D Battery Vs. C Battery
When it comes to powering everyday devices, the choice between D batteries and C batteries can greatly affect how well and how long they run. D batteries, with their larger size and capacity, are well-suited for devices that need steady and long-lasting power. On the other hand, C batteries offer a more compact option for medium-power devices, balancing size and power efficiency. This article explores the features, uses, and advantages of both D and C batteries, helping you understand which battery type best fits your needs.
Catalog

Figure 1: D Battery vs. C Battery
What Is a D Battery?
A D battery is a type of battery that is shaped like a cylinder. It is about 34.2 mm wide and 61.5 mm long. Because of its size and shape, it is often used in devices that need a steady and long-lasting power source. These devices include flashlights, portable radios, and boomboxes, which all benefit from the battery's ability to store a lot of energy.

Figure 2: D Battery
A D battery usually delivers a voltage of 1.5 volts. This is a common voltage for many household batteries. One of the main features of a D battery is its high energy capacity, which is around 18,000 milliampere-hours (mAh). This means it can power devices that use a lot of energy for a long time, which reduces the need to replace the battery often.
The high capacity and steady voltage output of D batteries come from their larger size compared to other common batteries like AA or AAA. Because they are bigger, they can hold more internal chemical materials. This allows them to store and deliver more energy, making them a good choice for devices that need power for a long period.
Types of D Batteries
Alkaline D Batteries

Figure 3: Alkaline D Battery
Alkaline D batteries are very popular because they perform well and last long. They are made from two main materials: manganese dioxide and zinc. In these batteries, manganese dioxide is used for the positive side (cathode), and zinc is used for the negative side (anode).
The battery generates electrical energy through chemical reactions. When you use the battery, manganese dioxide and zinc react together, creating a flow of electrons. This flow of electrons produces the electric current that powers your device.
Alkaline D batteries are appreciated for their long shelf life, meaning they can be stored for a long time without losing much of their charge. This feature makes them great for emergency devices or gadgets that you don't use often. Additionally, they can store a lot of energy for their size, providing plenty of power.
These batteries are reliable and long-lasting, making them suitable for many uses. You can use them in flashlights, portable radios, toys, and medical devices. Their steady performance ensures that your devices work well for a longer time compared to other types of batteries.
Carbon Zinc D Batteries

Figure 4: Carbon Zinc D Batteries
Carbon Zinc D batteries are a cost-effective choice, often used in low-power devices such as clocks, remote controls, and simple flashlights. These batteries consist of a carbon rod (the positive part) and a zinc case (the negative part), with an acidic substance that helps the electric current flow.
One of the main features of Carbon Zinc D batteries is their low price, making them a budget-friendly option for consumers. However, this cost-saving comes with some drawbacks. The energy storage of Carbon Zinc batteries is lower than that of alkaline batteries, meaning they hold less energy and need to be replaced more often in devices that need a steady or high amount of power.
Also, Carbon Zinc D batteries have a shorter shelf life. They tend to lose their charge more quickly over time, even when not in use, compared to alkaline batteries. This makes them less suitable for devices that need long-term, reliable power or are used infrequently but must be ready to work when needed, like emergency flashlights or smoke detectors.
Lithium D Batteries

Figure 5: Lithium D Batteries
Lithium D batteries are designed to meet high-performance needs, making them perfect for devices that require a lot of power. These batteries provide a steady energy output, ensuring that devices run smoothly for long periods. Their long life is a big advantage, offering a reliable power source for high-demand electronics such as portable speakers, medical equipment, and strong flashlights.
The technology behind lithium D batteries uses lithium, a lightweight and highly reactive metal. This reactivity allows for higher energy storage compared to traditional alkaline batteries. As a result, lithium D batteries can hold more energy in the same amount of space, giving longer usage time before needing replacement.
In terms of performance, lithium D batteries keep their voltage output steady, even as the battery drains. This is important for devices that need a stable power supply to work correctly. Traditional batteries often see a drop in voltage as they run out, which can lead to reduced performance or malfunction of the device. However, lithium D batteries maintain a constant voltage, ensuring that the device works well until the battery is nearly dead.
Rechargeable NiMH D Batteries

Figure 6: Rechargeable NiMH (Nickel-Metal Hydride) D Batteries
Rechargeable NiMH (Nickel-Metal Hydride) D batteries are a more eco-friendly choice compared to single-use batteries. These batteries can be recharged hundreds of times, which makes them cheaper over time and reduces environmental waste.
NiMH D batteries have a higher capacity compared to their single-use counterparts, meaning they can store more energy and last longer between charges. This makes them suitable for a wide range of devices, from high-power gadgets like digital cameras and handheld gaming consoles to low-power items such as remote controls and clocks.
The ability to recharge these batteries multiple times significantly cuts down on the number of batteries that end up in landfills. NiMH batteries do not contain toxic metals like cadmium, which is found in some other rechargeable batteries, making them safer for the environment.
In terms of performance, NiMH D batteries have a lower self-discharge rate compared to older rechargeable technologies. This means they keep their charge for longer periods when not in use. However, they may still lose some charge over time, so it's a good idea to charge them before using them in high-power devices.
Using NiMH rechargeable batteries can also be cost-effective. While the initial purchase price is higher than single-use batteries, the long-term savings are significant due to their reusability. This cost-saving, combined with their environmental benefits, makes NiMH D batteries a preferred choice for many consumers and environmentally-conscious users.
Popular D Battery Chemistry
D batteries are popular because they last long and provide strong power. Most D batteries use alkaline chemistry. These batteries have a zinc anode and a manganese dioxide cathode, which work together to create about 1.5 volts of electricity. People like alkaline D batteries because they store more energy and last longer on the shelf than other types.
There are other kinds of D batteries too, like carbon-zinc, nickel-cadmium, and nickel-metal hydride. Carbon-zinc batteries are cheaper, but they don't store as much energy and aren't as efficient. Nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries can be recharged and give a steady voltage, but they have a memory effect. This means they can lose capacity if not fully discharged before recharging. Nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries are also rechargeable and hold more energy than NiCd batteries, but they can lose their charge faster.
Alkaline D batteries are the top choice because they are affordable, efficient, and reliable. While other types of batteries can be useful for certain tasks, they don't provide the same overall performance and convenience for everyday use.
Pros and Cons of D Batteries
Pros:
• High capacity, providing long-lasting power.
• Consistent power output throughout their life.
• Widely available and compatible with various devices.
• Easy to replace and use.
Cons:
• Larger and heavier, making them less portable.
• More expensive than other types.
• Can have a negative environmental impact if not disposed of properly.
• High discharge rate, losing charge quickly if unused.
Applications of D Batteries
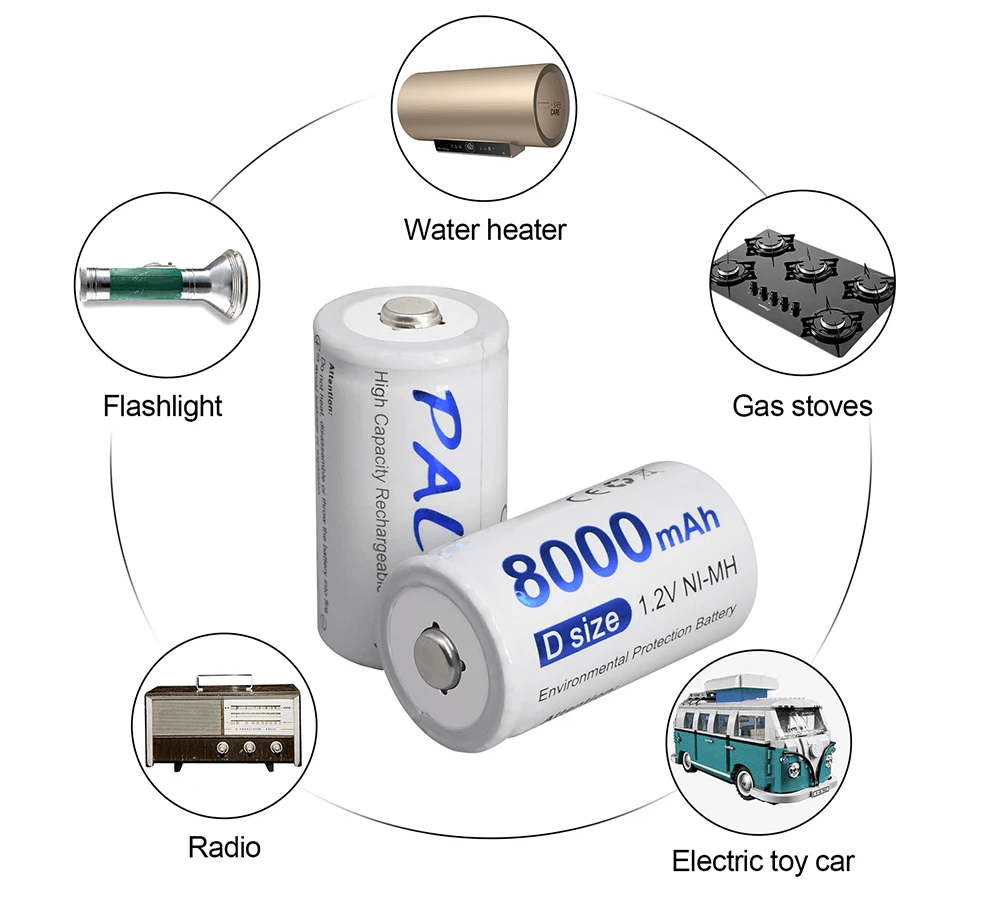
Figure 7: Common Uses of D Batteries
D batteries are cylindrical batteries often used in devices that need strong, long-lasting power. They are used in high-powered flashlights, portable boomboxes, radios, older power tools, and larger children's toys.
High-powered flashlights use D batteries because they give the needed power for a bright, strong light. The large capacity of D batteries allows the flashlight to work for a long time without needing frequent battery changes, making them perfect for emergencies and outdoor activities.
In portable boomboxes and radios, D batteries are preferred because they provide a steady power supply. This steadiness is necessary to keep the sound quality good and prevent interruptions while using them. The large energy storage of D batteries lets these devices run for many hours, which is helpful for events, travel, and outdoor use where you might not have access to electrical outlets.
Older power tools, like drills and saws, also use D batteries. These tools often need a lot of power to work well. The high capacity and durability of D batteries make sure these tools work efficiently, reducing the need for frequent recharging or battery changes, which is especially useful in work settings.
Larger children's toys, like motorized cars or complex action figures, often need a lot of energy to work properly. D batteries are good for these toys because they can provide the continuous power needed for long play sessions. The strong energy supply helps keep the toys running smoothly, ensuring children can enjoy them without frequent stops to change batteries.
D batteries are chosen for these uses because they can provide strong, long-lasting power, which is needed for devices that require steady and substantial energy. Their design and energy storage abilities make them a great choice for making sure high-powered and energy-hungry devices work reliably.
What Is a C Battery?

Figure 8: C Battery
A C battery is a type of dry cell battery that is round and measures about 26.2 mm in width and 50 mm in length. These batteries are often used in many household and portable devices, such as flashlights, portable radios, and toys. They supply a voltage of 1.5 volts and have a capacity of around 8,000 milliampere-hours (mAh). This means they can provide a current of 8,000 milliamperes for one hour before running out.
C batteries are also called other names, including R14, LR14, and baby batteries. The name "R14" is the standard size code for these batteries, while "LR14" refers to an alkaline version. The nickname "baby batteries" comes from their relatively small size compared to larger batteries like the D cell.
A C battery usually has a metal outer casing, which acts as the positive terminal, and a central rod that acts as the negative terminal. Inside the battery, there are chemicals that react to produce electrical energy. The most common types of C batteries are alkaline, zinc-carbon, and rechargeable nickel-metal hydride (NiMH).
The capacity and voltage of C batteries make them good for devices that need a moderate amount of power over a long time. Their energy density is lower than smaller batteries like AA or AAA, but they provide more total energy because they are bigger.
Types of C Batteries
C batteries are round power sources used in many devices. They give energy using different chemical make-ups. These chemical types include alkaline, carbon-zinc, nickel-metal hydride (NiMH), and others. The type of chemical used changes how much power the battery can hold, how well it works, and what it can be used for.
Alkaline C Batteries
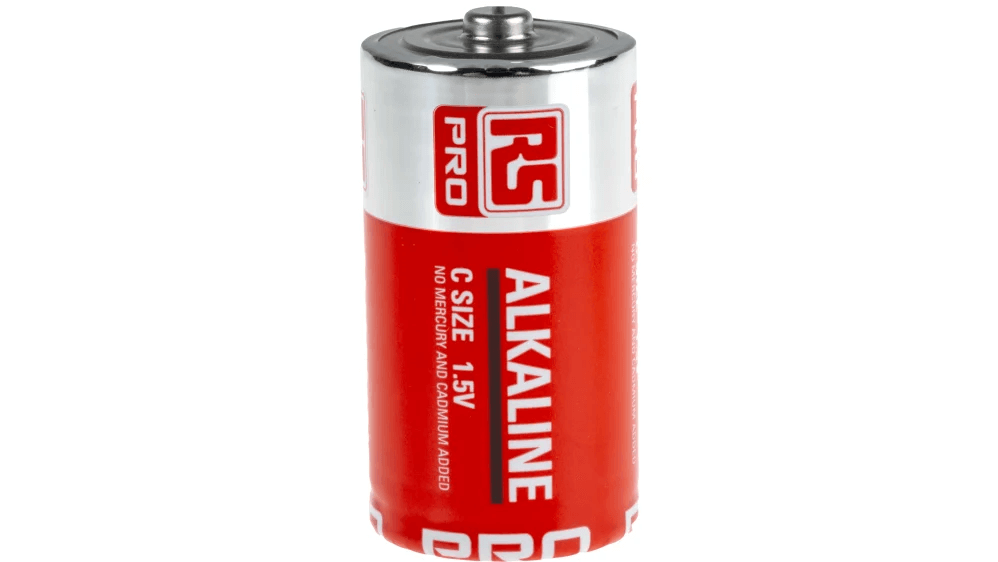

Figure 9: Alkaline C Battery
Alkaline C batteries are popular because they offer a good balance of capacity, shelf life, and affordability. These batteries are great for medium-drain devices like toys, flashlights, and remote controls. While they have a lower capacity than D batteries due to their smaller size, C batteries still provide reliable performance for many household gadgets.
The capacity of an alkaline C battery usually ranges from 7,800 to 8,000 milliampere-hours (mAh). This allows the battery to power devices that don't need a lot of continuous energy but do need a steady supply of power over time. For example, a flashlight using a C battery will last for several hours of continuous use, making it useful for everyday needs.
Another advantage of alkaline C batteries is their long shelf life. These batteries can retain their charge for up to 10 years if stored properly. This means they can be kept as backups without losing power quickly.
Alkaline C batteries are also affordable and widely available, making them accessible for most people. The cost per unit of power they provide is reasonable, especially when considering their longevity and reliability.
Carbon-zinc C batteries
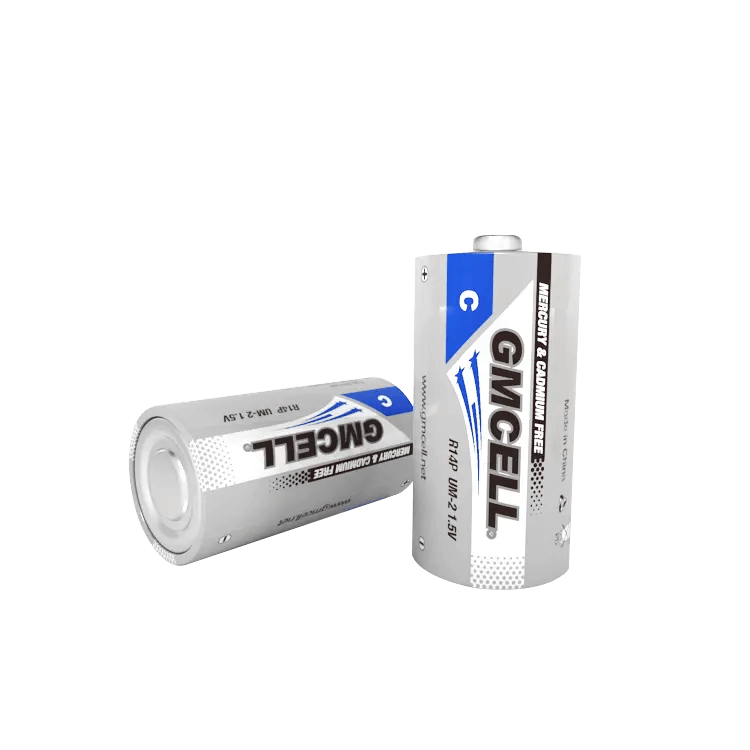

Figure 10: Carbon-Zinc C Batteries
Carbon-zinc C batteries are an older battery type that has mostly been replaced by newer technologies. These batteries are commonly used in devices with low power needs because they have limited energy capacity and a shorter lifespan. One of the main features of carbon-zinc C batteries is their low cost. They are less expensive compared to other battery types, making them a budget-friendly option for low-drain devices.
Carbon-zinc batteries use a zinc anode and a manganese dioxide cathode with an acidic electrolyte, usually ammonium chloride or zinc chloride. This chemical makeup limits their performance in high-drain applications. When used in high-drain devices, such as digital cameras or motorized toys, carbon-zinc batteries run out of power quickly. They are better suited for devices like remote controls, clocks, and flashlights, which do not need a lot of continuous power.
Carbon-zinc batteries generally have a shorter shelf life compared to alkaline or lithium batteries. This means they are more likely to lose their charge over time, even when not in use. Therefore, they may not be the best choice for emergency equipment or devices that need to be stored for long periods.
While they offer a lower initial cost, the need for more frequent replacements in higher-drain devices can make carbon-zinc batteries less economical over time. For devices with higher power needs or where long-term reliability is important, alternatives like alkaline or rechargeable batteries are usually recommended.
Nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) C Batteries

Figure 11: Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) C Batteries
Nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) C batteries are rechargeable and good for devices that require a lot of power, such as digital cameras, handheld gaming systems, and portable audio devices. These batteries might have a higher initial cost, but their ability to be recharged many times makes them more economical in the long run.
One of the main advantages of NiMH C batteries is their lower self-discharge rate compared to older rechargeable batteries like nickel-cadmium (NiCd). This means they retain their charge longer when not in use, making them more reliable for infrequent use. NiMH batteries can hold a lot of energy, providing steady power over longer periods, which is especially useful for high-drain applications.
The chemistry of NiMH batteries allows them to be charged and discharged hundreds of times without losing much capacity, which increases their lifespan and reduces the need for frequent replacements. This not only saves money but also helps the environment by reducing battery waste.
In terms of technical details, NiMH batteries operate at a nominal voltage of 1.2 volts per cell, which is slightly lower than the 1.5 volts of standard alkaline batteries. Despite this, their ability to deliver a higher current makes them more efficient for devices with high power needs. The typical capacity of NiMH C batteries ranges from 2,200 to 4,500 milliampere-hours (mAh), indicating how much charge they can store.
Lithium C Batteries

Figure 12: Lithium C Batteries
Lithium C batteries, while available, are less common in everyday consumer products. These batteries are known for their higher capacities and longer shelf lives compared to standard alkaline or other primary battery types. The higher capacity means they can store more energy, allowing devices to run longer between battery changes. Additionally, their long shelf life makes them suitable for long-term storage, maintaining their charge for years without significant degradation.
However, the main reason lithium C batteries are not as widely used in consumer products is their cost. They are more expensive to make due to the materials and technology involved. This higher cost limits their use to specialized applications where their benefits outweigh the additional expense.
Special uses for lithium C batteries include medical devices, military equipment, and certain high-performance consumer electronics. In these cases, the need for reliability, long operational life, and the ability to function in extreme conditions justifies the higher cost.
Pros and Cons of C Batteries
Pros:
• Medium capacity suitable for moderate power needs.
• Widely available and compatible with various devices.
• More affordable than larger batteries like D or 9V.
• Easy to use and replace.
Cons:
• Larger and heavier than AA or AAA batteries, making them less portable.
• May not be compatible with all devices due to specific size requirements.
Uses of C Batteries
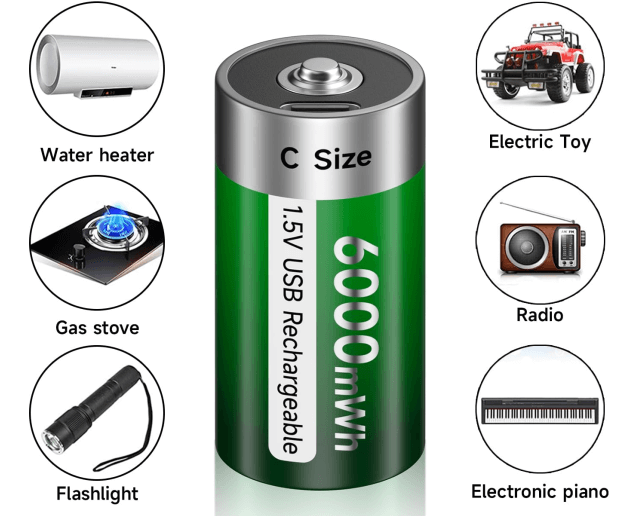

Figure 13: Common Uses of C Batteries
C batteries, also called R14 batteries, are cylindrical dry cells commonly used in various devices that need a reliable, medium-capacity power source. They are particularly good for devices where long-lasting power is needed.
In children's toys, C batteries are often chosen because they can keep toys running for longer periods. Toys like remote-controlled cars, musical instruments, and interactive dolls depend on the steady energy that C batteries provide, allowing them to work smoothly without frequent battery changes.
For smaller flashlights, C batteries are a popular choice because they balance size and power well. These flashlights are often used in homes, outdoor activities, and emergencies. The batteries’ capacity allows for extended use, making them dependable in situations where continuous light is needed.
In clocks, especially wall clocks and larger tabletop models, C batteries provide a steady power supply that helps keep accurate time. The long life of C batteries means that clocks can run for long periods without needing frequent battery changes, ensuring they stay functional and accurate.
Some medical devices also use C batteries, particularly those that need portable power sources with reliable performance. Devices like portable nebulizers, some types of blood pressure monitors, and motorized massagers benefit from the steady and long-lasting power of C batteries. In medical uses, the reliability of these batteries is key to making sure the devices work effectively and consistently.
Which Is Better, D or C Battery?
Size and Dimensions
The size difference between D and C batteries greatly affects their use and fit with devices. The larger size of D batteries lets them store more energy, making them good for devices that need long-lasting power. In contrast, C batteries are smaller and fit into devices where space is limited but still need a reasonable amount of power.
Capacity and Performance
Capacity, measured in milliampere-hours (mAh), shows how much energy a battery can store. D batteries, with their higher capacity, can power devices longer than C batteries. This makes them better for devices with high energy use over long periods. C batteries, with a lower capacity range, are more efficient for medium-power uses, providing enough power without the need for the larger size of D batteries.
Weight Considerations
The weight of a battery affects how portable the device it powers is. D batteries, being heavier, add more weight to the device, which can be important for handheld or portable uses. C batteries, being lighter, are more suitable for devices where weight matters, such as portable radios or small electronic devices.
Application and Suitability
The choice between D and C batteries mainly depends on the power needs of the device. High-power devices, like strong flashlights, portable radios, or large toys, benefit from the longer life of D batteries. Medium-power devices, which do not need as much power, such as small toys and some musical instruments, are better with the more compact and lighter C batteries.
Conclusion
Both D and C batteries serve different purposes based on their size, capacity, and performance. D batteries, with their larger energy storage, are ideal for devices that need power for a long time, such as strong flashlights, portable radios, and large toys. C batteries, being more compact, are better suited for medium-power uses like smaller flashlights, children's toys, and clocks. Understanding the specific power needs of your devices will help you choose the right battery type, ensuring they work well and efficiently.
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
1. Can you use C for D batteries?
You cannot use a C battery instead of a D battery because D batteries are bigger and hold more power. Using a C battery in a device that needs a D battery might result in the device not working well or not working at all.
2. Is 1.5 V battery C or D?
A 1.5 V battery can be either a C or a D battery. Both types usually provide 1.5 volts of power, but they differ in size and power capacity.
3. Which battery is bigger in size, C or D?
A D battery is bigger in size than a C battery. D batteries have a larger diameter and length compared to C batteries.
4. What is C vs D size batteries?
The difference between C and D size batteries is mainly their physical size and power capacity. D batteries are larger and store more power, making them good for devices that use a lot of power. C batteries are smaller and are used for devices that need medium power.
5. How do I know if my battery is C or D?
You can tell if your battery is a C or D by checking its size and any labels on the battery. A C battery is about 26.2 mm wide and 50 mm long, while a D battery is about 34.2 mm wide and 61.5 mm long. The packaging or the battery itself often has the type (C or D) clearly marked.
About us
ALLELCO LIMITED
Read more
Quick inquiry
Please send an inquiry, we will respond immediately.
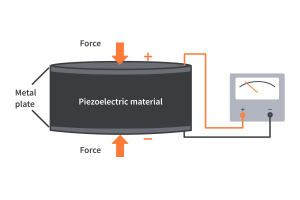
Exploring Piezoelectric Materials: Types, Properties, and Technological Impact
on July 26th

CR927 Battery Equivalents and Replacements
on July 25th
Popular Posts
-
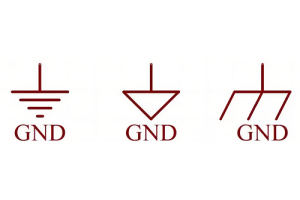
What is GND in the circuit?
on January 1th 3172
-

RJ-45 Connector Guide: RJ-45 Connector Color Codes, Wiring Schemes, R-J45 Applications, RJ-45 Datasheets
on January 1th 2747
-
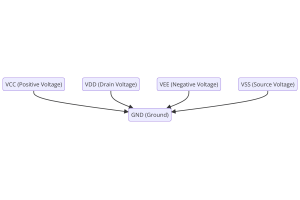
Understanding Power Supply Voltages in Electronics VCC, VDD, VEE, VSS, and GND
on November 17th 2413
-

Fiber Connector Types: SC Vs LC And LC Vs MTP
on January 1th 2216
-

Comparison Between DB9 and RS232
on January 1th 1836
-

What Is An LR44 Battery?
Electricity, that ubiquitous force, quietly permeates every aspect of our daily lives, from trivial gadgets to life-threatening medical equipment, it plays a silent role. However, truly grasping this energy, especially how to store and efficiently output it, is no easy task. It is against this background that this article will focus on a type of coin cell battery that may seem insignificant on the...on January 1th 1808
-
Understanding the Fundamentals:Inductance Resistance, andCapacitance
In the intricate dance of electrical engineering, a trio of fundamental elements takes center stage: inductance, resistance, and capacitance. Each bears unique traits that dictate the dynamic rhythms of electronic circuits. Here, we embark on a journey to decipher the complexities of these components, to uncover their distinct roles and practical uses within the vast electrical orchestra. Inductan...on January 1th 1763
-

CR2430 Battery Comprehensive Guide: Specifications, Applications and Comparison to CR2032 Batteries
What is CR2430 battery ?Benefits of CR2430 BatteriesNormCR2430 Battery ApplicationsCR2430 EquivalentCR2430 VS CR2032Battery CR2430 SizeWhat to look for when buying the CR2430 and equivalentsData Sheet PDFFrequently Asked Questions Batteries are the heart of small electronic devices. Among the many types available, coin cells play a crucial role, commonly found in calculators, remote controls, and ...on January 1th 1731
-
What Is RF and Why Do We Use It?
Radio Frequency (RF) technology is a key part of modern wireless communication, enabling data transmission over long distances without physical connections. This article delves into the basics of RF, explaining how electromagnetic radiation (EMR) makes RF communication possible. We will explore the principles of EMR, the creation and control of RF signals, and their wide-ranging uses. The article ...on January 1th 1723
-
Comprehensive guide to hFE in transistors
Transistors are crucial components in modern electronic devices, enabling signal amplification and control. This article delves into the knowledge surrounding hFE, including how to select a transistor's hFE value, how to find hFE, and the gain of different types of transistors. Through our exploration of hFE, we gain a deeper understanding of how transistors work and their role in electronic circu...on November 17th 1706
















































