How to Choose Between BC547 and 2N2222
Transistors are widely used components in electronics, playing a major role in switching and amplifying signals. This article will explore the features, applications, and differences between two popular transistors, the BC547 and 2N2222. By understanding their characteristics, you’ll be able to choose the right one for your projects.Catalog
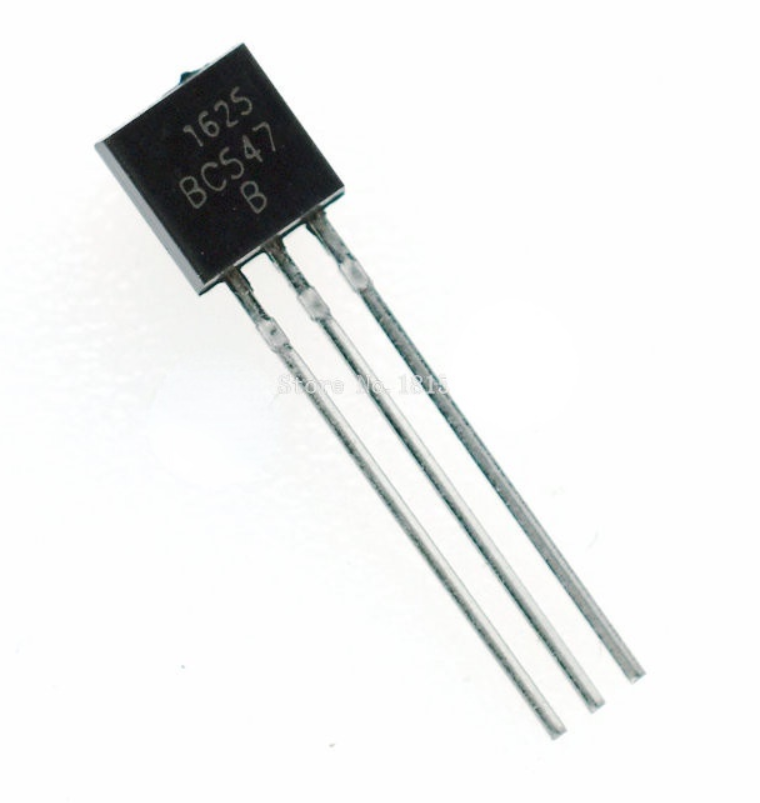
Introduction to BC547 Transistor
The following figure is the pin configuration of the BC547 transistor.

The BC547 transistor is an NPN bipolar transistor commonly used for general-purpose amplification and switching tasks. Its gain, ranging from 110 to 800 hFE, indicates its ability to amplify signals effectively, making it a versatile component for various circuit designs.The maximum collector current it can handle is 800mA, ensuring reliable performance as long as the current stays within this limit. This capacity allows the transistor to manage moderate loads without risk of damage. The bias current for the BC547 is capped at 5mA, which is essential for setting the transistor's base correctly during operation. Staying within this limit ensures proper functionality and prevents overheating. With a transition frequency of 30 MHz, the BC547 is suitable for low to medium-speed switching applications, performing reliably in circuits that operate within this frequency range.
Overview of 2N2222 Transistor
The 2N2222 transistor is an NPN-type bipolar transistor widely used for amplification and switching. Its maximum current gain, which measures how much it can amplify, is 300 hFE, making it efficient for various circuits requiring moderate amplification.The maximum collector current it can handle is 800mA. This means the transistor can safely pass this current without overheating or damage, ensuring reliable performance within this limit. The bias voltage at the trigger terminal can reach up to 200mV, while the maximum allowable bias current is 200mA. These values are critical for setting up the transistor correctly, helping you avoid issues like saturation or overloading during operation. The transistor can operate at frequencies as high as 250 MHz, which is its transition frequency. This capability makes it suitable for applications involving high-speed signal switching or radio frequency operations.
Pin Configuration of 2N2222 Transistor
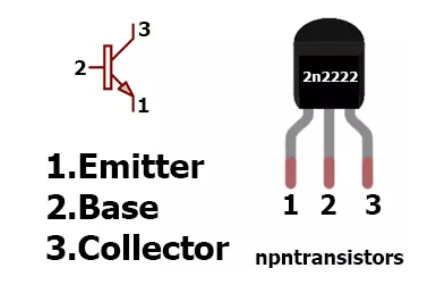
Features Comparison: BC547 vs 2N2222
BC547 Features
NPN BJT Transistor
The BC547 is an NPN bipolar junction transistor, making it a reliable option for various amplification and switching tasks.
DC Current Gain
With a gain range between 110 and 800 hFE, the BC547 provides flexibility in amplifying signals in circuits that need precise gain control.
Collector Current
The BC547 can handle up to 100mA of collector current, suitable for small to medium current loads in circuits.
Emitter to Base Voltage
It has an emitter-to-base voltage limit of 6V, ensuring stable operation in circuits that involve low voltage applications.
Collector to Emitter Voltage
The maximum collector-to-emitter voltage is 45V, allowing the transistor to operate effectively in circuits with moderate voltage levels.
Collector to Base Voltage
With a collector-to-base voltage of 50V, the BC547 is capable of withstanding relatively higher voltages on its collector.
Base Current
The transistor has a maximum base current of 5mA, making it ideal for energy-efficient circuits.
Package
The BC547 comes in a TO-92 package, a compact and lightweight design that makes it convenient to use in small spaces.
2N2222 Features
NPN BJT Transistor
The 2N2222 is also an NPN transistor, known for its durability and ability to handle larger currents.
DC Current Gain
With a gain range of 30 to 300 hFE, it offers reliable amplification for medium-power circuits.
Collector Current
The 2N2222 can handle up to 800mA of collector current, making it suitable for circuits with higher current demands.
Emitter to Base Voltage
Its emitter-to-base voltage is rated at 5V, allowing it to function well in low-voltage configurations.
Collector to Emitter Voltage
The maximum collector-to-emitter voltage is 30V, making it a good fit for moderate voltage circuits.
Collector to Base Voltage
With a collector-to-base voltage of 60V, the 2N2222 can manage higher voltage levels on its collector.
Base Current
The maximum base current for the 2N2222 is 200mA, providing flexibility in controlling higher current loads.
Transition Frequency
It has a transition frequency of 250MHz, enabling it to handle high-speed switching tasks effectively.
Package
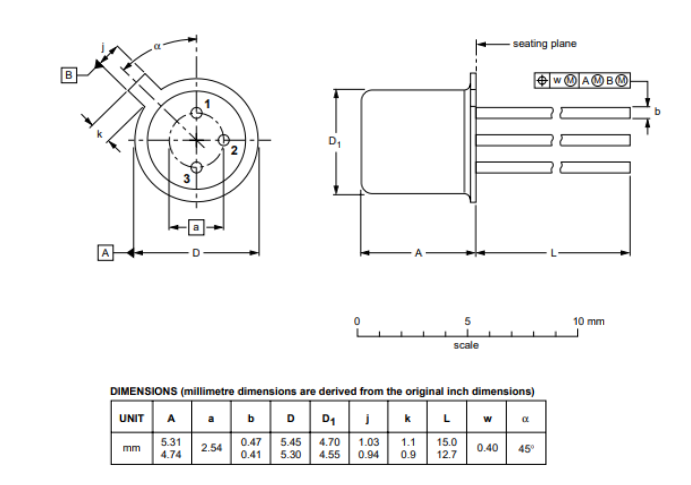
The 2N2222 is available in a TO-18 package, which is often metallic, providing better heat dissipation for higher load circuits.
5 Applications Comparison: BC547 vs 2N2222
BC547 Applications
Amplifier Circuits
The BC547 is often used in amplifier circuits to enhance weak signals, making them suitable for audio and sensor applications.
Preamp Circuits
This transistor is ideal for preamplifier circuits that prepare weak signals for further amplification.
Driver Circuits
In driver circuits, the BC547 acts as an intermediary to control other components like LEDs or relays.
Switching Circuits
The BC547 is commonly used for switching low-power devices, enabling or disabling components efficiently.
PWM Circuits
It is a popular choice for pulse-width modulation circuits where precise control over signal timing is required.
Alarm Circuits
The BC547 works well in alarm circuits, detecting and amplifying small signals to trigger alerts.
Water Level Indicator Circuits
It plays a key role in water level indicators, helping to sense and signal water levels in tanks.
Sensor Circuits
The BC547 is widely used in sensor circuits, where it amplifies or switches signals from sensors.
Touch Switch Circuits
In touch-sensitive switch circuits, the BC547 detects and amplifies the small signals generated by a touch.
Volume Level Changing Circuits
It is used in circuits designed to adjust audio volume levels, ensuring smooth and efficient operation.
2N2222 Applications
Low Power Applications
The 2N2222 is suitable for low-power applications, offering reliable performance with minimal energy consumption.
Preamp
It is often found in preamplifier circuits where initial amplification of signals is required.
Motor Driver Circuits
The 2N2222 can drive small motors effectively, making it a good choice for motor driver circuits.
Inverter Circuits
It is used in inverter circuits to control the flow of current, converting DC to AC efficiently.
Amplifier Circuits
The 2N2222 performs well in amplifier circuits, especially those that need moderate power amplification.
Switching Circuits
It is commonly used in switching circuits to control the on/off operation of devices with higher current demands.
Sensor Circuits
In sensor circuits, the 2N2222 amplifies signals from sensors, enabling them to interact with other components effectively.
Amplifier Circuit: BC547 vs 2N2222
BC547 Amplifier Circuit
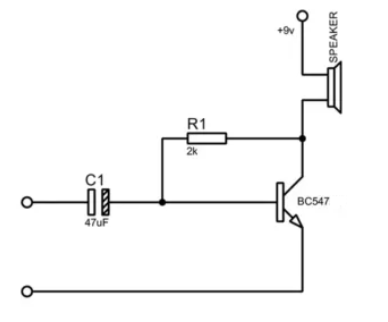
The simple amplifier circuit using the BC547 transistor is illustrated in the diagram and requires just four components. An input resistor and capacitor are included as bypass elements, with the resistor functioning to set the biasing for the BC547. When an audio signal is applied to the input, the transistor amplifies the signal and delivers it to the output, such as a speaker, enabling clear sound amplification.
2N2222 Amplifier Circuit
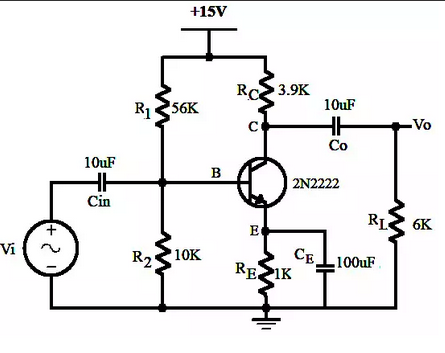
The amplifier circuit using the 2N2222 transistor is depicted in the diagram. It operates in a common emitter configuration, which is one of the most effective setups for voltage amplification with an NPN transistor like the 2N2222. This configuration enhances the signal's strength, and the design of the 2N2222 allows for a higher gain, making it suitable for applications requiring amplified output.
Using BC547 and 2N2222 as a Switch
BC547 As a Switch
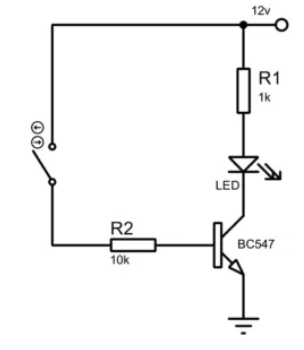
The 2N2222 transistor is used as a switch in the circuit, as shown in the diagram. An input resistor is connected to the transistor to control its operation, while another resistor is used to drive the LED. When the switch is closed, the transistor activates, allowing current to flow and turning the LED on. The value of the resistors determines the timing of the LED’s ON and OFF intervals, making it a simple yet effective switching setup.
2N2222 As a Switch
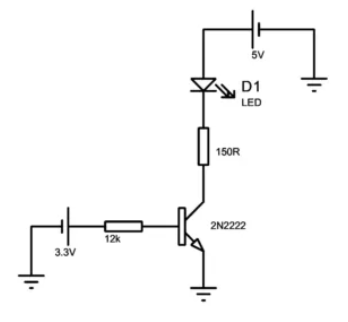
The basic circuit of the BC547 as a switch is illustrated in the diagram. It includes two resistors: one for driving the LED and another for controlling the transistor's bias terminal. When the switch is closed, current flows through the circuit, allowing the transistor to act as a switch and complete the connection. A timer can also be added to control when the LED turns on and off, providing a simple way to manage the circuit’s operation.
Technical Specifications of BC547 and 2N2222
| Specification | BC547 | 2N2222 |
| Collector to Base Voltage (VCB) | 50V | 60V |
| Collector to Emitter Voltage (VCE) | 35V | 30V |
| Emitter to Base Voltage (VEB) | 6V | 5V |
| Collector Current (IC) | 100mA | 800mA |
| Power Dissipation | 500mW | 500mW |
| Junction Temperature (TJ) | 150°C | 200°C |
| Transition Frequency (FT) | 300MHz | 250MHz |
| Noise (N) | 5dB | 4dB |
| Gain (hFE) | 110 – 800 hFE | 30 – 300 hFE |
| Package | TO-92 | TO-18 |
Parts with Similar Specifications to BC547 and 2N2222
BC547 Equivalents
Transistors in the BC series are great alternatives to the BC547, including:
• BC549
• BC639
The following can also serve as replacements for specific applications:
• 2N2222
• BC639 (also replaces 2N2369, 2N3055, 2N3904, 2N3906, and 2SC5200 in PNP configurations)
2N2222 Equivalents
The following transistors are suitable replacements for the 2N2222:
• 2N3904
• BC547
• BC548
• 2N3906
Package Details: BC547 vs 2N2222
BC547 Package
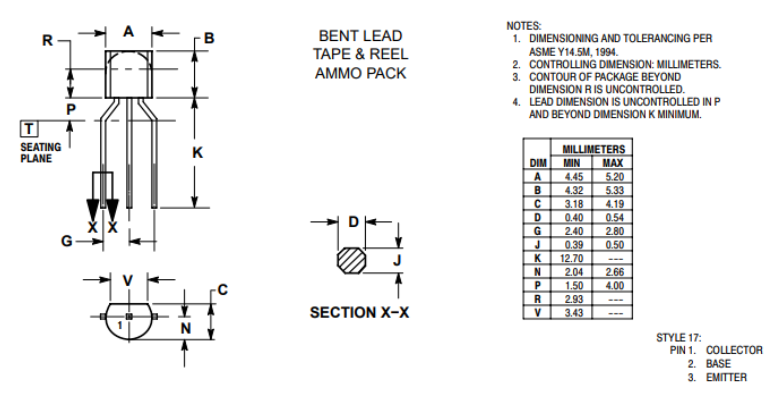
2N2222 Package
Interchangeability of BC547 and 2N2222
The BC547 and 2N2222 transistors can be used interchangeably in some circuits, depending on the requirements. While the 2N2222 is more powerful and suitable for higher loads, the BC547 is compact and energy-efficient for low-power designs. They differ in pin configurations—BC547 uses collector, base, emitter, while 2N2222 uses emitter, base, collector—requiring careful placement in circuits. Choosing the right one depends on your project’s specific needs.
About us
ALLELCO LIMITED
Read more
Quick inquiry
Please send an inquiry, we will respond immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
1. Can a BC547 transistor replace a 2N2222 transistor?
Yes, a BC547 can replace a 2N2222 in certain circuits, but you need to check the specific current and voltage requirements. The 2N2222 can handle higher current and voltage compared to the BC547, so if your circuit demands a higher load, the replacement might not work as expected. For low-power applications, though, the BC547 can serve as a good alternative.
2. Which transistor is similar to the 2N2222?
The 2N3904 is a common NPN transistor with characteristics similar to the 2N2222. However, the 2N3904 can handle less current, so it works best in circuits with lower current needs. If you require a closer match, the 2N2219 is another option to consider for higher current applications.
3. Why is the BC547 commonly used?
The BC547 is widely used because it is reliable, affordable, and works well in low-power circuits. It is versatile enough to be used in amplifiers, switching circuits, and various sensor applications. Its small size and efficient operation make it a favorite for hobbyists and professionals alike.
4. Can the 2N2222A replace the 2N2222?
Yes, the 2N2222A can replace the 2N2222 in most cases. The two are very similar, but the 2N2222A often comes in a plastic TO-92 package, whereas the original 2N2222 typically has a metal TO-18 package. Functionally, they perform almost the same, making them interchangeable for most uses.
5. Can the BC548 replace the BC547?
The BC548 can replace the BC547 in many circuits, except in cases where higher voltage handling is needed. The BC547 has a higher collector-emitter voltage rating, so if your circuit operates near the voltage limit of the BC548, you might face issues. Otherwise, they can be used interchangeably.
6. What is the difference between BC547 and BC557?
The main difference between these two transistors is that the BC547 is an NPN transistor, while the BC557 is a PNP transistor. This means they work in opposite configurations in a circuit. Their other electrical characteristics are similar, but their usage depends on the circuit design.
7. What is the current gain range of the BC547 transistor?
The BC547 has a current gain range of 110 to 800 hFE, which determines how much it can amplify an input signal. This makes it versatile enough for various amplification tasks.
8. How much current can the BC547 handle?
The BC547 can handle a maximum collector current of 100mA, which makes it suitable for low to medium current applications.
9. What is the maximum frequency of the 2N2222 transistor?
The 2N2222 has a maximum frequency of 250 MHz, allowing it to perform efficiently in high-speed switching and amplification circuits.

Why Choose PESD1 for Automotive Circuits
on November 20th

Exploring the BMP280 Sensor
on November 20th
Popular Posts
-
What is GND in the circuit?
on January 1th 3315
-

RJ-45 Connector Guide: RJ-45 Connector Color Codes, Wiring Schemes, R-J45 Applications, RJ-45 Datasheets
on January 1th 2839
-
Understanding Power Supply Voltages in Electronics VCC, VDD, VEE, VSS, and GND
on November 21th 2736
-

Fiber Connector Types: SC Vs LC And LC Vs MTP
on January 1th 2275
-

Comparison Between DB9 and RS232
on January 1th 1895
-

What Is An LR44 Battery?
Electricity, that ubiquitous force, quietly permeates every aspect of our daily lives, from trivial gadgets to life-threatening medical equipment, it plays a silent role. However, truly grasping this energy, especially how to store and efficiently output it, is no easy task. It is against this background that this article will focus on a type of coin cell battery that may seem insignificant on the...on January 1th 1855
-
What Is RF and Why Do We Use It?
Radio Frequency (RF) technology is a key part of modern wireless communication, enabling data transmission over long distances without physical connections. This article delves into the basics of RF, explaining how electromagnetic radiation (EMR) makes RF communication possible. We will explore the principles of EMR, the creation and control of RF signals, and their wide-ranging uses. The article ...on January 1th 1833
-
Understanding the Fundamentals:Inductance Resistance, andCapacitance
In the intricate dance of electrical engineering, a trio of fundamental elements takes center stage: inductance, resistance, and capacitance. Each bears unique traits that dictate the dynamic rhythms of electronic circuits. Here, we embark on a journey to decipher the complexities of these components, to uncover their distinct roles and practical uses within the vast electrical orchestra. Inductan...on January 1th 1823
-

CR2430 Battery Comprehensive Guide: Specifications, Applications and Comparison to CR2032 Batteries
What is CR2430 battery ?Benefits of CR2430 BatteriesNormCR2430 Battery ApplicationsCR2430 EquivalentCR2430 VS CR2032Battery CR2430 SizeWhat to look for when buying the CR2430 and equivalentsData Sheet PDFFrequently Asked Questions Batteries are the heart of small electronic devices. Among the many types available, coin cells play a crucial role, commonly found in calculators, remote controls, and ...on January 1th 1816
-
Comprehensive guide to hFE in transistors
Transistors are crucial components in modern electronic devices, enabling signal amplification and control. This article delves into the knowledge surrounding hFE, including how to select a transistor's hFE value, how to find hFE, and the gain of different types of transistors. Through our exploration of hFE, we gain a deeper understanding of how transistors work and their role in electronic circu...on November 21th 1814


















































