Differences Between RG6 and RG11 Coaxial Cables
Coaxial cables play a major role in audio-visual (AV) setups, allowing for efficient signal transmission across various devices and systems. Among the popular types, RG6 and RG11 stand out due to their unique attributes, each catering to specific needs. In this article, we’ll explore the differences between RG6 and RG11 coaxial cables, examining their construction, performance, and ideal applications. Understanding these distinctions can help you make an informed choice, enhancing your AV experience by selecting the right cable for your specific requirements.Catalog

Understanding RG Coaxial Cables
RG coaxial cables are basic to the seamless operation of various telecommunications systems. These cables find their versatile application in satellite communication, radar systems, and mobile networks, in addition to providing robust connectivity within buildings. Mostly noteworthy is their role in marine communication setups, where they guarantee consistent signal quality in demanding conditions.
In the world of marine navigation, RG coaxial cables are requisite. They facilitate uninterrupted AM/FM radio communication, used for ensuring smooth voyages across expansive waters. These cables prove their mettle in video broadcasting environments, where stability and clarity of signals are dominant. High-rise structures, with their myriad of architectural complexities, also rely heavily on these cables to maintain stable connectivity across multiple levels. The challenges posed by these structures often echo those in other scenarios where signal consistency must be maintained despite physical barriers.
The integration of RG coaxial cables must account for shielding effectiveness in environments susceptible to interference. Success in such settings calls for careful planning and a thorough grasp of electromagnetic compatibility principles to boost performance levels. Selecting the appropriate type of RG cable to meet specific frequency and signal demands emphasizes the precision required. By diligently addressing signal interference, communication networks achieve heightened operational efficiency.
Coaxial Cable Construction
Core Conductor Design
At the center, part of a coaxial cable is the core conductor, typically made from copper or sometimes copper-clad steel. It plays a remarkable role in the efficient transmission of high-frequency signals. You must weigh the decision between pure copper and copper-clad steel to achieve a balance between conductivity and tensile strength, based on specific application needs. Historically, it has been noted that pure copper enhances signal quality due to its superior conductivity, which is useful in fields like data communication that demand high precision.
Dielectric Insulation Layer
The core conductor is a dielectric insulator, usually crafted from various plastic materials. This insulator is responsible for maintaining separation between conductive layers, preserving signal fidelity by preventing unintended losses or interference. Its insulating characteristics are intrinsic to the coaxial cable's overall performance. Recent advances in technology have led to innovative material developments that optimize thermal stability and reduce signal attenuation, especially in fields such as telecommunications and broadcasting.
Protective Metallic Shield
Covering the dielectric insulation is a metallic shield, commonly a braid made of copper or aluminum. This shield serves to guard against electromagnetic interference (EMI), which can disrupt operations in areas crowded with wiring or industrial settings. Experiences from long-term applications highlight the shield's need for both flexibility and strength to not only combat interference effectively but also to maintain durability over periods of use.
External Rubber Jacket
The outermost component of the coaxial cable is a sturdy rubber jacket that is designed to protect it from physical harm and environmental hazards such as sunlight, moisture, and abrasion. In outdoor settings, additional protective measures—utilizing environmental engineering techniques—are often applied to prolong the cable's lifespan in challenging conditions. This strategic approach is continually reinforced by seasoned field technicians who adapt the cable's design to overcome diverse environmental hurdles effectively.
Overview of RG6 Cable
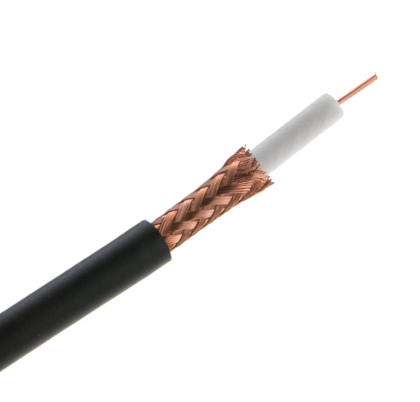

RG6 cables come with a protective sheath designed through meticulous engineering, paired with a slim and flexible structure tailored for residential networking and indoor setups. The 18-gauge center conductor ensures efficient transmission. This efficiency is further supported by the use of F-type or coaxial RF connectors, which facilitate seamless household connections. These elements highlight the practicality and accessible design of RG6 cables.
Although RG6 cables offer cost-efficient and space-saving benefits, one must consider that signal quality may degrade over extended distances. This aspect introduces challenges for certain specific installations, making it required to weigh the pros and cons based on individual circumstances. In various scenarios, RG6 cables are predominantly utilized in domestic settings. They deliver satisfactory performance for basic internet and cable television services, fostering a sense of stability for everyday household needs. For achieving the best results, careful planning is advisable for distance and the installation environment. Some strategic measures include minimizing bends in the cable and avoiding sources of electromagnetic interference.
Overview of RG11 Cable
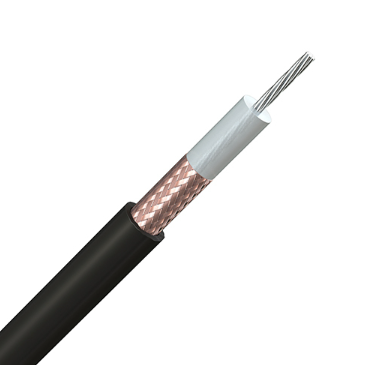
RG11 cable, distinguished by its comparatively larger diameter, finds favor in scenarios requiring extended coverage and outdoor use. This preference aligns with its capacity to maintain signal integrity over long stretches, thus curbing unwanted variations. The center of the cable features a 14-gauge conductor, which bolsters signal transmission, ensuring durability even amidst challenging environmental conditions.
With its inherent qualities, RG11 emerges as an ideal candidate for situations necessitating superior signal reliability. It's mostly apt for settings exposed to shifts in weather or potential physical wear. Such ruggedness makes these cables well-suited for linking satellite dishes or cable TV networks. Despite RG11’s capability to preserve signal strength attributed to its thickness, it poses challenges regarding flexibility. This inflexibility can complicate its use in homes where detailed routing or frequent bends are needed. In practice, you are required to carefully strategize the cable's path to handle its rigidity while maintaining performance.
Individuals often employ RG11 cables effectively over large spans without notable degradation, highlighting their reliability. Installation specialists emphasize that strategic cable management can alleviate some of its bendability issues. This often involves utilizing cable trays or adjustable brackets, which provide support against gravitational forces while accommodating required changes in direction.
Attenuation Characteristics
Planned with precision, RG11 cables aim to minimize signal loss more effectively than RG6. They excel in maintaining strong signal quality over longer distances, which translates into consistent performance in installations demanding long-distance connectivity. While attenuation might eventually impact RG11 over very extended cables, their ability to sustain signal strength is superior across broader spans compared to RG6.
In scenarios, deciding between RG6 and RG11 is largely influenced by the specific needs of the installation. For typical, shorter cable runs often found in home settings, RG6 is usually sufficient and offers a budget-friendly option.
On the other hand, when cables must bridge considerable distances, such as in vast commercial installations or extensive outdoor setups, RG11 presents itself as a more suitable option. Its capability to sustain signal quality over sprawling lengths reduces the need for additional transmission aids like boosters or repeaters, ensuring a more dependable connection.
Variations in Applications
When discussing coaxial cables, it's fascinating to observe how their physical attributes define their application range. RG6 cables, featuring a familiar diameter of 7mm, are frequently utilized in cable television setups, satellite installations, and broadband internet provisioning. They are uniquely crafted for satisfactory performance over distances up to 450 meters. Installers frequently express an exact appreciation for the equilibrium between a cable's pliability and the simplicity of its installation process, mostly in home environments where agility and adaptability are often prioritized. The versatile nature of RG6 makes it favored in spaces where spatial restrictions or complex installation routes demand innovative solutions.
In contrast, RG11 cables, known for their substantial 10mm diameter, serve similar functions as RG6 with additional enhancements. Their more robust build encourages effective signal transmission across greater lengths, covering up to 600 meters, proving instrumental in demanding settings where environmental challenges or notable distances exist between the origin of the signal and the receiving device. You can often rely on RG11 due to its remarkable ability to maintain signal integrity over substantial distances, a feature that becomes mostly used to avoid signal distortion, mostly in industrial or expansive commercial projects. This characteristic positions RG11 as a judicious selection for initiatives aimed at preserving signal robustness over long spans.
Pricing Dynamics of RG Cables
RG11 cables are crafted using high-quality materials and robust structures. This meticulous construction involves precise manufacturing techniques, resulting in superior performance and long-lasting quality. These factors lead to a higher price point. The manufacturing processes are enhanced by advanced technologies designed to resist environmental challenges, which appeals to those considering investments for specific, long-term applications.
While offering less in terms of durability compared to RG11, RG6 cables provide a cost-effective solution that doesn't heavily sacrifice efficiency, especially suitable for installations that are shorter or less demanding. The affordability of RG6 cables is largely attributed to their use of lighter materials and simpler production methods. These characteristics make them mostly appealing for residential settings or small-scale projects.
Choosing the right cable often involves balancing future benefits with current financial limitations. In the decision-making process, you can evaluate the installation environment, alongside potential needs for future scale expansions, to identify the most economical choice. Opting between RG11 and RG6 frequently represents a calculated compromise between existing financial assets and anticipated technological demands.
Flexibility Insights
The considerable thickness of RG11 coaxial cables introduces a layer of complexity in installations that demand navigation through confined or intricate layouts, often encountered in residential settings. These cables are less pliable, leading to potential challenges in areas where space constraints require sharp turns and threading through tight passageways. You can report that dealing with RG11 in such settings often necessitates specialized gear or additional manpower, influencing project duration and cost.
In contrast, RG6 cables, known for their slimmer design, are preferred for household configurations. They accommodate tighter bends and thread seamlessly through walls and ceilings, making them a practical option for home networking. Home networks, where cost considerations and installation speed are used, benefit from the straightforward handling of RG6. This favorable maneuverability not only streamlines installation but also diminishes the risk of signal degradation in straightforward environments.
For scenarios extending beyond household applications, such as establishing enduring long-distance connections or supporting backbone network systems, the use of RG11 is justified despite its limited flexibility. Its robust construction minimizes signal loss over long distances, which is basic for sustaining data integrity and high-performance levels in expansive network infrastructures. In these cases, the choice of more rigid and thick cables like RG11 is counterbalanced by the long-term benefits in performance and enhanced reliability they provide.
Rg6 vs Rg11 Detailed Comparison
|
Categories |
RG6 |
RG11 |
|
Uses |
Mostly used for satellite cables |
Only reserved for special uses |
|
Price |
Less expensive |
More expensive |
|
Thickness |
0.375 inches, weak signal strength |
0.75 inches, good signal strength |
|
Flexibility |
More flexible and less stiff |
Less flexible and stiffer |
|
Attenuation |
More signal loss |
Less signal loss |
|
Center Conductor |
18 AWG |
14 AWG |
|
Connector Types |
F-type connectors |
F-type connectors |
Conclusion
Choosing between RG6 and RG11 cables ultimately depends on the unique needs of your AV setup, including factors like installation environment, distance, and budget. While RG6 offers flexibility and cost-efficiency for everyday, shorter connections, RG11 is better suited for extended runs and applications where signal integrity is dominant. By carefully considering these factors, you can select the most appropriate cable to optimize performance, ensuring reliable, high-quality AV connections tailored to your specific setup.
About us
ALLELCO LIMITED
Read more
Quick inquiry
Please send an inquiry, we will respond immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
1. When should I use RG11?
RG11 cables find their place in cases where robust signal transmission across expansive distances is basic, commonly seen in external TV and CCTV setups. The cable's enhanced signal integrity, owing to its thicker design, contrasts with its lack of flexibility, making it mostly apt for outdoor environments rather than indoor ones. Factors like environmental impact and complexity of setup often warrant careful evaluation when considering RG11 implementation.
2. What is RG6 used for?
RG6 cables are favored in modern residential environments, especially for home television and satellite signal distribution. Their flexibility and ease of installation within buildings make them well-suited for indoor use. Beyond just installation benefits, the aspects of cost efficiency and accessibility frequently drive their application in domestic networking systems.
3. What is RG11 cable used for?
The RG11 cable is recognized for its proficiency in conveying broadband signals over extensive stretches, acting as a cornerstone for high-definition TV and surveillance systems. It is instrumental in maintaining data fidelity during long-distance signal transmission. Understanding its structural advantages is beneficial for determining its use in sturdy network infrastructures.
4. What coaxial cable is best for HDTV?
Selecting RG11 for HDTV setups is advisable, given its superior gauge that ensures effective signal management active for high-definition broadcasts. Considerations around signal quality and cable durability highlight the importance of selecting appropriate cabling for achieving top-tier audiovisual experiences.
5. Does coax cable affect Internet speed?
Coaxial cables themselves do not inherently reduce Internet speed, but their potential can be significantly elevated by leveraging MoCA technology to boost data transfer rates. This perspective highlights the importance of recognizing technological advances that can optimize existing systems to enhance service standards. Engaging in discussions about maximizing current technologies often uncovers avenues for superior connectivity outcomes.
CD4011 Nand Gate IC: Datasheet, Pinout, and Features
on November 5th

STM32F405RGT6: Specifications, Alternatives, and Datasheet
on November 5th
Popular Posts
-
What is GND in the circuit?
on January 1th 2881
-

RJ-45 Connector Guide: RJ-45 Connector Color Codes, Wiring Schemes, R-J45 Applications, RJ-45 Datasheets
on January 1th 2458
-

Fiber Connector Types: SC Vs LC And LC Vs MTP
on January 1th 2055
-
Understanding Power Supply Voltages in Electronics VCC, VDD, VEE, VSS, and GND
on November 7th 1826
-

Comparison Between DB9 and RS232
on January 1th 1746
-

What Is An LR44 Battery?
Electricity, that ubiquitous force, quietly permeates every aspect of our daily lives, from trivial gadgets to life-threatening medical equipment, it plays a silent role. However, truly grasping this energy, especially how to store and efficiently output it, is no easy task. It is against this background that this article will focus on a type of coin cell battery that may seem insignificant on the...on January 1th 1698
-
Understanding the Fundamentals:Inductance Resistance, andCapacitance
In the intricate dance of electrical engineering, a trio of fundamental elements takes center stage: inductance, resistance, and capacitance. Each bears unique traits that dictate the dynamic rhythms of electronic circuits. Here, we embark on a journey to decipher the complexities of these components, to uncover their distinct roles and practical uses within the vast electrical orchestra. Inductan...on January 1th 1641
-

CR2430 Battery Comprehensive Guide: Specifications, Applications and Comparison to CR2032 Batteries
What is CR2430 battery ?Benefits of CR2430 BatteriesNormCR2430 Battery ApplicationsCR2430 EquivalentCR2430 VS CR2032Battery CR2430 SizeWhat to look for when buying the CR2430 and equivalentsData Sheet PDFFrequently Asked Questions Batteries are the heart of small electronic devices. Among the many types available, coin cells play a crucial role, commonly found in calculators, remote controls, and ...on January 1th 1512
-
What Is RF and Why Do We Use It?
Radio Frequency (RF) technology is a key part of modern wireless communication, enabling data transmission over long distances without physical connections. This article delves into the basics of RF, explaining how electromagnetic radiation (EMR) makes RF communication possible. We will explore the principles of EMR, the creation and control of RF signals, and their wide-ranging uses. The article ...on January 1th 1499
-

CR2450 vs CR2032: Can The Battery Be Used Instead?
Lithium manganese batteries do have some similarities with other lithium batteries. High energy density and long service life are the characteristics they have in common. This kind of battery has won the trust and favor of many consumers because of its unique safety. Expensive tech gadgets? Small appliances in our homes? Look around and you'll see them everywhere. Among these many lithium-manganes...on January 1th 1482















































