Complete Guide to the 2N3906 PNP Transistor
The 2N3906 transistor is a popular PNP transistor used in simple amplifying and switching circuits. This guide covers its features, uses, pin layout, and practical applications to help you understand its role in various electronic projects.Catalog
Overview of 2N3906 Transistor
The 2N3906 is a commonly used PNP transistor that serves well in low-power amplification and switching tasks. Designed to handle moderate voltage levels and small currents, it operates by toggling the collector and emitter junctions between open and closed states depending on the base pin's voltage. When the base pin is grounded, the transistor is in a forward-biased state, allowing current to flow from the emitter to the collector. When a signal is applied to the base, it goes into a reverse-biased state, stopping current flow.
With a gain value between 110 and 300, this transistor can effectively amplify small signals. However, it has a current limit on its collector, so it’s best suited for applications where the current requirement stays under 200mA. The 2N3906 has two main operational states: saturation, where the transistor is fully on, allowing maximum current flow, and cutoff, where it’s entirely off with no current between the emitter and collector. These properties make it versatile for many general-purpose applications, whether in basic amplifiers or simple switch circuits.
Pin Layout for 2N3906 Transistor
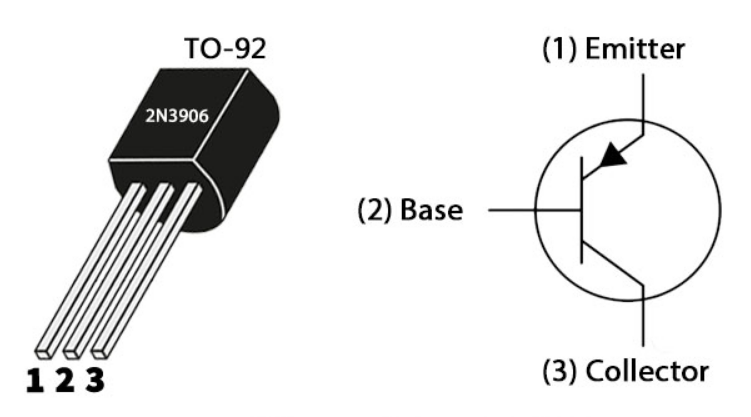
Pin Configuration
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
| 1 | Emitter | Current drains out through emitter |
| 2 | Base | Controls the biasing of the transistor |
| 3 | Collector | Current flows in through collector |
2N3906 CAD Model
2N3906 Symbol
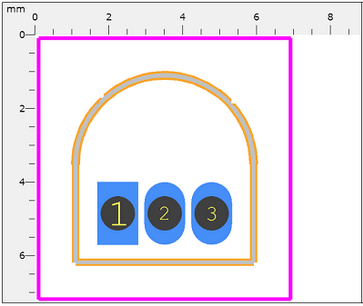
2N3906 Footprint
2N3906 3D Model
Key Features of 2N3906 Transistor
PNP Transistor Design
The 2N3906 is a PNP transistor, meaning it conducts current when its base is at a lower voltage than the emitter. This design allows it to control current flow effectively in low-power circuits where this type of polarity is needed.
High DC Current Gain
With a DC current gain (hFE) of up to 300, the 2N3906 can amplify small base currents to produce larger collector currents. This feature makes it a good choice for applications requiring moderate signal amplification.
Moderate Current Handling
The transistor can handle a continuous collector current of 200mA. This capacity enables it to control low-power devices without overheating or needing additional cooling measures, provided that the current remains within its safe range.
Emitter-Base Voltage
An emitter-base voltage (VBE) of 5V means that the 2N3906 can manage circuits with a reasonable voltage range, making it suitable for typical low-voltage applications without requiring complex adjustments.
Compact To-92 Package
The 2N3906 is available in a TO-92 package, which is small and convenient for use on breadboards and in compact circuits. This makes it easy to integrate into projects where space is limited.
2N3906 Transistor Specifications
Technical specifications, features, characteristics, and components with comparable specifications of ON Semiconductor 2N3906BU.
| Type | Parameter |
| Lifecycle Status | ACTIVE (Last Updated: 2 days ago) |
| Factory Lead Time | 6 Weeks |
| Mount | Through Hole |
| Mounting Type | Through Hole |
| Package / Case | TO-226-3, TO-92-3 (TO-226AA) |
| Number of Pins | 3 |
| Weight | 179mg |
| Transistor Element Material | SILICON |
| Collector-Emitter Breakdown Voltage | 40V |
| Number of Elements | 1 |
| hFEMin | 100 |
| Operating Temperature | -55°C~150°C TJ |
| Packaging | Bulk |
| Published | 2007 |
| JESD-609 Code | e3 |
| Pbfree Code | yes |
| Part Status | Active |
| Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL) | 1 (Unlimited) |
| Number of Terminations | 3 |
| ECCN Code | EAR99 |
| Terminal Finish | Tin (Sn) |
| Voltage - Rated DC | -40V |
| Max Power Dissipation | 625mW |
| Terminal Position | BOTTOM |
| Current Rating | -200mA |
| Frequency | 250MHz |
| Base Part Number | 2N3906 |
| Element Configuration | Single |
| Power Dissipation | 625mW |
| Transistor Application | SWITCHING |
| Gain Bandwidth Product | 250MHz |
| Polarity/Channel Type | PNP |
| Transistor Type | PNP |
| Collector Emitter Voltage (VCEO) | 40V |
| Max Collector Current | 200mA |
| DC Current Gain (hFE) (Min) @ Ic, Vce | 100 @ 10mA 1V |
| Vce Saturation (Max) @ Ib, Ic | 400mV @ 5mA, 50mA |
| Transition Frequency | 250MHz |
| Collector Base Voltage (VCBO) | -40V |
| Emitter Base Voltage (VEBO) | -5V |
| Turn On Time-Max (ton) | 70ns |
| Height | 5.33mm |
| Length | 5.2mm |
| Width | 4.19mm |
| REACH SVHC | No SVHC |
| Radiation Hardening | No |
| RoHS Status | ROHS3 Compliant |
| Lead Free | Lead Free |
Circuit Applications of 2N3906
Delay and Rise Time Equivalent Test Circuit
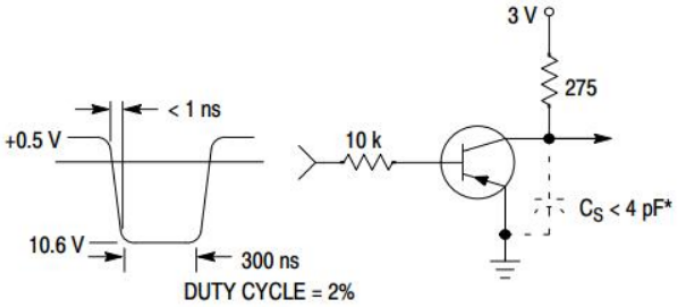
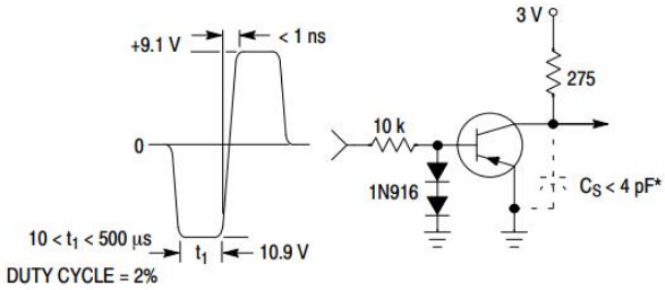
Storage and Fall Time Equivalent Test Circuit
Equivalents of 2N3906 Transistor
| Model Number | Manufacturer | Description |
| 2N3906D26Z | Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation | Small Signal Bipolar Transistor, 0.2A I(C), 40V V(BR)CEO, 1-Element, PNP, Silicon, TO-92 |
| 2N3906D27Z | Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation | Small Signal Bipolar Transistor, 0.2A I(C), 40V V(BR)CEO, 1-Element, PNP, Silicon, TO-92 |
| 2N3906RLRMG | On Semiconductor | Small Signal PNP Bipolar Transistor, TO-92 40 V, 0.2 A, TO-92 (TO-226) 5.33mm Body Height, 2000-FNFLD |
| 2N3906RLRA | Motorola Semiconductor Products | Small Signal Bipolar Transistor, 0.2A I(C), 40V V(BR)CEO, 1-Element, PNP, Silicon, TO-92 |
| 2N3906AMO | NXP Semiconductors | TRANSISTOR 200 mA, 40 V, PNP, Si, SMALL SIGNAL TRANSISTOR, TO-92, BIP General Purpose Small Signal |
| 2N3906RLRPG | Rochester Electronics LLC | 200mA, 40V, PNP, Si, SMALL SIGNAL TRANSISTOR, TO-92, CASE 29-11, TO-226, 3 PIN |
| 2N3906G | Micro Commercial Components | Small Signal Bipolar Transistor, 0.2A I(C), 40V V(BR)CEO, 1-Element, PNP, Silicon, TO-92, PLASTIC PACKAGE-3 |
| 2N3906TA | On Semiconductor | 200 mA, 40 V PNP Small Signal Bipolar Junction Transistor, 2000-FNFLD |
| 2N3906STOB | Zetex / Diodes Inc | Small Signal Bipolar Transistor, 0.2A I(C), 40V V(BR)CEO, 1-Element, PNP, Silicon, TO-92 STYLE, E-LINE PACKAGE-3 |
Alternative Options for 2N3906
• BC157
• BC558
• 2SA1943
• BD140
• S8550
• TIP127
• TIP42
Functionality of 2N3906 in a PNP Circuit
In a basic PNP circuit using the 2N3906, the transistor typically functions as either a switch or an amplifier. To operate as a switch, the emitter is connected to a positive voltage source, such as +3V, while a pushbutton switch is placed at the base. With the button unpressed, no current flows to the base, keeping the transistor in an "on" state by default. This configuration allows current to flow through to the collector, powering any connected component, such as an LED.
When the button is pressed, the voltage at the base becomes greater than that at the emitter, which blocks current flow between the emitter and collector, effectively switching off any connected component. This setup demonstrates the core principle of a PNP transistor: it remains in an "on" state as long as the base voltage is lower than the emitter. When the base voltage exceeds the emitter, it blocks current flow, thus turning the circuit "off."
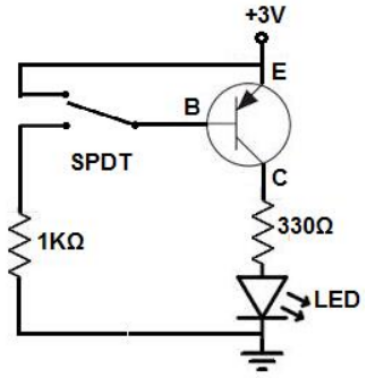
Uses of 2N3906 Transistor
The 2N3906 is widely applicable for switching and amplification tasks. Its structure makes it ideal for switching high-voltage, low-current loads, especially when working within its 200mA current limit. It can be used in circuits where consistent, low-level amplification is needed, though its gain limit means it isn’t suited for heavy-duty amplifying. Due to its PNP nature, it’s often chosen when reverse-polarity configurations are required, making it versatile for various low-power applications, including signal control, LED circuits, and low-current motor drivers.
Guide to Operating the 2N3906 as a Switch
Operating the 2N3906 as a switch is straightforward. In a standard PNP configuration, the transistor is usually "on" when the base pin is grounded. This default "on" state allows current to flow from the emitter to the collector. To turn the switch "off," a voltage source is applied to the base pin, which prevents current from flowing between the emitter and collector. This design helps with controlling small loads without requiring complex setup.
To protect the transistor in switch mode, it’s common to place a resistor between the base and the controlling input, calculated using the formula RB = VBE / IB. This resistor ensures that the current flowing to the base pin remains within safe limits, preventing any potential damage to the transistor. When configured with this resistor, the 2N3906 can reliably control a range of low-current devices, such as small motors or LEDs.
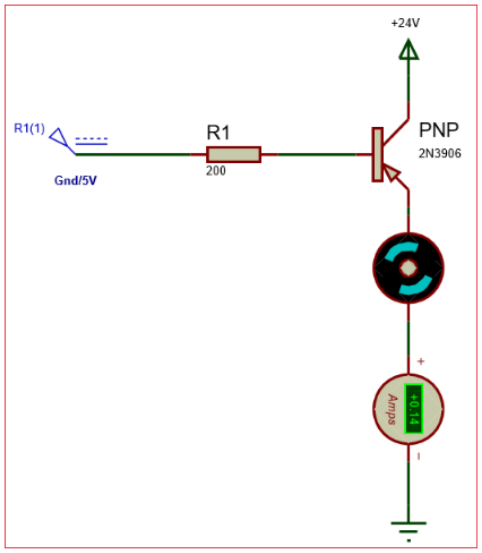
Parts with Similar Specifications to 2N3906 Transistor
The parts on the right have specifications similar to the ON Semiconductor 2N3906BU.
| Manufacturer | 2N3906BU | 2N3906TA | 2N3906TFR |
| ON Semiconductor | Through Hole | Through Hole | Through Hole |
| Package / Case | TO-226-3, TO-92-3 | TO-226-3, TO-92-3 (TO-226AA) | TO-226-3, TO-92-3 (TO-226AA) |
| Collector Emitter B. | 40 V | 40 V | 40 V |
| Max Collector Curr. | 200 mA | 200 mA | 200 mA |
| Transition Frequency | 250 MHz | 250 MHz | 250 MHz |
| Collector Emitter S. | -400 mV | -400 mV | -250 mV |
| hFE Min | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Max Power Dissipa. | 625 mW | 625 mW | 625 mW |
Applications of 2N3906 Transistor
Low-Power Switching
The 2N3906 is commonly used for switching low-current, high-voltage loads. It’s ideal for circuits where you need a reliable switch that doesn’t draw much power, such as LED arrays or simple relay controls.
Signal Amplification
Its moderate gain allows it to amplify signals in low-power audio circuits and other small amplification setups. While it’s not suitable for high-power amplification, it’s a great fit for smaller, consistent signal boosts.
Inverter and Converter Circuits
The PNP design makes the 2N3906 useful in inverter and converter circuits, particularly where current direction control is needed. It can be set up to switch currents, supporting conversion functions in simple power management designs.
Dual LED or Lamp Flasher
The transistor can also be used in circuits designed to flash LEDs or lamps. By controlling current flow based on the input signal, it creates a simple flasher effect, useful in indicator lights or warning signals.
Darlington Pair Configurations
For applications needing higher gain, the 2N3906 can be paired with another transistor in a Darlington configuration. This setup amplifies current even further, making it possible to drive slightly larger loads while maintaining good performance.
2N3906 Package Types
TO-92 (Bulk)
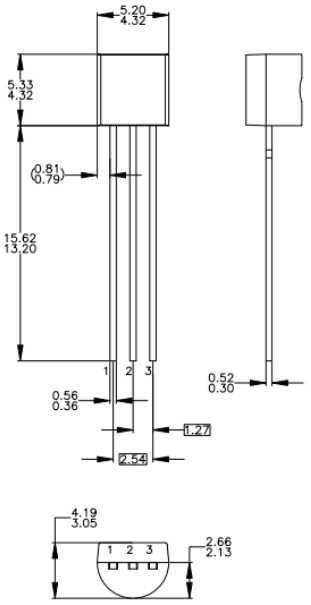
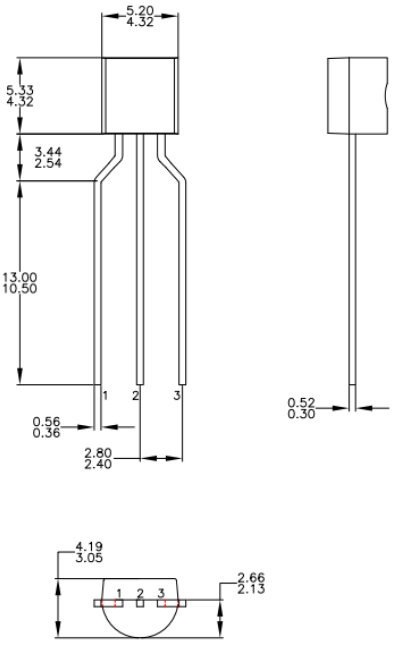
TO-92 (Ammo, Tape, and Reel)
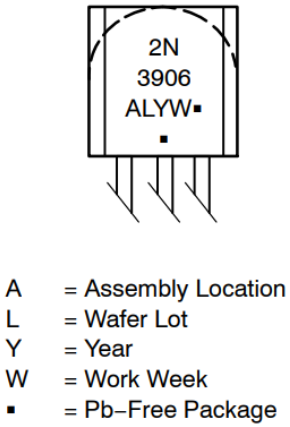
Marking Diagram for 2N3906 Transistor
About the Manufacturer of 2N3906
ON Semiconductor, a widely respected manufacturer, focuses on providing efficient power and signal management solutions. Their products, including the 2N3906, are designed to meet the needs of a broad range of applications, from automotive and communications to computing, consumer electronics, and industrial systems. Known for their innovation and commitment to quality, ON Semiconductor offers reliable components that are used by engineers and designers worldwide to create effective, sustainable solutions. Their focus on power efficiency helps support environmentally friendly and energy-saving projects across multiple industries.
Datasheet PDF
2N3906TA Datasheet:
2N3906BU Datasheet:
2N3906TA Datasheet:
2N3906TFR Datasheet:
About us
ALLELCO LIMITED
Read more
Quick inquiry
Please send an inquiry, we will respond immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
1. How many pins does the 2N3906BU transistor have?
The 2N3906BU transistor has 3 pins, which are the emitter, base, and collector.
2. What is the operating temperature range of the 2N3906BU?
The 2N3906BU operates within a temperature range of -55°C to 150°C, which supports use in various conditions.
3. What type of transistor is the 2N3906?
The 2N3906 is a PNP bipolar junction transistor, meaning it allows current flow when the base is at a lower voltage than the emitter.
4. How fast can the 2N3906 operate?
The 2N3906 operates at moderately high speeds, making it suitable for quick-switching tasks in circuits.
5. What roles does the 2N3906 typically perform in circuits?
The 2N3906 transistor is commonly used as a switch or an amplifier, depending on the circuit configuration.
6. What makes the 2N3906 transistor unique?
The 2N3906 has a high collector-to-emitter voltage, allowing it to handle higher voltages in low-current applications.
7. What is the base-emitter voltage (VBE) of the 2N3906?
The VBE for the 2N3906 is 5V, which defines the voltage needed to activate the base and allow current flow.
8. In which regions does the 2N3906 operate?
The 2N3906 operates in two main regions: the saturation region, where it is fully on, and the cutoff region, where it is fully off.

What Is a DB9 Connector and How Is It Used?
on November 14th

How the J113 N-Channel Transistor Works in Electronic Circuits?
on November 14th
Popular Posts
-
What is GND in the circuit?
on January 1th 3197
-

RJ-45 Connector Guide: RJ-45 Connector Color Codes, Wiring Schemes, R-J45 Applications, RJ-45 Datasheets
on January 1th 2765
-
Understanding Power Supply Voltages in Electronics VCC, VDD, VEE, VSS, and GND
on November 18th 2465
-

Fiber Connector Types: SC Vs LC And LC Vs MTP
on January 1th 2223
-

Comparison Between DB9 and RS232
on January 1th 1847
-

What Is An LR44 Battery?
Electricity, that ubiquitous force, quietly permeates every aspect of our daily lives, from trivial gadgets to life-threatening medical equipment, it plays a silent role. However, truly grasping this energy, especially how to store and efficiently output it, is no easy task. It is against this background that this article will focus on a type of coin cell battery that may seem insignificant on the...on January 1th 1821
-
Understanding the Fundamentals:Inductance Resistance, andCapacitance
In the intricate dance of electrical engineering, a trio of fundamental elements takes center stage: inductance, resistance, and capacitance. Each bears unique traits that dictate the dynamic rhythms of electronic circuits. Here, we embark on a journey to decipher the complexities of these components, to uncover their distinct roles and practical uses within the vast electrical orchestra. Inductan...on January 1th 1774
-

CR2430 Battery Comprehensive Guide: Specifications, Applications and Comparison to CR2032 Batteries
What is CR2430 battery ?Benefits of CR2430 BatteriesNormCR2430 Battery ApplicationsCR2430 EquivalentCR2430 VS CR2032Battery CR2430 SizeWhat to look for when buying the CR2430 and equivalentsData Sheet PDFFrequently Asked Questions Batteries are the heart of small electronic devices. Among the many types available, coin cells play a crucial role, commonly found in calculators, remote controls, and ...on January 1th 1748
-
What Is RF and Why Do We Use It?
Radio Frequency (RF) technology is a key part of modern wireless communication, enabling data transmission over long distances without physical connections. This article delves into the basics of RF, explaining how electromagnetic radiation (EMR) makes RF communication possible. We will explore the principles of EMR, the creation and control of RF signals, and their wide-ranging uses. The article ...on January 1th 1737
-
Comprehensive guide to hFE in transistors
Transistors are crucial components in modern electronic devices, enabling signal amplification and control. This article delves into the knowledge surrounding hFE, including how to select a transistor's hFE value, how to find hFE, and the gain of different types of transistors. Through our exploration of hFE, we gain a deeper understanding of how transistors work and their role in electronic circu...on November 18th 1721














































