How to Reduce Your Energy Bill with the Right Toaster Choice
In today’s fast-paced lifestyle, toasters have become a staple in modern kitchens, offering both functionality and convenience for breakfast preparations. As households become more energy-conscious, understanding the diverse range of toaster models—particularly in terms of power consumption and operational efficiency—is more critical than ever. This exploration begins with a detailed comparison of two-slice and four-slice toasters, which are popular choices among consumers. These models not only differ in capacity but also in their energy requirements and suitability for different family sizes or culinary needs. Delving deeper, we will analyze how various factors like wattage, toaster type, and the number of heating elements influence the overall power consumption of these everyday appliances.Catalog

Figure 1: Toaster
Different Types of Toasters and Their Power Consumption
In modern kitchens, toasters have become essential due to their convenience and functionality. As consumers choose from a variety of models, they often select based on family size and usage habits, with two-slice and four-slice toasters being the most common.
Two-Slice Toasters

Figure 2: Two-Slice Toasters
Two-slice toasters are favored by small families or individuals because of their compact design and affordability. These toasters fit well in kitchens with limited counter space and do not take up much room. They are generally designed to be energy-efficient, with power ratings ranging from 650W to 1600W. The average power in the U.S. is about 880W, while in the U.K., it's slightly higher at approximately 985.91W, with power varying between 780W to 1670W. Users can adjust the browning settings from light to dark according to personal taste. For thicker slices of bread, it may be necessary to adjust the bread slot or flip the bread to ensure even heating.
Four-Slice Toasters

Figure 3: Four-Slice Toasters
Four-slice toasters are better suited for larger families or those who need to prepare multiple breakfasts at once. These models typically have four separate heating slots, each with its own heating element, allowing for the simultaneous toasting of four slices, which enhances cooking efficiency. In the U.S., the power range for four-slice toasters is wide, from 900W to 1800W, with an average power of about 1515.3W. The U.K. market shows higher efficiency, with power ranging from 1400W to 2300W and an average power of 1787.41W. It's important to ensure that the bread slices are evenly distributed in the slots to avoid uneven toasting or undercooking.
Overall, whether it's a two-slice or a four-slice toaster, choosing the right model can greatly satisfy daily needs and improve breakfast preparation efficiency. The two-slice models are ideal for energy savings and space conservation in smaller households, while four-slice models meet the demands of larger families or gatherings.
Main Factors Affecting Toaster Power Consumption
The power consumption of a toaster is influenced by several factors including the type and number of heating elements, the size and capacity of the toaster, and the integration of advanced features.
Firstly, the type of heating element significantly impacts power usage. Traditional toasters often use metal alloy elements like nichrome, which, despite being cost-effective, are less efficient in heat conduction and require longer preheating times. In contrast, toasters with quartz heating elements can heat up almost instantly when turned on, greatly reducing energy loss. Quartz elements are known for their efficient heat conductivity and rapid response time, quickly transferring heat directly to the bread and minimizing heat dissipation into the air, thereby lowering overall energy consumption.
Secondly, the size and capacity of the toaster directly influence its total power usage. Larger toasters typically have more heating elements or larger heating areas, which, while able to handle more slices of bread at once, also increase energy consumption. For households or situations where multiple slices need toasting simultaneously, choosing a toaster with the right capacity is key to balancing energy efficiency with functionality.
Next, advanced features, such as convection heating technology, also contribute to increased power consumption. Convection toasters use a built-in fan to force air circulation, improving the even distribution of heat and effectively toasting food. However, while this technology enhances heating performance, it also increases energy use, as both the fan and its control systems require additional electricity.
|
2 Slice Toaster Wattage Category |
US |
UK |
|
Average |
880W |
985.91W |
|
Most common |
750W |
850W |
|
Highest |
1600W |
1670W |
|
Lowest |
650W |
780W |
Chart 1: Usage Power Table of Two-Slice Toaster in UK and US
|
4 Slice Toaster Wattage Category |
US |
UK |
|
Average |
1515.3W |
1787.41W |
|
Most common |
1300W |
1800W |
|
Highest |
1800W |
2300W |
|
Lowest |
900W |
1400W |
Chart 2: Usage Power Table of Four-Slice Toaster in UK and US
How to Calculate the Cost of Toaster?

Figure 4: How to Calculate the Cost of Toaster?
Understanding the energy costs of baking bread can help you manage your household budget and make informed decisions about purchasing or replacing kitchen appliances. By calculating the costs associated with using a toaster, consumers can keep track of small daily expenses and make smarter choices regarding their appliances. To calculate the energy cost of toasting bread, consider these key parameters: the toaster's wattage, the duration of use, and the electricity rate. For instance, using a common toaster with a power rating of 1200 watts (W), if each toasting session lasts for 3 minutes, you can estimate the energy consumption as follows:
First, convert the power rating from watts to kilowatt-hours (kWh), which is the unit of measurement for electricity billing. A power rating of 1200 W is equivalent to 1.2 kilowatts (kW). Therefore, if the toaster runs for 3 minutes, the operation time in hours is 0.05 hours (3 minutes divided by 60 minutes). The electricity used is then 1.2 kW multiplied by 0.05 hours, resulting in an energy consumption of 0.06 kWh.
Next, to calculate the cost of this energy consumption, take the average electricity price in the U.S., for example, $0.15 per kWh. The cost per toasting session is then calculated as follows:
Cost = Energy (kWh) × Price ($/kWh) = 0.06 kWh × $0.15/kWh = $0.009.
While this calculation might seem straightforward, it highlights the practical value of energy-efficient appliances in daily life. By comparing toasters with different power ratings and efficiencies, users can see how much they can save over time with more energy-efficient devices.
This method of calculation is not only applicable to toasters but also to other household appliances. By using this approach, consumers can evaluate the cost-effectiveness of various devices, aiding in more rational purchasing decisions. This savvy consumption not only helps households manage their budgets more effectively but also promotes the choice of environmentally friendly and efficient appliances.
|
|
750W |
900W |
1000W |
|
1 min/day |
$1.51 |
$1.81 |
$2.01 |
|
2 min/day |
$3.01 |
$3.61 |
$4.02 |
|
3 min/day |
$4.52 |
$5.42 |
$6.02 |
|
4 min/day |
$6.02 |
$7.23 |
$8.03 |
|
5 min/day |
$7.53 |
$9.03 |
$10.04 |
Chart 3: Costing of a Two-Slice Toaster
|
|
1400W |
1700W |
2000W |
|
1 min/day |
$2.81 |
$3.41 |
$4.02 |
|
2 min/day |
$5.62 |
$6.83 |
$8.03 |
|
3 min/day |
$8.43 |
$10.24 |
$12.05 |
|
4 min/day |
$11.24 |
$13.65 |
$16.06 |
|
5 min/day |
$14.05 |
$17.06 |
$20.08 |
Chart 4: Costing of a Four-Slice Toaster
Outdoor Power Solutions for Toasters
Figure 5: Outdoor Power Solutions for Toasters
For outdoor enthusiasts or those who need to operate a toaster in environments without electrical outlets, finding the right power solution is crucial for ensuring a continuous power supply. The availability of modern portable power solutions has significantly expanded, making outdoor cooking more convenient and practical. There are three common types of equipment for powering devices outdoors: portable power stations, inverters, and generators, each with its own advantages and suitable applications.
Portable Power Stations
Portable power stations typically use high-capacity lithium batteries, offering a lightweight and easy-to-carry design ideal for short camping trips or outdoor gatherings. For instance, a 2000W portable power station can not only provide stable power for a 1200W toaster but also handle other small household appliances, ensuring both continuous and stable power supply.

Figure 6: Portable Power Stations
Inverters
Inverters, which convert direct current (DC) from a vehicle battery into alternating current (AC), are perfect for connecting car batteries to outdoor appliances. This is particularly useful during road trips, as the inverter can efficiently transform the vehicle’s DC into AC needed for a toaster and other appliances.
Generators
Generators are a more robust power solution suitable for long-term camping or activities in remote areas. While generators are heavier and noisier, their high power output can support multiple appliances simultaneously, including toasters, greatly enhancing the comfort and convenience of outdoor activities.
When choosing the best outdoor power solution, users should consider factors such as capacity, weight, operational noise, and energy efficiency. Safety is also a critical aspect. It's important to select power devices that meet safety standards and certifications to prevent electrical malfunctions or fire hazards. By carefully selecting the appropriate power solution, users can ensure smooth operation of their toaster and other devices while enjoying their outdoor activities safely.

Figure 7: Generator
Energy-Saving Tips for Toasters
Properly using these devices can not only save energy but also help reduce household expenses. There are several effective strategies to decrease energy consumption with a toaster through simple practices.
Opt for a Toaster with Adjustable Browning Settings
First, we can choose a toaster with adjustable browning settings. These toasters typically offer a range of options for how darkly toasted you want your bread. By precisely controlling the toasting time and temperature, you can prevent excessive heating, which wastes energy, and ensure that the food reaches the desired flavor and texture. For instance, lightly toasted bread requires less energy compared to dark, crispy toast. Users should set the toaster according to personal taste to avoid unnecessary energy use.
Bake Multiple Slices of Bread at Once
Another strategy to conserve energy is to toast multiple slices at once. Most toasters undergo a rapid preheating phase when first turned on. If you toast only one slice at a time, the energy used in this preheating phase is not utilized efficiently. On the other hand, toasting multiple slices simultaneously maximizes the use of this initial high temperature, reducing the energy wasted on multiple preheating sessions. Additionally, this method not only saves energy but also time, making it ideal for busy mornings when you need to prepare breakfast quickly.
Disconnect the Toaster When Not Using It
A further important tip for saving energy involves disconnecting the toaster when not in use. Many appliances continue to consume a small amount of "vampire power" even when turned off but still plugged in. While the consumption per use might be minimal, it can add up to a significant cost over time. Therefore, it is advisable to unplug the toaster after each use, completely cutting off power and preventing any unnecessary energy loss. This simple step can significantly enhance energy efficiency in your home.
Recommendations for Low Wattage Toasters
For those looking to reduce household energy consumption further, opting for a low-wattage toaster is a smart choice. The market offers a variety of low-power toasters that meet daily needs while helping to cut down on energy bills, achieving both economic and environmental benefits. Some low wattage toasters will be provided here for everyone to choose and refer to.
|
US Toasters |
Model |
Wattage |
|
Lowest wattage toaster |
Nostalgia – MyMini |
500W |
|
Lowest wattage 2 slice toaster |
Nostalgia – Kraft Deluxe |
650W |
|
Lowest wattage 4 slice toaster |
Gevi – 5402 |
900W |
Chart 5: Best Recommended Lowest Wattage Toaster in the US
|
UK Toasters |
Model |
Wattage |
|
Lowest wattage toaster |
Laura Ashley – VQSBT582WSUK |
780W |
|
Lowest wattage 4 slice toaster |
Coolworks |
1400W |
Chart 6: Best Recommended Lowest Wattage Toaster in the UK
Conclusion
The quest for efficiency in kitchen appliances, especially toasters, extends beyond just selecting a model with suitable capacity or aesthetic appeal. It encompasses a strategic approach to managing household energy consumption and reducing operational costs. As we have explored, making informed choices about toaster wattage and features, such as adjustable browning settings and energy-efficient designs, can lead to significant savings and environmental benefits. For those venturing outdoors or seeking to minimize their kitchen's energy footprint, adopting portable power solutions or opting for low-wattage toasters provides practical pathways to achieve these goals. Ultimately, whether it's through understanding the cost implications of using different toasters or implementing energy-saving tips, consumers are empowered to make decisions that align with both their lifestyle needs and sustainability goals.
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
1. Does a toaster use a lot of power?
No, compared to larger appliances like ovens or air conditioners, toasters use relatively moderate amounts of power. However, their power usage can be considered significant for their size and the brief duration they are typically used.
2. How many watts does a two-slice toaster use?
A two-slice toaster generally uses between 650 watts and 1600 watts, with the most common wattage around 750 watts in the US and 850 watts in the UK.
3. Should I unplug my toaster every day?
Yes, it is advisable to unplug your toaster when not in use to avoid the risk of fire and to prevent phantom energy use, which can contribute to unnecessary power consumption.
4. Why does the toaster need so much power?
Toasters need a significant amount of power to rapidly generate enough heat to toast bread efficiently. This high power is required to quickly bring the heating elements to a high temperature, which ensures the bread is toasted evenly and swiftly.
5. How many watts does a four-slice toaster use?
A four-slice toaster typically uses between 900 watts and 1800 watts in the US, with higher efficiencies observed in the UK, where they range from 1400 watts to 2300 watts. These higher wattages allow for more slices to be toasted simultaneously and effectively.
About us
ALLELCO LIMITED
Read more
Quick inquiry
Please send an inquiry, we will respond immediately.
Mastering Schematic Symbols: A Guide to Electronic Circuit Design
on May 13th
Comparison and Selection of UJT and BJT
on May 11th
Popular Posts
-
What is GND in the circuit?
on January 1th 3259
-

RJ-45 Connector Guide: RJ-45 Connector Color Codes, Wiring Schemes, R-J45 Applications, RJ-45 Datasheets
on January 1th 2806
-
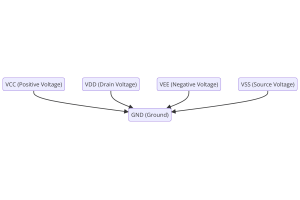
Understanding Power Supply Voltages in Electronics VCC, VDD, VEE, VSS, and GND
on November 20th 2620
-

Fiber Connector Types: SC Vs LC And LC Vs MTP
on January 1th 2253
-

Comparison Between DB9 and RS232
on January 1th 1869
-

What Is An LR44 Battery?
Electricity, that ubiquitous force, quietly permeates every aspect of our daily lives, from trivial gadgets to life-threatening medical equipment, it plays a silent role. However, truly grasping this energy, especially how to store and efficiently output it, is no easy task. It is against this background that this article will focus on a type of coin cell battery that may seem insignificant on the...on January 1th 1836
-
Understanding the Fundamentals:Inductance Resistance, andCapacitance
In the intricate dance of electrical engineering, a trio of fundamental elements takes center stage: inductance, resistance, and capacitance. Each bears unique traits that dictate the dynamic rhythms of electronic circuits. Here, we embark on a journey to decipher the complexities of these components, to uncover their distinct roles and practical uses within the vast electrical orchestra. Inductan...on January 1th 1791
-
What Is RF and Why Do We Use It?
Radio Frequency (RF) technology is a key part of modern wireless communication, enabling data transmission over long distances without physical connections. This article delves into the basics of RF, explaining how electromagnetic radiation (EMR) makes RF communication possible. We will explore the principles of EMR, the creation and control of RF signals, and their wide-ranging uses. The article ...on January 1th 1782
-

CR2430 Battery Comprehensive Guide: Specifications, Applications and Comparison to CR2032 Batteries
What is CR2430 battery ?Benefits of CR2430 BatteriesNormCR2430 Battery ApplicationsCR2430 EquivalentCR2430 VS CR2032Battery CR2430 SizeWhat to look for when buying the CR2430 and equivalentsData Sheet PDFFrequently Asked Questions Batteries are the heart of small electronic devices. Among the many types available, coin cells play a crucial role, commonly found in calculators, remote controls, and ...on January 1th 1781
-
Comprehensive guide to hFE in transistors
Transistors are crucial components in modern electronic devices, enabling signal amplification and control. This article delves into the knowledge surrounding hFE, including how to select a transistor's hFE value, how to find hFE, and the gain of different types of transistors. Through our exploration of hFE, we gain a deeper understanding of how transistors work and their role in electronic circu...on November 20th 1769
















































