Features and Differences: 2N3904 vs. 2N2222
Transistors play a role in contemporary electronics, being embedded in an array of devices. From televisions and stereos to mobile phones and computers, their importance is evident across various applications. Acting as amplifiers, switches, and other versatile components, these transistors form the backbone of numerous electronic systems. This article delves deeply into a comparison of two widely-used NPN bipolar transistors, the 2N3904 and the 2N2222. It emphasizes not only their distinct characteristics but also their practical applications.Catalog

Overview of the 2N3904
The 2N3904 is a budget-friendly and multifaceted NPN transistor known for its extensive range of applications in electronic circuits. It delivers considerable performance at an economical price with a maximum collector current of 200mA and a collector-emitter voltage limit of 40V. The transistor's structure is based on N-type and P-type semiconductor material layers, enabling efficient current control. At its core, the 2N3904 functions by permitting current to flow from the collector to the emitter when an appropriate voltage is applied to the base. Its effective and dependable current control mechanism makes it great in switching and amplification tasks across various electronic projects.
The 2N3904’s performance is largely driven by the use of N-type material layers surrounding a P-type layer. These layers are require for managing high frequencies and low currents, providing flexibility in numerous circuit designs. Its robust design ensures it can manage continuous power delivery for extended periods, reaching up to 30 hours without overheating. This reliability is use for sustaining device longevity and consistency.
The 2N3904 transistor is distinguished by its rapid switching capabilities and low voltage demands. Its economic production costs coupled with operational efficiency make it valuable for educational purposes, projects, and uses. It excels in consumer electronics that require sustained and dependable operation. Its foreseeable behavior and sturdiness under certain voltage and current conditions lead to its wide adoption. The 2N3904 NPN transistor's combination of affordability, effectiveness, and versatility cements its role as a main component in electronic circuit design.
Overview of the 2N2222
The 2N2222 is an NPN bipolar junction transistor frequently employed in higher current load applications. Designed to handle currents up to 1A and maintain a collector-emitter voltage rating of 40V, it becomes great in high-power applications. These include digital cameras, LED flashlights, and various electronic devices that demand substantial current management to function effectively.
Given its capacity for high current, the 2N2222 finds its place in circuits performance. In digital cameras, the 2N2222 ensures stable operation under varying power demands, for the reliable function of complex circuitry. In LED flashlights, its ability to manage higher currents allows for brighter illumination and enhances the device's longevity.
Despite its superior current handling, the 2N2222 is not an all-encompassing solution for every circuit. Selecting the appropriate transistor depends on various factors. Load requirements, voltage ratings, and thermal management considerations. The practical use of the 2N2222 in electronic design highlights the importance of aligning a transistor's specifications with the application's demands to achieve optimal performance.
The 2N2222 is indeed a main component for high-current applications, but contextualizing its usage within specific requirements can yield advantages. Balancing its capabilities with design constraints can influence the performance and reliability of high-power electronic systems. The adept selection and implementation of the 2N2222 can be the keystone in enhancing the functionality and durability of various electronic designs.
2N3904 and 2N2222 Pinout
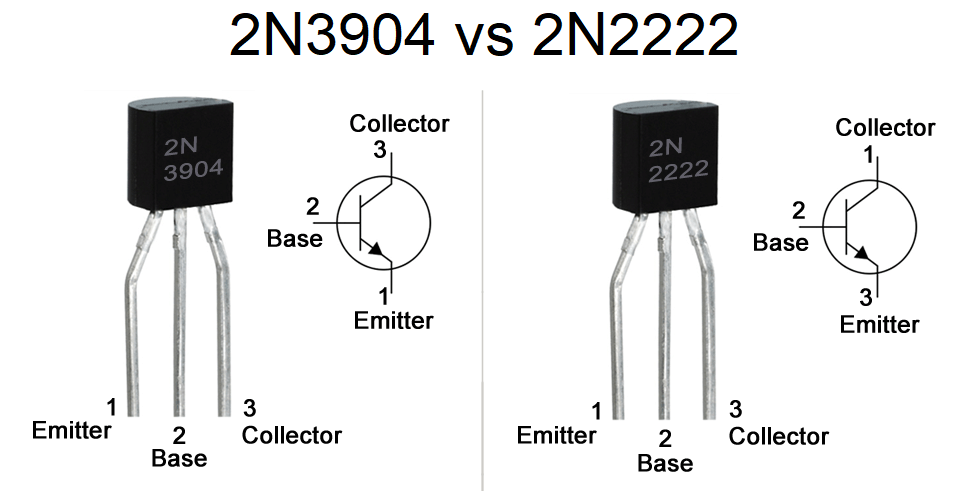
Both the 2N3904 and 2N2222 transistors feature a three-layer structure comprising the emitter, base, and collector regions. In an NPN configuration, the emitter and collector regions are crafted from N-type materials, while the base is a P-type material. When a forward bias voltage is applied at the emitter junction, electrons initiate their journey from the emitter to the base and then towards the collector. This electron flow not only forms the crux of current amplification but also drives the operation of bipolar junction transistors (BJTs). The intricate control of electron flow results in capabilities ranging from signal amplification to switching, enabling numerous electronic applications.
Specifications of 2N3904 and 2N2222
|
Specification |
2N3904 |
2N2222 |
|
Type |
NPN |
PNP |
|
Current (IC) |
200 mA |
800 mA |
|
VCE Max |
40 V |
40 V |
|
VCB Max |
60 V |
75 V |
|
VBE Max |
6 V |
6 V |
|
Power (Pc) |
625 mW |
625 mW |
|
Frequency (fT) |
300 MHz |
250 MHz |
|
Gain (hFE) |
100-300 |
35-300 |
Similarities Between 2N3904 and 2N2222
Both the 2N3904 and 2N2222 are NPN transistors, modulating the collector current through the base current, and operating analogously in circuit designs. This shared operational mode offers flexibility, allowing them to be swapped in various applications, given respect to their specific parameter limits. Their functional consistency enables their use in amplification, switching, and signal modulation tasks. Recognizing their core similarities and subtle differentiations allows you to effectively integrate these transistors into any projects. The same encapsulation and thermal range further contribute to their reliable performance under standard operating conditions. Both transistors hold valuable positions in electronic design. Selecting the right transistor based on defined electrical characteristics ensures that circuits function optimally, validating the importance of both 2N3904 and 2N2222 in driving numerous electronic projects.
How to Choose the Right Transistor?
Selecting the most fitting transistor for your application requires a thorough comprehension of their operational nuances and ensuring they are in alignment with your project goals. Both the 2N3904 and 2N2222 transistors play an instrumental role in electronic circuits due to their proficient base current control, enabling effective amplification of collector-emitter current.
Though the 2N3904 and 2N2222 transistors share voltage ratings, they exhibit differences in their current handling capabilities. The 2N3904 supports currents up to 200mA, making it ideal for smaller-scale projects. Conversely, the 2N2222 can accommodate up to 1A, positioning it as an apt choice for applications involving higher current, such as driving multiple motors or LEDs. Your selection hinges on the specific current requirements of your circuit.
When current demands are under 200mA, the 2N3904 emerges as an efficient and reliable solution. Its lower current rating pairs well with minor signal amplification or low-power switches. For demands beyond this, up to 1A, the 2N2222 stands out. Its capability to handle up to 1A makes it suitable for moderate power tasks, effectively driving components with increased current needs.
For scenarios surpassing 1A, transistors like the TIP122 or TIP3055 are more fitting. The TIP122 manages up to 5A. The TIP3055 can handle up to 15A. Handling such elevated currents necessitates careful consideration of risks such as thermal runaway and component failure. Implementing proper heat dissipation via adequate heatsinks and adhering to safety protocols is good for maintaining system integrity and safeguarding the circuit.
Choosing a transistor transcends mere technicality, it also involves strategic decision-making. A careful focus on current handling capacity, application specifics, and safety considerations forms the foundation of a sound design. Mastery and application of these principles can influence the performance and durability of electronic projects.
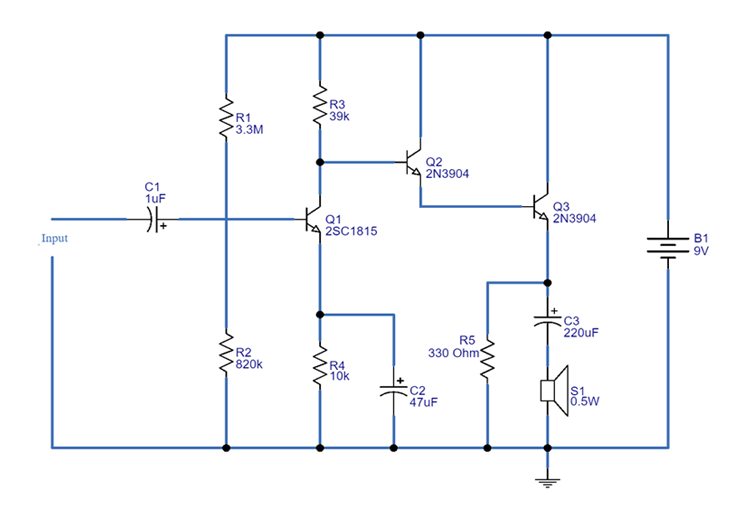
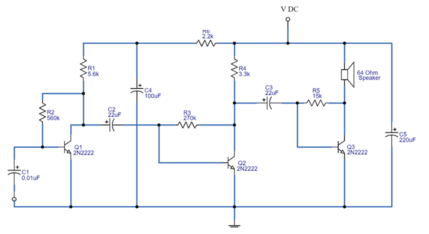
Applications of 2N3904 and 2N2222 Transistors
Both the 2N2222A/PN2222 and the 2N3904 transistors are well-regarded components in many electronic applications due to their specific characteristics and adaptability.
Switching Applications
The 2N2222A/PN2222 transistor exhibits exceptional efficiency in switching applications. Its robust current-handling capacity makes it suitable for controlling loads such as motors and solenoids. Moreover, this transistor is often utilized in circuits requiring high-speed switching, ensuring minimal delay and energy loss. Others frequently select the 2N2222A when designing circuits precision timing and reliability.
Amplification Applications
The 2N2222A/PN2222 excels as a powerful amplifier. It is commonly employed in audio circuits for tasks such as audio amplification and preamplification. This transistor enhances audio signals effectively, ensuring clarity and fidelity. The 2N3904 is also used for signal and audio amplification but is adept at driving LED and relay modules. Its lower current gain is advantageous in projects where less power is sufficient, ensuring efficiency without over-complicating the circuit. Many employ the 2N3904 in DIY projects to achieve crisp and clear signal amplification.
Radio Frequency (RF) Applications
A advantage of the 2N2222A/PN2222 is its high performance in RF circuits. This transistor's ability to operate efficiently at higher frequencies makes it a preferred choice in radio frequency applications, communication devices, and signal processing circuits. Designing RF amplifiers or oscillators often rely on the 2N2222A for its stability and performance.
Sensor Circuit Applications
In sensor circuits, the 2N2222A/PN2222 stands out due to its superior current handling and switching capabilities. These transistors are integral in circuits requiring precise control of sensor outputs. They provide reliable amplification and switching, for accurate sensor data processing. Incorporate the 2N2222A in environmental monitoring systems and industrial automation. Sensor accuracy is great in these applications.
Fast Switching Applications
For applications involving fast switching, such as Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), the 2N3904 is advantageous. Its swift response time ensures efficiency in circuits requiring rapid and repetitive switching. This characteristic is beneficial in power supply designs and motor control circuits. PWM techniques are commonly employed in these scenarios, highlighting the reliability of the 2N3904 across varied electronic projects.
Reliability and Efficiency
Both the 2N2222A/PN2222 and the 2N3904 are celebrated for their reliability and efficiency. These transistors are staples in diverse projects, performing consistently across various applications. Their robustness makes them highly adaptable in both prototyping and production environments. Choosing between them often depends on specific requirements, such as current capacity, frequency response, and switching speed.
Datasheet PDF
2N3904 Datasheets:
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
1. Can these transistors be recycled?
Yes, transistors can be recycled. Semiconductor recycling involves complex and costly procedures. However, ongoing efforts aim to enhance sustainability in these processes. For instance, silicon transistors in solar panels can be recycled through physical methods, like immersion in liquid nitrogen, followed by pyrolysis and mechanical screening. Recycling preserves valuable materials and curtails electronic waste, aligning with environmental sustainability goals.
2. Are 2N3904 and 2N2222 interchangeable in circuits?
They are not completely interchangeable due to their differing characteristics. The 2N3904 is optimized for high-speed switching and small signal amplification. The 2N2222 is better suited for higher current and voltage applications. Choosing the appropriate transistor ensures circuit performance and longevity, emphasizing the need to understand each component's specifications and limitations.
3. What are the voltage ratings for 2N3904 and 2N2222 transistors?
The 2N3904 has a maximum collector-emitter voltage of 40V. The 2N2222's maximum collector-emitter voltage is about 30V. Other factors include current rating and frequency response. Matching these parameters to your circuit's needs can prevent potential failures or inefficiencies. Careful consideration of voltage ratings helps avoid over-stressing the components, thereby bolstering the electronic system's reliability and safety.
4. What are the applications of the 2N3904 transistor?
The 2N3904 is often employed in small signal amplification, driving modules, and fast switching applications. Its fast response and high voltage control capabilities render it invaluable in educational and other electronic projects. From amplifiers in communication devices to signal modulators in diverse equipment, its widespread usage highlights the importance of a dependable component capable of managing varied functionalities. Its frequent application in prototyping and experimental setups reinforces its reputation for performance and reliability.
About us
ALLELCO LIMITED
Read more
Quick inquiry
Please send an inquiry, we will respond immediately.

Exploring the 2N4401 NPN Transistor: Features, Specs, and Uses
on October 8th

Understanding the 2N5551 Transistor: Features, Pinout, and Applications
on October 8th
Popular Posts
-
What is GND in the circuit?
on January 1th 2937
-

RJ-45 Connector Guide: RJ-45 Connector Color Codes, Wiring Schemes, R-J45 Applications, RJ-45 Datasheets
on January 1th 2498
-

Fiber Connector Types: SC Vs LC And LC Vs MTP
on January 1th 2088
-
Understanding Power Supply Voltages in Electronics VCC, VDD, VEE, VSS, and GND
on November 9th 1888
-

Comparison Between DB9 and RS232
on January 1th 1759
-

What Is An LR44 Battery?
Electricity, that ubiquitous force, quietly permeates every aspect of our daily lives, from trivial gadgets to life-threatening medical equipment, it plays a silent role. However, truly grasping this energy, especially how to store and efficiently output it, is no easy task. It is against this background that this article will focus on a type of coin cell battery that may seem insignificant on the...on January 1th 1712
-
Understanding the Fundamentals:Inductance Resistance, andCapacitance
In the intricate dance of electrical engineering, a trio of fundamental elements takes center stage: inductance, resistance, and capacitance. Each bears unique traits that dictate the dynamic rhythms of electronic circuits. Here, we embark on a journey to decipher the complexities of these components, to uncover their distinct roles and practical uses within the vast electrical orchestra. Inductan...on January 1th 1651
-

CR2430 Battery Comprehensive Guide: Specifications, Applications and Comparison to CR2032 Batteries
What is CR2430 battery ?Benefits of CR2430 BatteriesNormCR2430 Battery ApplicationsCR2430 EquivalentCR2430 VS CR2032Battery CR2430 SizeWhat to look for when buying the CR2430 and equivalentsData Sheet PDFFrequently Asked Questions Batteries are the heart of small electronic devices. Among the many types available, coin cells play a crucial role, commonly found in calculators, remote controls, and ...on January 1th 1545
-
What Is RF and Why Do We Use It?
Radio Frequency (RF) technology is a key part of modern wireless communication, enabling data transmission over long distances without physical connections. This article delves into the basics of RF, explaining how electromagnetic radiation (EMR) makes RF communication possible. We will explore the principles of EMR, the creation and control of RF signals, and their wide-ranging uses. The article ...on January 1th 1537
-

CR2450 vs CR2032: Can The Battery Be Used Instead?
Lithium manganese batteries do have some similarities with other lithium batteries. High energy density and long service life are the characteristics they have in common. This kind of battery has won the trust and favor of many consumers because of its unique safety. Expensive tech gadgets? Small appliances in our homes? Look around and you'll see them everywhere. Among these many lithium-manganes...on January 1th 1505