STM32F103RCT6 Microcontroller: Alternatives, Pinout, and Strengths
Microcontrollers are important in modern electronics, serving as the brains behind countless devices in our daily lives. This article delves into the valuable aspects of microcontrollers, particularly the STM32F103RCT6 model from STMicroelectronics. We will explore its defining features, components, applications in embedded systems, and advantages and disadvantages. By understanding these elements, we can appreciate how microcontrollers drive innovation in smart devices, industrial automation, and medical technologies, ultimately enhancing efficiency and performance in diverse fields.Catalog
Understanding Microcontrollers
A microcontroller is an integrated circuit enveloping a processor core, memory, input/output ports, and various peripheral interfaces, all within a solitary chip. This compact device functions akin to a miniature computer, deftly executing data processing and control tasks at remarkable speeds. Unlike traditional microprocessors, microcontrollers boast reduced size, lower power consumption, and heightened integration. These characteristics render them exceptionally suitable for embedded systems applications.
Microcontrollers contain several elements enabling them to undertake diverse and complex tasks. The processor core, responsible for executing program instructions. Memory components, comprising RAM and flash, which store data and code. Input/output (I/O) ports, facilitating interaction with other devices. Peripheral interfaces, such as timers, serial communication modules, and analog-to-digital converters, which diversify functionality.
Microcontrollers are extensively employed in embedded systems, which are purpose-built computer systems tailored for specific tasks. Common uses include household appliances, automotive controls, medical devices, and industrial automation systems. The advantageous integration and minimal power needs of microcontrollers make them favorable for battery-operated devices, enhancing convenience and efficiency in everyday life.
What is the STM32F103RCT6 Microcontroller?
• STM32: Signifies the 32-bit microcontroller line from STMicroelectronics.
• F103: Defines the series within the product line. "F" denotes FLASH memory, "1" indicates the first generation, and "03" designates the performance level.
• RCT6: "R" describes an LQFP package, "C" represents a 64-pin version, and "T6" signifies a 72 MHz clock frequency.
The STM32F103RCT6 microcontroller, crafted by STMicroelectronics, operates as a sophisticated 32-bit device utilizing the ARM Cortex-M3 core. This microcontroller runs at an impressive 72 MHz, integrating 256 KB of program memory via FLASH technology. Additionally, it boasts 512 KB of FLASH memory and 64 KB of SRAM, providing ample space for complex software applications and extensive data storage requirements. To enhance system reliability and security, this microcontroller incorporates several protection mechanisms. These include cyclic redundancy check (CRC) checks, watchdog timers, and multiple low-power modes. Such features become need in specific applications where maintaining operational integrity and effective power management.
STM32F103RCT6 Alternatives
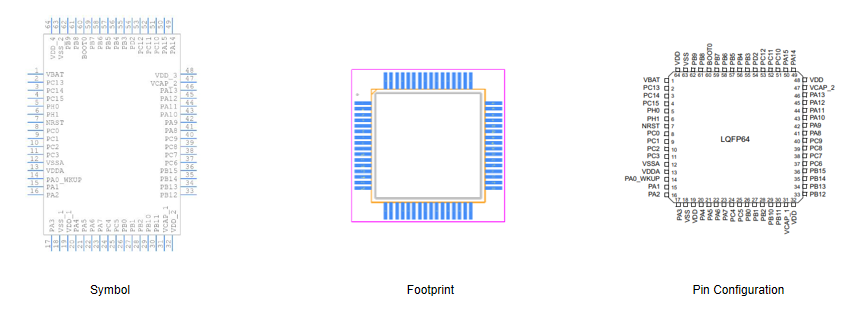
STM32F103RCT6 Pinout, Symbol and Footprint
Symbol
The symbol of a component transcends mere graphical representation. It acts as a bridge linking schematic drawings and practical applications. A symbol’s simplified portrayal of a component allows designers to intuitively grasp its role and connections within larger circuits. In integrated circuit design, a well-crafted symbol fosters seamless collaboration, nurturing a shared understanding that minimizes potential design errors. This mutual comprehension becomes the bedrock of successful projects.
Footprint
The footprint of an electronic component outlines the specific board layout requirements. This includes pad sizes and spacing needed for reliable soldering and optimal electrical performance. When creating printed circuit boards (PCBs), careful attention to footprint specifications ensures flawless alignment. Misalignment or incorrect sizing in footprints can trigger soldering defects or compromise electrical integrity. Precision in footprint design is central to achieving compatibility with automated assembly processes, bolstering the reliability of the final product. This optimization process weighs both electrical and thermal performance factors to achieve the best results.
Pin Configuration
Pin configuration specifies the pin assignments and their respective functions; this serves as a blueprint for connectivity. Each pin on a component has its distinct purpose from power supply and ground connections to signal input/output functions. Accurate understanding and implementation of these pin assignments prove to be important. Errors in pin connections can lead to malfunction or irreversible damage to the component and surrounding circuitry. Annotations on datasheets and application notes become invaluable references.
STM32F103RCT6 Microcontroller Features
The STM32F103RCT6 microcontroller is designed for low power consumption, which greatly extends battery life in portable devices. Think of it like optimizing your smartphone's battery settings to maximize usage without sacrificing features. It includes various connection options such as UART, SPI, I2C, USB, timers, and ADCs, making it easy to integrate different sensors and communication modules, much like how input/output ports in laptops allow for diverse device connections.
Its onboard DMA controller enables fast data transfers, easing the CPU's workload. This is similar to using a dedicated graphics card to handle rendering, freeing the main processor for other tasks. Additionally, it has integrated SRAM for quick data access and onboard flash for secure storage, resembling how both RAM and SSDs work together in computers.
The development support is robust, with debugging interfaces and software libraries that streamline the process and enhance productivity, much like integrated development environments (IDEs) in software development. Its advanced interrupt controller prioritizes urgent tasks efficiently, akin to an office manager balancing high-priority assignments with routine duties.
Powered by an ARM Cortex-M3 core at up to 72MHz, the STM32F103RCT6 achieves impressive performance while remaining energy-efficient, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from industrial automation to consumer electronics. Its combination of low-power modes, versatile interfaces, efficient data handling, memory options, and strong development tools makes it a standout choice.
What are the Technical Specifications of the STM32F103RCT6?
|
Product Attribute |
Attribute Value |
|
Manufacturer |
ST Microelectronics |
|
Package / Case |
LQFP-64 |
|
Packaging |
Tray |
|
Length |
10 mm |
|
Width |
10 mm |
|
Height |
1.4 mm |
|
Supply Voltage |
2 V ~ 3.6 V |
|
Maximum Clock Frequency |
72 MHz |
|
Program Memory Size |
256 kB |
|
ADC Resolution |
12 bit |
|
Data Bus Width |
32 bit |
|
Operating Temperature |
-40°C ~ 85°C |
|
Data RAM Size |
48 kB |
|
Data RAM Type |
SRAM |
|
Mounting Style |
SMD/SMT |
|
Number of I/Os |
51 |
|
Number of Timers/Counters |
8 |
|
Number of ADC Channels |
16 |
|
Pin Count |
64 |
|
Product Type |
ARM Microcontrollers - MCU |
STM32F103RCT6 Microcontroller Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
• Budget-friendly for small to medium-sized embedded systems: STM32F103RCT6 is attractively priced, aligning well with cost-sensitive projects. Its affordability makes it a popular choice that need moderate processing capabilities without hefty financial commitments.
• Extensive peripheral support (USB, CAN, SPI, I2C, USART): The microcontroller’s wide range of peripheral interfaces allows for versatile application development. By supporting multiple communication protocols, it becomes a strong candidate for diverse industries, including industrial automation, healthcare devices, and consumer electronics.
• 64KB flash and 20KB SRAM for code and data storage: With ample memory, STM32F103RCT6 efficiently handles complex firmware and data management.
• 72MHz clock speed for moderate computing demands: Operating at a 72MHz clock frequency, this microcontroller strikes a balance between performance and power consumption. It is ideal for tasks requiring timely execution, such as motor control, real-time monitoring, and basic machine learning algorithms.
• 32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 core delivering powerful performance and energy efficiency: The ARM Cortex-M3 core provides strong computational power while remaining energy-efficient. This dual benefit is useful for battery-powered devices that need prolonged operational periods. The architecture supports intensive processing tasks without draining the power supply quickly.
Disadvantages
• Limited to 3.3V operation imposes integration challenges: One drawback is its reliance on a 3.3V power supply, complicating its use with 5V systems.
• Single-chip mode restrictions for complex systems: STM32F103RCT6’s support for single-chip mode limits its use in multi-chip systems. This restriction makes it less suitable for high-end applications like advanced robotics or expansive industrial systems that depend on multiple microcontrollers for parallel processing.
• Lack of DSP instructions impedes intensive signal processing: The absence of dedicated Digital Signal Processing (DSP) instructions reduces its efficacy in handling complex signal processing tasks. This limitation makes it unsuitable for advanced audio processing, high-speed communications, and other DSP-specific applications requiring specialized hardware.
• Steep learning curve for newcomers in microcontroller programming: Mastering STM32F103RCT6 can be challenging for beginners. It demands a strong grasp of embedded systems concepts and familiarity with the associated development tools. This initial complexity might deter new users, driving them towards more user-friendly platforms.
STM32F103RCT6 Size and Package
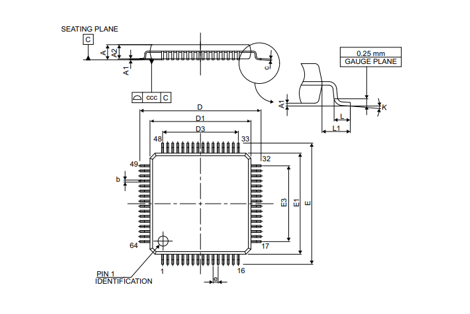
The STM32F103RCT6 microcontroller boasts a compact form, measuring 10mm in length and width, with a height of 1.4mm. This precise sizing is achieved by employing an LQFP (Low-profile Quad Flat Package). The LQFP packaging is renowned for its superior heat dissipation properties, enabling it to accommodate a higher pin count efficiently. This packaging choice becomes cherished in applications that require numerous interfaces and peripherals.
What Applications Use the STM32F103RCT6?
Smart Instrumentation
In smart instrumentation, the STM32F103RCT6, intelligently control of devices like water meters and gas meters. Utilizing USART and UART interfaces, it ensures seamless and reliable communication between devices and central monitoring systems. The ability to implement precise control algorithms enhances the efficiency and accuracy of these instruments. For example, the microcontroller can dynamically adjust flow rates based on real-time data, optimizing resource management.
Medical Equipment
Medical equipment leverages the STM32F103RCT6 to manage analog signals via ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) and DAC (Digital-to-Analog Converter) interfaces. This capability is good for the control required in devices such as insulin pumps and ECG monitors. Accurate signal conversion and processing are need for consistent and reliable performance in healthcare applications. Applications include, developing portable diagnostic devices that demand high precision and reliability.
Wireless Communication Technologies
The STM32F103RCT6 contributes to wireless communication technologies, including Zigbee and LoRa, which are ideal for various IoT (Internet of Things) applications. The microcontroller's adept handling of communication protocols makes it an excellent choice for creating mesh networks in smart cities or rural remote monitoring systems. Roles in wireless communication are facilitating low-power, long-range communication, and ensuring consistent data transmission over long distances.
Industrial Control
In industrial control systems, the STM32F103RCT6 is good for managing processes, motion control, and robotics. With SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface), I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit), and USART (Universal Synchronous/Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter) interfaces, it ensures precise synchronization and communication between system components. This precise control is use in automating complex processes, reducing manual intervention, and increasing productivity. Practical uses include CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines, where exact motion control to producing high-precision parts.
Smart Homes
Within smart home ecosystems, the STM32F103RCT6 enables the control of various devices such as lighting, thermostats, and security systems via wireless communication protocols. Its capability for remote control and monitoring reshapes home management, enhancing convenience and security. Involve, allowing homeowners to adjust their environment remotely. Leading to energy savings and a more responsive living space.
Using the STM32F103RCT6 Development Board
To connect the STM32F103RCT6 development board to your computer, you can either use a USB-to-serial module or a direct USB connection. You can also enhance the board's functionality by connecting various devices like sensors and actuators.
First, set up your development environment. Install tools like Keil or IAR Embedded Workbench, and configure them according to the STM32F103RCT6 specifications, focusing on clock settings and memory mappings. This setup is need for effective programming and debugging.
Next, start coding based on your project needs. Use sample codes and documentation to help you with tasks like configuring GPIO pins or integrating communication protocols like I2C and SPI.
Make sure to utilize the debugging features in your IDE. Use single-step debugging, set breakpoints, and monitor variables to find and fix issues efficiently.
As you test, download your initial code to the development board. Use debugging tools to identify logical errors or hardware problems. Adjust your code based on what you learn from these tests.
When testing, take a modular approach. Test each module or function individually to ensure everything works well before bringing them together into the complete system.
Finally, when you're ready to deploy, program the STM32F103RCT6 chip or other targets. Create a firmware image if needed. Document all development and testing processes thoroughly, as this will help with future maintenance and upgrades.
Comparing STM32F103RCT6 and STM32F103RBT6
Voltage Range Differences
The STM32F103RCT6 operates within a range from 2V to 3.6V, a span that offers flexibility for applications needing exact power adjustments. In contrast, the STM32F103RBT6 supports 2V to 3.3V, which narrows down its scope but offers a slightly different power dynamic. This voltage range difference, seemingly minor, impacts suitability for specialized applications. Devices requiring higher power efficiency or longer battery life could benefit from the RCT6's broader range.
Package Type Variations
The STM32F103RCT6 is encapsulated in an LQFP (Low Quad Flat Package). This package type simplifies assembly and inspection, making it a favorite among developers during prototyping stages. The STM32F103RBT6 is offered in an LFBGA (Low Footprint Ball Grid Array) package, which requires more precision during assembly. However, LFBGA packages excel in thermal performance and offer a smaller footprint, aligning them with densely packed designs.
Hardware Interfaces and Peripheral Support
Both the RCT6 and RBT6 support an array of peripherals, including AVRs, USBs, and multiple GPIOs. This extensive peripheral support makes them versatile, suiting everything from simple motor controls to intricate communication systems. Although their peripheral offerings are similar, subtle differences can impact their application. For instance, discrepancies in I2C or SPI configurations can lead to prefer one over the other for specific sensor interfacing needs in embedded systems.
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
1. What is the STM32F103RCT6?
The STM32F103RCT6, a microcontroller from STMicroelectronics, belongs to the STM32F1 series. Built on the ARM Cortex-M3 core, it promises high performance coupled with low power consumption. This microcontroller finds extensive use in various applications, ranging from consumer electronics to intricate industrial systems, where reliability and efficiency are paramount.
2. How is the STM32F103RCT6 programmed?
The STM32F103RCT6 can be programmed using several integrated development environments (IDEs): STM32CubeIDE, Keil MDK, and Arduino IDE with the STM32 Arduino core. Choosing an environment often hinges on the project's specific needs. Some may seek advanced debugging features, while others might prioritize compatibility with existing codebases. For instance, STM32CubeIDE offers extensive resources from STMicroelectronics, including rich libraries and robust support, which can be invaluable for complex projects.
3. What are the replacements for STM32F103RCT6?
Potential replacements for the STM32F103RCT6 include STM32F103RCT6TR and STM32F103RCT7. These alternatives provide similar functionalities with slight variations to cater to specific requirements. When considering a replacement, it is wise to evaluate the exact pin configurations and feature sets to ensure seamless integration and avoid disruptions in application performance.
4. What is the clock frequency of STM32F103RCT6?
The STM32F103RCT6 supports a maximum CPU frequency of up to 72MHz. This capability enables efficient data processing and control in real-time applications. The relatively high clock speed, combined with the microcontroller’s capabilities, suits tasks that demand swift computations and rapid response times.
5. What is STM32F103?
The STM32F103 microcontrollers, utilizing the ARM Cortex-M3 core, can operate at speeds up to 72 MHz. They encompass a wide range of memory sizes, from 16 KB to 1 MB, addressing various application needs. These microcontrollers feature motor control peripherals, USB full-speed interfaces, and CAN capabilities. Their versatility makes them a popular choice in fields ranging from automotive systems to consumer electronics, proving invaluable wherever adaptability and performance are required.
About us
ALLELCO LIMITED
Read more
Quick inquiry
Please send an inquiry, we will respond immediately.

TLP250 Driver for MOSFET and IGBT: Manufacturer Overview, Footprint, and Application Guide
on September 27th

BC639 Transistor: Features, Pin Configuration, and Applications
on September 27th
Popular Posts
-
What is GND in the circuit?
on January 1th 3126
-

RJ-45 Connector Guide: RJ-45 Connector Color Codes, Wiring Schemes, R-J45 Applications, RJ-45 Datasheets
on January 1th 2681
-
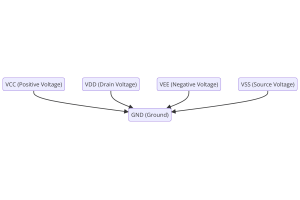
Understanding Power Supply Voltages in Electronics VCC, VDD, VEE, VSS, and GND
on November 15th 2234
-

Fiber Connector Types: SC Vs LC And LC Vs MTP
on January 1th 2188
-

Comparison Between DB9 and RS232
on January 1th 1804
-

What Is An LR44 Battery?
Electricity, that ubiquitous force, quietly permeates every aspect of our daily lives, from trivial gadgets to life-threatening medical equipment, it plays a silent role. However, truly grasping this energy, especially how to store and efficiently output it, is no easy task. It is against this background that this article will focus on a type of coin cell battery that may seem insignificant on the...on January 1th 1778
-
Understanding the Fundamentals:Inductance Resistance, andCapacitance
In the intricate dance of electrical engineering, a trio of fundamental elements takes center stage: inductance, resistance, and capacitance. Each bears unique traits that dictate the dynamic rhythms of electronic circuits. Here, we embark on a journey to decipher the complexities of these components, to uncover their distinct roles and practical uses within the vast electrical orchestra. Inductan...on January 1th 1731
-

CR2430 Battery Comprehensive Guide: Specifications, Applications and Comparison to CR2032 Batteries
What is CR2430 battery ?Benefits of CR2430 BatteriesNormCR2430 Battery ApplicationsCR2430 EquivalentCR2430 VS CR2032Battery CR2430 SizeWhat to look for when buying the CR2430 and equivalentsData Sheet PDFFrequently Asked Questions Batteries are the heart of small electronic devices. Among the many types available, coin cells play a crucial role, commonly found in calculators, remote controls, and ...on January 1th 1683
-
What Is RF and Why Do We Use It?
Radio Frequency (RF) technology is a key part of modern wireless communication, enabling data transmission over long distances without physical connections. This article delves into the basics of RF, explaining how electromagnetic radiation (EMR) makes RF communication possible. We will explore the principles of EMR, the creation and control of RF signals, and their wide-ranging uses. The article ...on January 1th 1680
-
Comprehensive guide to hFE in transistors
Transistors are crucial components in modern electronic devices, enabling signal amplification and control. This article delves into the knowledge surrounding hFE, including how to select a transistor's hFE value, how to find hFE, and the gain of different types of transistors. Through our exploration of hFE, we gain a deeper understanding of how transistors work and their role in electronic circu...on November 15th 1642