. RS485: Differences in the Total Number of Transmitters and Receivers
RS232 is designed for simple, point-to-point communication, connecting just two devices—a single transmitter and a single receiver. This straightforward setup makes it ideal for direct data transfer between two devices, like a computer and a modem. In contrast, RS485 can support up to 32 devices on the same network, making it a much better choice for systems that need to connect multiple devices and maintain communication over longer distances.
While modern technology often leans toward USB interfaces due to their convenience and plug-and-play nature, integrating USB with RS232 or RS485 can be challenging. This conversion is necessary in industrial and older systems where connecting new equipment with legacy devices is essential. For example, a factory using older machinery with an RS232 or RS485 interface might require converters to link with newer computers or control systems. This compatibility allows continued use of reliable older equipment while taking advantage of modern technology.
In scenarios that involve multiple device connections and long-distance communication, RS485’s capacity becomes indispensable. For example, in a large manufacturing plant, RS485 can link multiple sensors and devices across the facility, ensuring stable communication without interference. This capability allows for reliable data exchange, even in challenging environments.
Choosing between RS232 and RS485 often depends on the specific requirements of your setup. RS232’s simplicity is ideal for applications where straightforward, direct communication is needed, while RS485’s versatility makes it suitable for complex systems that require robust performance over long distances. Understanding these differences will help you make the most out of both protocols in specialized applications, ensuring reliable and efficient communication across your network.
RS232 vs. RS485: Differences in Data Speed
RS232 and RS485 differ significantly in terms of data speed and distance capabilities. RS232 supports reliable, short-range communication with speeds reaching up to 1 Mbps over a distance of up to 50 feet. It’s ideal for applications where moderate speed is sufficient, such as connecting peripherals like keyboards or modems to computer serial ports. In these cases, RS232’s straightforward setup and adequate speed make it a practical choice for short-distance connections.
RS485, on the other hand, is designed for higher data transfer rates and longer distances. It can reach speeds up to 10 Mbps over 50 feet and maintain steady communication at 100 kbps over distances as long as 4,000 feet. This versatility makes RS485 suitable for scenarios that require high-speed data exchange across extended distances, such as in industrial environments or remote data acquisition systems.
Additionally, RS485’s differential signaling offers robust noise resistance, ensuring stable communication in electrically noisy environments. This characteristic is especially useful in industrial settings, where maintaining data integrity is crucial despite challenging conditions.
Choosing between RS232 and RS485 depends largely on the specific requirements of your application. RS485’s support for multiple devices on a single bus can simplify network setup, reducing cabling and making it a more efficient choice for large-scale systems like building management or automated manufacturing lines. Its ability to handle high-speed communication over long distances makes it a reliable option for complex network configurations.
As industries evolve and applications like the Internet of Things (IoT) continue to grow, the need for reliable and efficient communication standards remains strong. RS485’s flexibility and proven performance over long distances ensure that it will continue to be a valuable standard in both current and future communication networks.
RS232 vs. RS485: Applications
RS232 and RS485 are commonly used in various fields, including scientific equipment, industrial wireless controls, computers, robotics, and medical devices. Each protocol serves unique communication needs, enhancing efficiency and reliability in specific scenarios.
Scientific Equipment
In scientific laboratories, RS232 and RS485 connect instruments such as spectrometers, chromatographs, and data loggers. Their ability to maintain accurate data transmission is essential for successful research. Precise measurements during experiments often rely on stable communication channels, making these protocols valuable in scientific applications.
Industrial Wireless Controls
In industrial settings, RS232 and RS485 are known for their stability over long distances and in environments with high electrical noise. They are widely used in automation systems, including automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and programmable logic controllers (PLCs). The RS485’s daisy-chaining capability simplifies infrastructure, helping to reduce both costs and maintenance needs.
Computer Interfaces
For communication between computers and peripheral devices, RS232 and RS485 offer straightforward, point-to-point connections or multi-drop configurations. RS232 is often seen in serial mice, modems, and older printers, showing its ability to integrate well with various peripherals.
Robotics
In robotics, RS232 and RS485 facilitate communication between controllers and sensors or actuators. Their reliable data transfer ensures real-time feedback and precise control, which is particularly useful in applications like robotic arms and autonomous systems.
Medical Devices
In the healthcare industry, medical devices like patient monitors, diagnostic equipment, and imaging systems use RS232 and RS485 for their dependable communication and ease of integration. This helps maintain the integrity of patient data transmitted between devices, ensuring smooth operation in healthcare environments.
Personal Perspective
An emerging trend is the growing use of RS485 in smart healthcare settings. It connects multiple sensors and devices within hospital systems, improving data accuracy and overall system efficiency. This shift highlights the adaptability of RS485 in supporting advanced healthcare technology solutions.
Conclusion
RS232 and RS485 each serve different communication purposes. RS232 is ideal for direct, short-distance connections, while RS485 excels in longer-distance, multi-device setups. Understanding these differences will help you decide which protocol suits your application best, ensuring stable and efficient communication. By choosing the right standard, you can optimize data transmission and enhance system performance.
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
1. Can I connect RS232 to RS485?
Yes, you can connect RS232 to RS485, but you will need an adapter cable to do so. Depending on your device’s protocol, you would use either a USB to RS232 adapter or a USB to RS485 adapter. This is because the adapter is equipped with a processor chip that helps translate the signals between the USB and the specific protocol, enabling proper communication between devices.
2. What are the 3 differences between RS232 and RS485?
The first difference is in communication type. RS232 supports full-duplex communication, which means it can send and receive data simultaneously, whereas RS485 operates in half-duplex mode, where it can either send or receive data, but not both at the same time. The second difference is in their transmission mode. RS232 uses single-ended transmission, sending data with reference to ground, while RS485 uses differential transmission, which helps minimize interference and allows for communication over longer distances. Lastly, while both are physical communication standards, RS232 relies on single-ended signaling, whereas RS485 uses differential signaling.
3. How many wires does RS485 use?
RS485 typically uses three conductors along with a shield. Although it’s often referred to as a “two-wire” network, it actually requires two conductors to carry the differential voltage signal and one additional shield wire. The shield is connected to the ground at one end to protect the network from external noise, ensuring better signal integrity.
4. Is Modbus RTU the same as RS485?
No, Modbus RTU and RS485 are not the same, but they often work together. Modbus is a communication protocol that determines how data is structured and transferred between devices. RS485, on the other hand, defines the electrical signal levels and physical characteristics used for communication. While Modbus frequently uses RS485 as its physical layer, they are two separate entities that complement each other to enable effective communication.
About us
ALLELCO LIMITED
Read more
Quick inquiry
Please send an inquiry, we will respond immediately.
Complete Overview of the SS9012 Transistor
on October 10th

D882 Transistor Explained with Practical Applications
on October 9th
Popular Posts
-
What is GND in the circuit?
on January 1th 2859
-

RJ-45 Connector Guide: RJ-45 Connector Color Codes, Wiring Schemes, R-J45 Applications, RJ-45 Datasheets
on January 1th 2436
-

Fiber Connector Types: SC Vs LC And LC Vs MTP
on January 1th 2039
-
Understanding Power Supply Voltages in Electronics VCC, VDD, VEE, VSS, and GND
on November 6th 1795
-

Comparison Between DB9 and RS232
on January 1th 1739
-

What Is An LR44 Battery?
Electricity, that ubiquitous force, quietly permeates every aspect of our daily lives, from trivial gadgets to life-threatening medical equipment, it plays a silent role. However, truly grasping this energy, especially how to store and efficiently output it, is no easy task. It is against this background that this article will focus on a type of coin cell battery that may seem insignificant on the...on January 1th 1691
-
Understanding the Fundamentals:Inductance Resistance, andCapacitance
In the intricate dance of electrical engineering, a trio of fundamental elements takes center stage: inductance, resistance, and capacitance. Each bears unique traits that dictate the dynamic rhythms of electronic circuits. Here, we embark on a journey to decipher the complexities of these components, to uncover their distinct roles and practical uses within the vast electrical orchestra. Inductan...on January 1th 1632
-

CR2430 Battery Comprehensive Guide: Specifications, Applications and Comparison to CR2032 Batteries
What is CR2430 battery ?Benefits of CR2430 BatteriesNormCR2430 Battery ApplicationsCR2430 EquivalentCR2430 VS CR2032Battery CR2430 SizeWhat to look for when buying the CR2430 and equivalentsData Sheet PDFFrequently Asked Questions Batteries are the heart of small electronic devices. Among the many types available, coin cells play a crucial role, commonly found in calculators, remote controls, and ...on January 1th 1503
-
What Is RF and Why Do We Use It?
Radio Frequency (RF) technology is a key part of modern wireless communication, enabling data transmission over long distances without physical connections. This article delves into the basics of RF, explaining how electromagnetic radiation (EMR) makes RF communication possible. We will explore the principles of EMR, the creation and control of RF signals, and their wide-ranging uses. The article ...on January 1th 1480
-

CR2450 vs CR2032: Can The Battery Be Used Instead?
Lithium manganese batteries do have some similarities with other lithium batteries. High energy density and long service life are the characteristics they have in common. This kind of battery has won the trust and favor of many consumers because of its unique safety. Expensive tech gadgets? Small appliances in our homes? Look around and you'll see them everywhere. Among these many lithium-manganes...on January 1th 1476














































