IC 7404 Comprehensive Guide - Truth Table, Uses, Pros and Cons, Applications, Pinouts
Catalog
1. 7404 Integrated Circuit Description
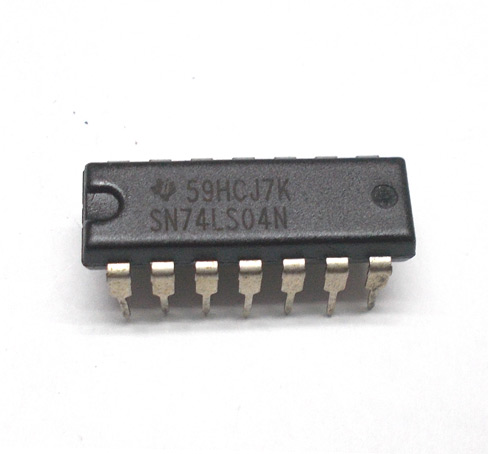

2. Characteristics and Parameter Specifications of IC 7404
2.1 Features:
- - Six inverted outputs: The 7404 IC has six inverters in one package, making it highly effective for complex circuits that require multiple inversions simultaneously.
- - Compatible output connections: The IC's outputs are compatible with CMOS, NMOS, and TTL logic families, enabling easy integration into various digital systems, thereby reducing complexity and enhancing reliability.
- - Multiple operating voltage ranges: It supports a wide range of operating voltages, allowing it to adapt to different power supplies and enhancing its application flexibility.
- - Broad operating conditions: The IC is optimized for various environmental conditions, providing the reliability and stability necessary for industrial and commercial applications.
2.2 Parameter Specifications:
- - Maximum current output: 8mA
- - Power supply voltage range: +4.75V to +5.25V
- - Operating temperature range: -70°C to +70°C
- - Maximum supply voltage: +7V
- - Maximum rise time: 15ns
- - Maximum fall time: 15ns
- - Output type: TTL
- - Logic type: Bipolar
3. IC 7404 Pin Configuration and Layout
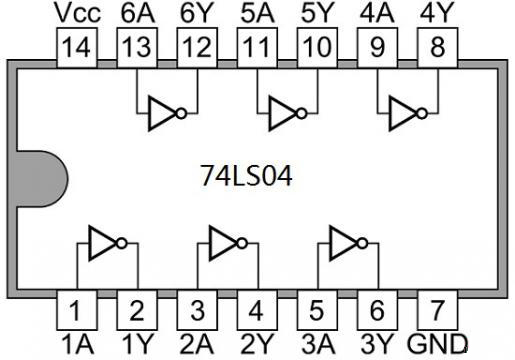
- - Pin 1, A input for gate 1
- - Pin 2, Y output for gate 1
- - Pin 3, A input for gate 2
- - Pin 4, Y output for gate 2
- - Pin 5, A input for gate 3
- - Pin 6, Y output for gate 3
- - Pin 7, Ground
- - Pin 8, Y output for gate 4
- - Pin 9, A input for gate 4
- - Pin 10, Y output for gate 5
- - Pin 11, A input for gate 5
- - Pin 12, Y output for gate 6
- - Pin 13, A input for gate 6
- - Pin 14, Positive power supply
4. 7404 IC Truth Table
|
importation(A) |
exports(Y) |
|
0 |
1 |
|
1 |
0 |
5. Functionality of the IC 7404
5.1 Inverter Operation
1. Input Signal Reception: Each inverter receives an individual input signal, which can exist in one of two states: high or low.
2. Signal Inversion Process: Upon receiving the signal, the inverter activates its logic mechanism to invert the state of the signal:
- - If the input is high (logical level 1), the output becomes low (logical level 0).
- - If the input is low (logical level 0), the output switches to high (logical level 1).
5.2 Utility in Logic Circuits
- - Building Complex Operations: By combining multiple NOT gates, complex logical functions required for advanced electronic systems can be built.
- - Multifunctional Applications: They are crucial for generating precise control and timing needed to manage various digital operations, from simple timing circuits to more complex computational logics.
5.3 Integration of Six Independent Inverters
- - Independent Operation: Each inverter operates autonomously, allowing multiple inversion operations simultaneously without interference.
- - Simplified Design and Assembly: By integrating multiple gates into one unit, the 7404 IC reduces the complexity and number of components needed on the circuit board, simplifying the design and speeding up the assembly process.
6. Advantages and Disadvantages of IC 7404
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
low power |
Limit output current |
|
high noise immunity |
Voltage range limitation |
|
user-friendly |
Not suitable for high speed applications |
|
inexpensive |
|
7. Equivalents of IC 7404
- - Pin Compatibility: Ensuring pin compatibility is crucial for seamless replacement when using an equivalent product.
- - Voltage and Current Ratings: Check the voltage and current ratings to confirm that the replacement part can meet the specific requirements of the circuit.
- - Additional Features: Depending on the application, consider whether additional features (such as the Schmitt trigger inputs in the 74LS14) may be beneficial.
8. Applications of IC 7404
- - General logic
- - Servers
- - Memory units
- - Personal computers and laptops
- - Digital Electronics
- - Networking
- - Digital systems
9. IC 7404 2D Packaging Model
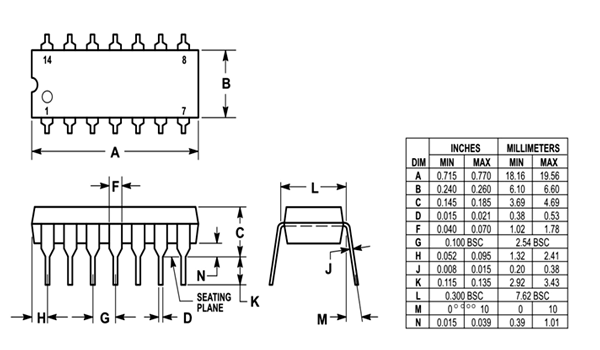
10. IC 7404 Datasheet
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
1. Is 7404 logic NOT gate or inverter?
2. Why is TTL better than CMOS?
3. How do I know if my IC is TTL or CMOS?
About us
ALLELCO LIMITED
Read more
Quick inquiry
Please send an inquiry, we will respond immediately.

Silver Oxide Batteries and Alkaline Batteries: Working Principle, Characteristics and Differences
on April 24th

AG10 Battery and Equivalent Battery Replacement
on April 23th
Popular Posts
-
What is GND in the circuit?
on January 1th 3251
-

RJ-45 Connector Guide: RJ-45 Connector Color Codes, Wiring Schemes, R-J45 Applications, RJ-45 Datasheets
on January 1th 2801
-
Understanding Power Supply Voltages in Electronics VCC, VDD, VEE, VSS, and GND
on November 19th 2605
-

Fiber Connector Types: SC Vs LC And LC Vs MTP
on January 1th 2249
-

Comparison Between DB9 and RS232
on January 1th 1867
-

What Is An LR44 Battery?
Electricity, that ubiquitous force, quietly permeates every aspect of our daily lives, from trivial gadgets to life-threatening medical equipment, it plays a silent role. However, truly grasping this energy, especially how to store and efficiently output it, is no easy task. It is against this background that this article will focus on a type of coin cell battery that may seem insignificant on the...on January 1th 1836
-
Understanding the Fundamentals:Inductance Resistance, andCapacitance
In the intricate dance of electrical engineering, a trio of fundamental elements takes center stage: inductance, resistance, and capacitance. Each bears unique traits that dictate the dynamic rhythms of electronic circuits. Here, we embark on a journey to decipher the complexities of these components, to uncover their distinct roles and practical uses within the vast electrical orchestra. Inductan...on January 1th 1789
-
What Is RF and Why Do We Use It?
Radio Frequency (RF) technology is a key part of modern wireless communication, enabling data transmission over long distances without physical connections. This article delves into the basics of RF, explaining how electromagnetic radiation (EMR) makes RF communication possible. We will explore the principles of EMR, the creation and control of RF signals, and their wide-ranging uses. The article ...on January 1th 1779
-

CR2430 Battery Comprehensive Guide: Specifications, Applications and Comparison to CR2032 Batteries
What is CR2430 battery ?Benefits of CR2430 BatteriesNormCR2430 Battery ApplicationsCR2430 EquivalentCR2430 VS CR2032Battery CR2430 SizeWhat to look for when buying the CR2430 and equivalentsData Sheet PDFFrequently Asked Questions Batteries are the heart of small electronic devices. Among the many types available, coin cells play a crucial role, commonly found in calculators, remote controls, and ...on January 1th 1775
-
Comprehensive guide to hFE in transistors
Transistors are crucial components in modern electronic devices, enabling signal amplification and control. This article delves into the knowledge surrounding hFE, including how to select a transistor's hFE value, how to find hFE, and the gain of different types of transistors. Through our exploration of hFE, we gain a deeper understanding of how transistors work and their role in electronic circu...on November 19th 1760

















































