USB Type C and USB 3.2
In the fast-changing world of technology, USB Type C and USB 3.2 have become very popular for making connections and transferring data. However, many people get confused about what each one does. This article will explain these technologies, showing their special features and how they work together to make our digital lives easier. By the end, you’ll clearly understand what makes USB Type C and USB 3.2 different and how using them together can help you in everyday tasks.
Catalog
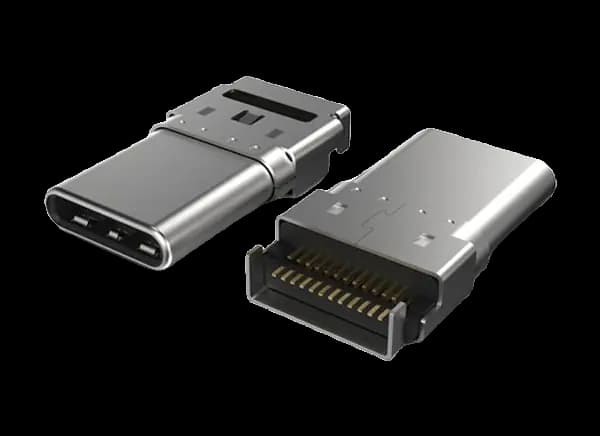

USB Type C Connector
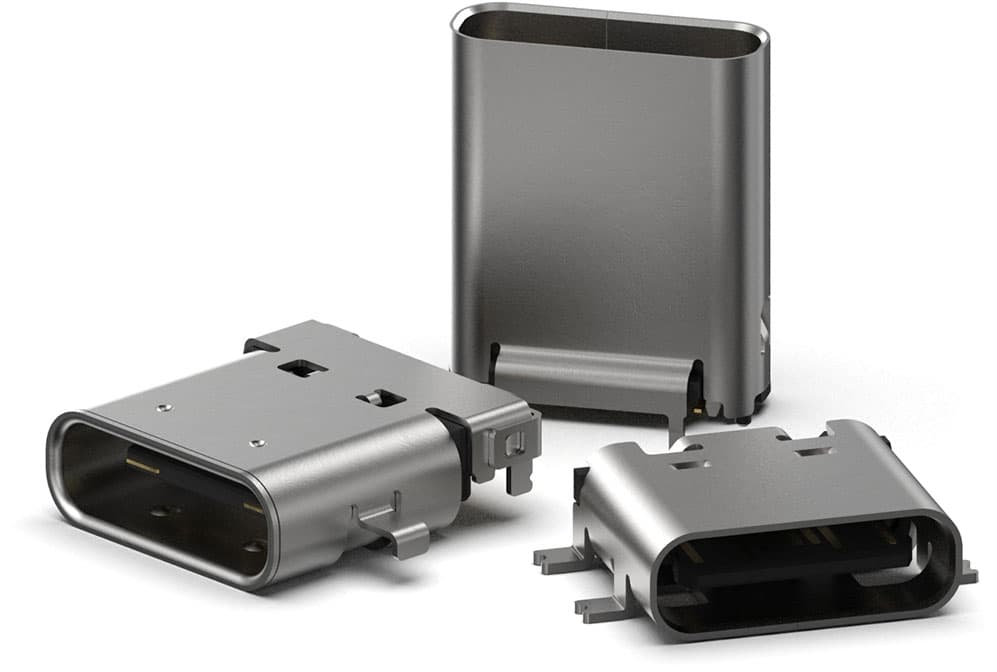

Figure 2: USB Type C Connector
USB Type C is a new type of connector that offers many improvements. One of its best features is its reversible design, which allows it to be plugged in either way. This feature makes it very user-friendly, as you don't have to worry about figuring out which side is up when you're trying to plug it in.
Another great advantage of USB Type C is its small size. Its compact form allows it to be used in many different devices, ranging from small smartphones to large laptops. This versatility makes it a suitable choice for a wide variety of gadgets, providing a universal solution that fits many needs.
USB Type C is also known for its high durability. It can withstand being plugged in and unplugged up to 10,000 times without breaking. In comparison, older USB Type A connectors can only handle about 1,500 cycles. This means that USB Type C connectors last much longer, even with frequent use, making them a more reliable choice for everyday use.
One of the technical improvements of the USB Type C connector is the increased number of pins. With 24 pins, it can handle more power and data transfer. This increase in conductors allows for faster charging and quicker data transfer speeds. This capability is especially useful for activities that require a lot of bandwidth, such as watching high-definition videos or transferring large files.
USB 3.2 Standard

Figure 3: USB 3.2 Standard
USB 3.2 is a standard that sets the rules for how fast data can be transferred and how power is delivered through USB connections. This standard includes several categories, each with different data transfer speeds.
The first category, USB 3.2 Gen 1, allows data transfer speeds up to 5 Gbps. This speed is good for quick file transfers and is suitable for most everyday tasks, like connecting external hard drives and other devices.
The next level, USB 3.2 Gen 2, doubles the speed of Gen 1, allowing data transfer rates up to 10 Gbps. This faster speed is useful for tasks that need more data to be moved quickly, such as transferring large files or streaming high-definition video.
The most advanced category, USB 3.2 Gen 2x2, further improves performance by using two lanes of 10 Gbps each, achieving a total data transfer rate of up to 20 Gbps. This setup is very helpful for high-performance storage devices and demanding data transfer tasks.
Misconceptions and Clarifications
Many people mistakenly believe USB Type C and USB 3.2 are the same, but they refer to different things. Understanding the difference between them helps in using these technologies properly.
USB Type C refers to the shape and design of the physical connector. This connector is small and can be plugged in either way, making it easy to use and eliminating the frustration of plugging it in the wrong way. The Type C connector can support different types of data transfer and power delivery, making it a popular choice for modern devices.
On the other hand, USB 3.2 refers to how data is transferred between devices and the speed at which this transfer happens. USB 3.2 includes several levels of data transfer speeds: USB 3.2 Gen 1 with speeds up to 5 Gbps, USB 3.2 Gen 2 with speeds up to 10 Gbps, and USB 3.2 Gen 2x2 with speeds up to 20 Gbps. These faster speeds allow for quicker data transfer, less delay, and better performance in tasks that use a lot of data.
While USB Type C connectors can support USB 3.2 speeds, they are not always linked to these speeds. USB Type C ports can also support other standards, such as USB 2.0 or USB 4.0, depending on the device's features. This means that a USB Type C connector does not guarantee USB 3.2 speeds unless it is clearly stated by the device maker.
Advantages of USB Type C
USB Type C connectors offer many benefits compared to older USB types, making them a great choice for modern devices.
One of the main benefits of USB Type C is that it can deliver more power. USB Type C supports higher current, up to 5 amps, and higher voltage, up to 20 volts, allowing it to transfer up to 100 watts of power. This capability means it can charge a wide range of devices, from smartphones and tablets to laptops and other devices that need more power. Furthermore, the USB Power Delivery (PD) 3.1 standard allows USB Type C to deliver up to 240 watts of power. This means it can even charge devices like gaming laptops and monitors, which older USB types couldn’t handle.
When it comes to transferring data, USB Type C is much faster. The USB4 standard, which works with USB Type C, supports data transfer speeds up to 40 gigabits per second (Gbps). This speed is a big improvement over older USB versions, allowing for much faster data transfers between devices. For example, large files such as high-resolution videos, extensive databases, or full backups can be transferred quickly, saving users a lot of time and making work more efficient.
Another great benefit of USB Type C is its versatility. Unlike older USB types, USB Type C can also send video signals along with data and power. This means that USB Type C can replace multiple cables with just one. For example, it can carry video signals for standards like DisplayPort and HDMI, allowing you to connect monitors and other displays without needing extra video cables. This reduces cable clutter and makes connecting devices simpler, especially in places where space and convenience are important, such as offices or for mobile device users.
USB Type C's design makes it very user-friendly. The connector is reversible, meaning it can be plugged in either way, which eliminates the common problem of trying to plug it in the wrong way with older USB connectors. This feature makes connecting devices quicker and easier.
USB Power Delivery (PD)
USB Power Delivery (PD) is a feature of USB Type-C technology that helps manage power between devices more efficiently and flexibly. This feature supports different levels of power, making it suitable for a variety of devices, from small gadgets to larger electronics.
One advantage of USB PD is its ability to handle different power levels. It can provide power ranging from a low 5 watts to a high 100 watts. This range means that a single USB PD-enabled port can charge many types of devices, such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, and even some small home appliances, all with the right amount of power they need.
Another useful feature of USB PD is that it allows power to flow both ways. Unlike older USB versions, which typically only allowed power to go in one direction—from the host to the device—USB PD lets devices both supply and receive power. This two-way power flow makes it possible to do things like reverse charging, where a smartphone can charge another device or accessory.
Furthermore, USB PD's smart power management adjusts the power flow based on what the connected devices need and the overall power available. This smart adjustment ensures that each device gets the right amount of power it needs, making the process more efficient and preventing problems like overcharging or overheating.
|
Specification |
Maximum
Power |
Maximum
Voltage |
Maximum
Current |
|
USB 2.0 |
2.5 W |
5 V |
500 mA |
|
USB 3.0 and 3.1 |
4.5 W |
5 V |
900 mA |
|
USB BC 1.2 |
7.5 W |
5 V |
1.5 A |
|
USB Type-C 1.2 |
15 W |
5 V |
3 A |
|
USB PD 3.0 |
100 W |
5/9/15/20 V |
5 A |
|
USB PD 3.1 |
240 W |
28/36/48 V |
5 A |
Table 1: Power Capabilities Comparison
Optimizing USB 3.2 Performance
To get the most out of USB 3.2, several important things need to be considered. First, the quality of the cable is very important. High-quality cables made specifically for USB 3.2 make sure that data transfer speeds and power delivery are at their best. Poor-quality cables can lead to slower performance and possible data loss.
Another thing to think about is the length of the cable. Shorter cables usually keep data quality and speed higher because they reduce the chances of signal weakening. Using longer cables increases the risk of interference and signal loss, which can hurt performance.
Device compatibility also matters. Both the main device (like a computer) and other devices (like external hard drives or flash drives) must support the same USB 3.2 standard. If the devices do not match in their USB specifications, the performance will default to the lower standard, which means you won’t get the benefits of USB 3.2.
Conclusion
In summary, USB Type C and USB 3.2 are big improvements in how we connect and transfer data between devices. USB Type C has a user-friendly design that can be plugged in either way, is small in size, very durable, and can be used for many different tasks. USB 3.2 offers various speeds for transferring data, suitable for different needs. Knowing the difference between the physical connector (USB Type C) and the data transfer rules (USB 3.2) helps you get the most out of your devices. By picking the right cables and devices, you can enjoy faster data transfers, better power delivery, and a simpler, more organized digital experience.
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
1. Does USB 3.2 work with USB-C?
Yes, USB 3.2 works with USB-C. The USB-C connector can handle USB 3.2 speeds, allowing for faster data transfer and better performance compared to older USB versions.
2. What are the features of USB 3.2 Type-C?
USB 3.2 Type-C has several features. It offers faster data transfer speeds, up to 20 Gbps with the USB 3.2 Gen 2x2 version. It also provides better power delivery for charging devices and can send video signals. The USB-C connector is reversible, so you can plug it in without worrying about which way is up.
3. What makes the USB Type-C connection different from all previous versions and types of USB?
The USB Type-C connection is different because of its reversible design, which means you can plug it in either way without checking its orientation. It is also smaller and can be used for more tasks, like transferring data, charging devices, and sending video signals, all with one cable.
4. What is the difference between USB-C and USB-III?
USB-C refers to the shape and design of the connector, which is small and can be plugged in either way. USB-III (more accurately called USB 3.0, USB 3.1, or USB 3.2) refers to different versions of USB technology that define how fast data can be transferred and how power is delivered. USB-C can support various USB versions, including USB 3.2, depending on what the device can handle.
5. Is USB 3.2 faster than Type-C?
Comparing USB 3.2 and Type-C is tricky because USB 3.2 is about data transfer speeds, while Type-C is about the connector type. USB 3.2 can be very fast and, when used with a USB-C connector, can achieve high speeds. So, when you use USB 3.2 with a USB-C connector, you get very fast data transfer.
About us
ALLELCO LIMITED
Read more
Quick inquiry
Please send an inquiry, we will respond immediately.

Guide to Ultrasonic Sensors: Technology, Uses, and Innovations
on August 2th

Fan Bearing Types: A Comprehensive Guide to Their Benefits and Hindrances
on August 1th
Popular Posts
-
What is GND in the circuit?
on January 1th 3036
-

RJ-45 Connector Guide: RJ-45 Connector Color Codes, Wiring Schemes, R-J45 Applications, RJ-45 Datasheets
on January 1th 2607
-

Fiber Connector Types: SC Vs LC And LC Vs MTP
on January 1th 2162
-
Understanding Power Supply Voltages in Electronics VCC, VDD, VEE, VSS, and GND
on November 13th 2067
-

Comparison Between DB9 and RS232
on January 1th 1789
-

What Is An LR44 Battery?
Electricity, that ubiquitous force, quietly permeates every aspect of our daily lives, from trivial gadgets to life-threatening medical equipment, it plays a silent role. However, truly grasping this energy, especially how to store and efficiently output it, is no easy task. It is against this background that this article will focus on a type of coin cell battery that may seem insignificant on the...on January 1th 1754
-
Understanding the Fundamentals:Inductance Resistance, andCapacitance
In the intricate dance of electrical engineering, a trio of fundamental elements takes center stage: inductance, resistance, and capacitance. Each bears unique traits that dictate the dynamic rhythms of electronic circuits. Here, we embark on a journey to decipher the complexities of these components, to uncover their distinct roles and practical uses within the vast electrical orchestra. Inductan...on January 1th 1704
-

CR2430 Battery Comprehensive Guide: Specifications, Applications and Comparison to CR2032 Batteries
What is CR2430 battery ?Benefits of CR2430 BatteriesNormCR2430 Battery ApplicationsCR2430 EquivalentCR2430 VS CR2032Battery CR2430 SizeWhat to look for when buying the CR2430 and equivalentsData Sheet PDFFrequently Asked Questions Batteries are the heart of small electronic devices. Among the many types available, coin cells play a crucial role, commonly found in calculators, remote controls, and ...on January 1th 1640
-
What Is RF and Why Do We Use It?
Radio Frequency (RF) technology is a key part of modern wireless communication, enabling data transmission over long distances without physical connections. This article delves into the basics of RF, explaining how electromagnetic radiation (EMR) makes RF communication possible. We will explore the principles of EMR, the creation and control of RF signals, and their wide-ranging uses. The article ...on January 1th 1618
-
Comprehensive guide to hFE in transistors
Transistors are crucial components in modern electronic devices, enabling signal amplification and control. This article delves into the knowledge surrounding hFE, including how to select a transistor's hFE value, how to find hFE, and the gain of different types of transistors. Through our exploration of hFE, we gain a deeper understanding of how transistors work and their role in electronic circu...on November 13th 1562
















































