7805 Voltage Regulator
The 7805 voltage regulator is a popular component used to provide a steady 5V output in electronic circuits, ensuring devices run smoothly even when the input voltage changes. This article explains how the 7805 works, its pin layout, the internal parts that help maintain the voltage, and the safety features it includes. We’ll also look at how it's used in devices like mobile chargers and systems that need stable power for small electronics.Catalog
Figure 1: 7805 Voltage Regulator
Introduction to Voltage Regulators
A voltage regulator helps keep the output voltage steady, even when the input voltage changes or the electrical load varies. Keeping the voltage stable is very useful for making sure electronic devices work well and don't get damaged by voltage changes.
Figure 2: Different Types of Voltage Regulators
Voltage regulators work by adjusting the current flow to keep the output voltage the same, even if the input voltage or load changes. If the input voltage goes up, the regulator reduces the current flow, and if the input voltage drops, it increases the current flow to maintain the correct output voltage.
In many modern devices, voltage regulators are built into integrated circuits (ICs), which are small and reliable. One common IC regulator is the 7805, which provides a steady +5V output. This type of regulator is often used in electronic devices that need a stable power supply, such as computers and mobile phone chargers.
What Is the Voltage Regulator 7805?

Figure 3: 7805 Voltage Regulator
The 7805 Voltage Regulator is a commonly used device that helps control and provide a steady 5V output in electronic circuits. It belongs to a family of regulators called the "78xx" series, where "xx" refers to the output voltage. In the case of the 7805, it is designed to give a fixed 5V. This regulator can take an input voltage anywhere from 7V to 35V and still ensure that the output stays at 5V.
The 7805 works by lowering the incoming voltage to the required 5V and getting rid of the extra energy as heat. It is called a "linear" regulator because it doesn't convert the extra energy efficiently, but simply burns it off as heat to bring the voltage down. For example, if you provide the regulator with 12V, it will reduce the output to 5V, and the rest of the energy (the difference between 12V and 5V) is turned into heat.
The main job of the 7805 is to keep the output voltage steady, even if the input voltage changes. However, this process creates heat, especially when the input voltage is much higher than 5V or when the circuit needs more current. To handle this heat, the 7805 often needs a heat sink or some other cooling method. Without a way to cool it down, the regulator can get too hot, which could affect how well it works or cause it to stop working altogether.
Pin Configuration of the 7805 IC
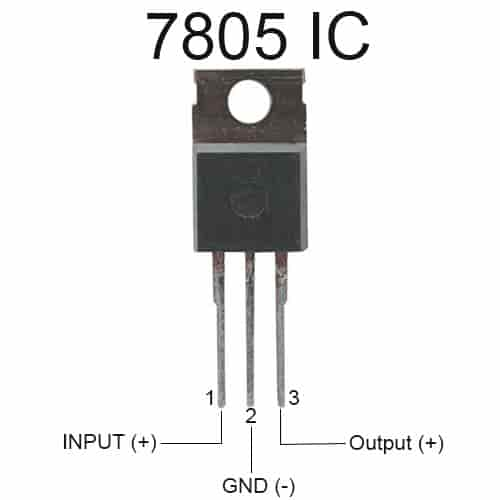
Figure 4: Pin Configuration of 7805 Voltage Regulator
• Pin 1 (Input): This is where you connect the voltage that hasn't been regulated yet. The voltage coming in must be at least 2V higher than the 5V output you want. So, to get a stable 5V output, the input voltage must be at least 7V.
• Pin 2 (Ground): This pin connects to the ground (or zero voltage) of your circuit. It serves as the reference point for both the input and output voltages.
• Pin 3 (Output): This is where the steady 5V output comes from. The output is typically between 4.8V and 5.2V, but it's meant to stay as close to 5V as possible.
How Does 7805 IC Work?
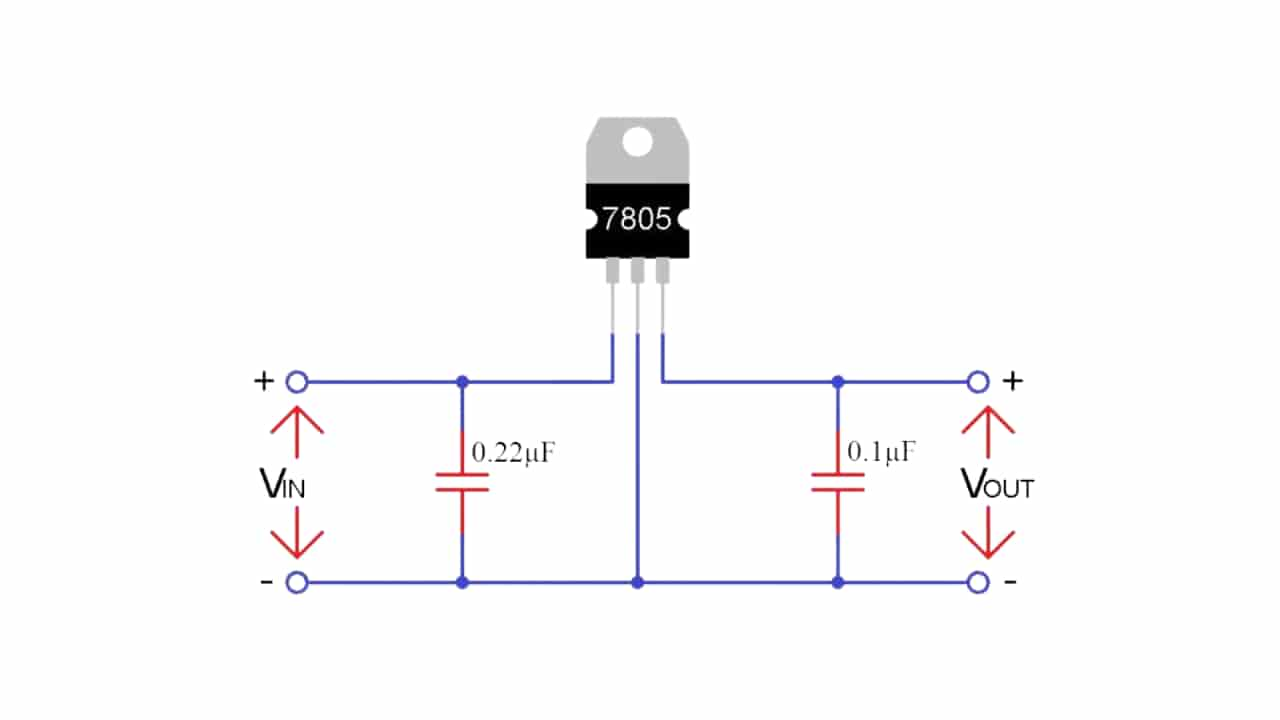
Figure 5: Circuit Diagram Showing How the 7805 Voltage Regulator Works
Inside the IC, several parts work together to keep the output voltage constant, even if there are changes in input voltage or load. Here's a simple explanation of how each part of the IC works to maintain that steady output.
Starting Circuit
The starting circuit is the first part to activate when the 7805 is powered on. Its job is to make sure all other internal parts of the IC are ready to begin working. Once power is applied, this circuit sets everything in motion, allowing the 7805 to start regulating the voltage.
Current Generator
The current generator manages how much current flows inside the IC. This part ensures that the other internal components get the right amount of current to function correctly. It helps the IC adapt to different situations, like when the load on the IC changes, so it can continue to deliver stable performance.
Reference Voltage (Zener Diode)
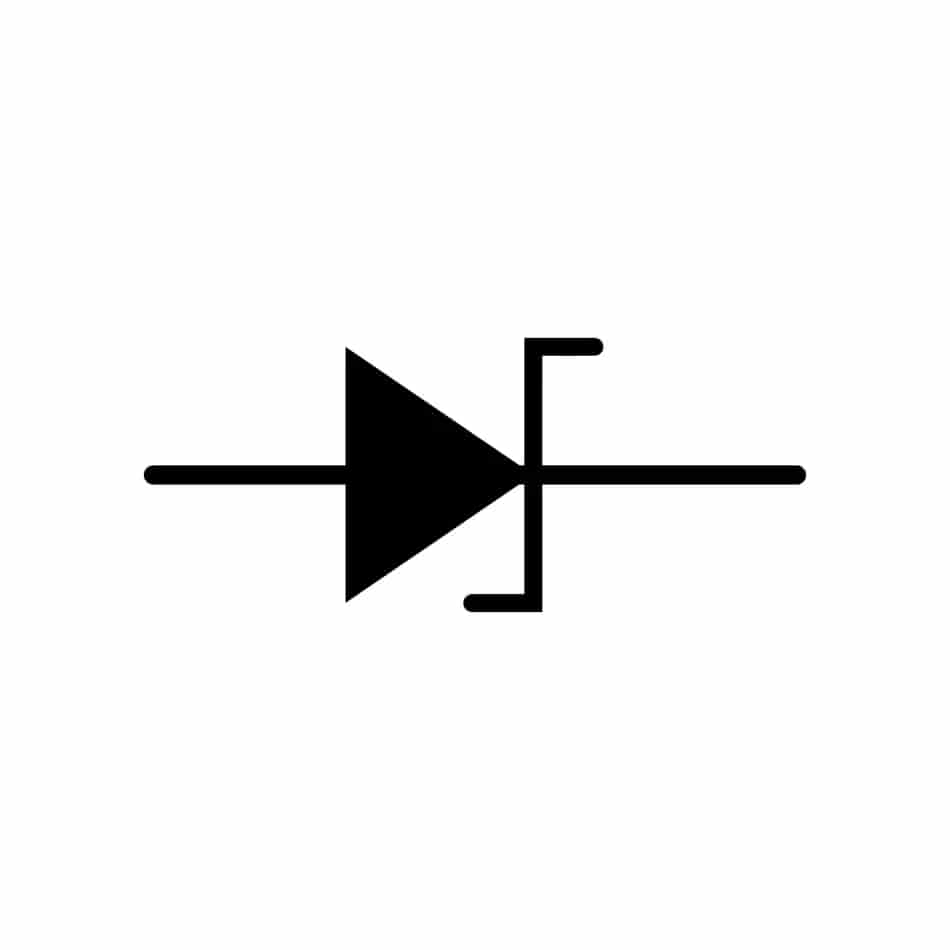
Figure 6: Zener Diode Symbol
The 7805 uses a Zener diode to create a steady reference voltage. This reference voltage acts as a guide that the IC uses to make sure the output voltage remains at 5V. The Zener diode is chosen because it can maintain a consistent voltage, which helps the IC compare and adjust the output voltage as needed.
Error Amplifier
The error amplifier is responsible for constantly checking the output voltage. It compares the actual output voltage to the reference voltage set by the Zener diode. If the output voltage is not exactly 5V, the error amplifier sends a signal to make adjustments. This way, the output voltage is corrected in real time, keeping it steady under changing conditions.
Series Pass Element (Transistor)
The series pass element, usually a transistor, controls the amount of current going to the output. It changes its resistance based on the signals it receives from the error amplifier. If the output voltage starts to go above or below 5V, the transistor adjusts the current flow to bring it back to the correct level. While doing this, the transistor also releases extra energy as heat, which is why the IC can become warm during use.
Thermal Protection Circuit
The thermal protection circuit helps prevent the IC from getting too hot. If the IC’s temperature rises too high, which can happen due to heavy use or high external temperatures, this circuit will step in to lower the current or even shut down the IC temporarily. This feature is important for protecting the IC and making sure it doesn't get damaged from overheating.
Safe Operating Area (SOA) Protection
The Safe Operating Area (SOA) protection keeps the 7805 from working outside its safe limits. This protection ensures the IC isn’t exposed to too much voltage or current, which could cause it to fail. If something goes wrong, like a short circuit or a sudden spike in input voltage, this protection will limit the IC’s operation to prevent damage. This feature helps the IC last longer and operate more reliably.
Managing Heat in the 7805 IC
Managing heat in the 7805 voltage regulator can be a challenge. The 7805 reduces a higher input voltage to a steady 5V output, but when the input voltage is much higher than 5V, the extra voltage is converted into heat. For example, if the input is 15V and the current is 0.5A, the regulator will produce 5 watts of heat. This can be too much heat for the 7805 to handle without cooling, potentially causing it to overheat and fail.
To reduce heat, it's best to keep the input voltage close to 7V, which is the minimum required for stable 5V output. The closer the input voltage is to 7V, the less excess energy the regulator needs to convert to heat. If a higher input voltage is necessary, a heat sink can be attached to the 7805 to help cool it down by spreading the heat over a larger surface area. The larger the heat sink, the better it will be at dissipating heat and keeping the regulator within a safe temperature range.
Features of the 7805 Voltage Regulator IC
Minimal External Components
One of the best things about the 7805 IC is that it needs very few extra parts to work. Usually, it only requires two small capacitors—one on the input side and one on the output side. These capacitors help to keep the voltage steady and reduce any sudden changes or noise in the power. Because the 7805 doesn't need many extra parts, it makes the design simpler and lowers the cost. This makes it a great choice for many projects.
Wide Input Voltage Range
The 7805 can work with a wide range of input voltages, from 7V to 35V. This means it can handle power from different sources, even if the voltage is higher or lower than expected. As long as the input voltage stays within this range, the 7805 will give a steady 5V output. This flexibility makes it useful for a variety of situations where the input power may not always be the same.
Current Capacity
The 7805 can provide up to 1.5A of current, which makes it useful for devices that need a moderate amount of power, such as small motors or sensors. It can reliably supply this current to different electronic parts, but the actual current depends on how much heat the IC generates and the input voltage. If it gets too hot or the input voltage is too low, the current might be reduced. Still, for most purposes, the 7805 can easily meet the power needs of many devices.
Low Standby Current
When the 7805 is not actively providing power to a device, it uses very little energy itself, usually around 5mA. This means it doesn’t waste much power, which is especially useful in devices that run on batteries. Since it doesn't drain power unnecessarily, it helps make systems more efficient, especially in designs where saving energy is a priority.
Built-in Protections
The 7805 IC comes with several safety features that protect both the IC and the devices it powers. It has thermal protection, which turns the IC off if it gets too hot. It also has a built-in current limiter that prevents too much current from flowing, protecting the circuit from damage. Finally, it can handle short circuits without failing, thanks to its internal safety measures. These built-in protections make the 7805 a reliable choice for many projects, even in environments where power conditions might change unexpectedly.
Benefits of Using the 7805 IC
Easy to Use
One of the biggest advantages of the 7805 IC is how simple it is to work with. You only need a few additional components, like capacitors, to stabilize the input and output voltages. This makes it easy to set up, even for people who are just starting out in electronics. The pin layout is easy to understand: one pin for the input voltage, one for ground, and one for the 5V output. This simplicity means that you can quickly add the 7805 to a circuit without needing to make complex adjustments or deal with any complicated setups.
Safety Features
The 7805 IC includes built-in safety features that protect it from damage. One such feature is thermal protection, which automatically shuts down the IC if it gets too hot. This prevents the IC and other parts in the circuit from getting damaged. This is especially helpful in situations where the circuit might get too warm or where cooling is a concern. Another useful feature is short-circuit protection. If there is a fault in the circuit causing a short circuit, the 7805 will limit the current flowing through it, protecting both itself and the rest of the circuit from harm. These protections make the 7805 a durable and reliable choice for many electronics projects.
Common Applications
The 7805 IC is widely used in circuits that need a stable 5V power supply. It is often found in devices that use low power, such as microcontroller projects, embedded systems, and many types of sensors. Many electronic components, like microprocessors, displays, and communication modules, need a steady 5V to work properly. The 7805 IC provides this stable power, which helps these components run smoothly. Because it’s easy to find and works well in a wide range of applications, the 7805 IC is trusted by both professionals and hobbyists in their projects.
Applications of the 7805 Voltage Regulator
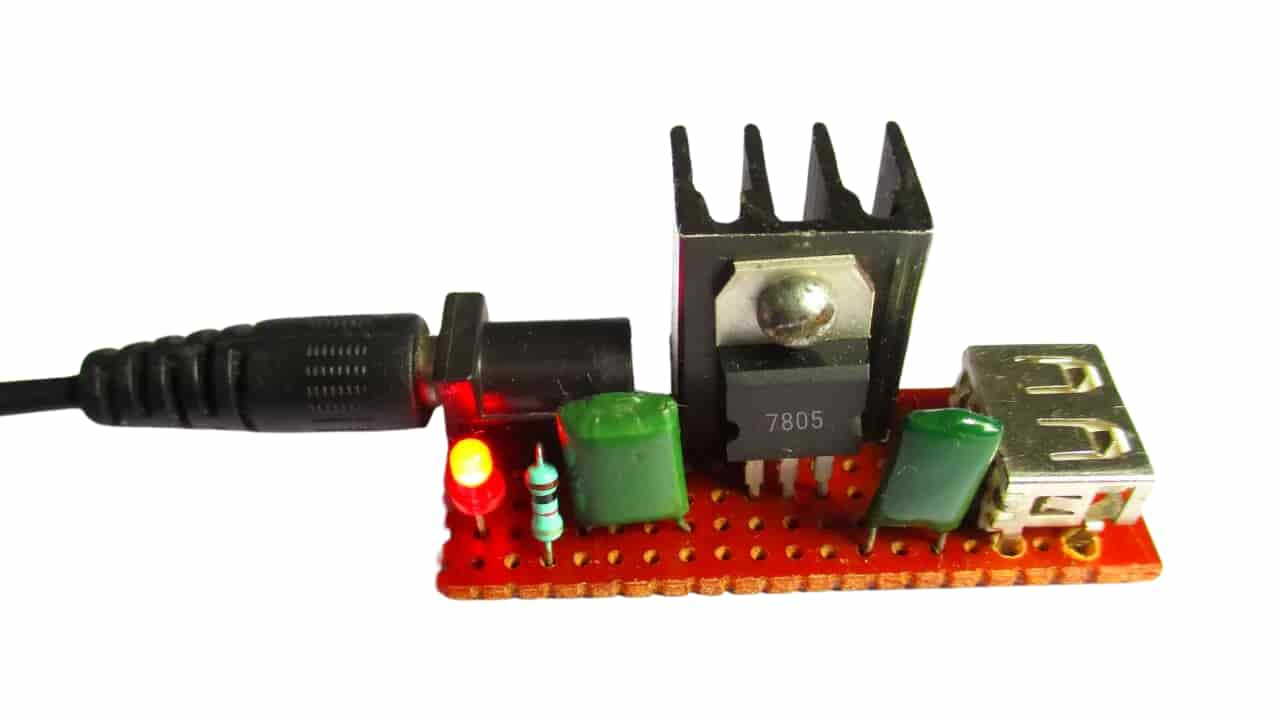
Figure 7: 12V To 5V USB Power Supply Using 7805 Voltage Regulator
The 7805 voltage regulator is a widely used component in many electronic devices. Its job is to provide a stable 5V output, which is useful for circuits that need a steady power supply.
For instance, in mobile phone chargers, the 7805 helps keep the voltage steady at 5V, even if the power coming from the wall socket changes. This is important for safely charging devices that require a consistent voltage. Similarly, it can be found in uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems, where it helps supply a constant voltage to circuits that can't afford interruptions or drops in power.
In devices like portable media players, the battery's voltage can fluctuate as it drains, but the 7805 ensures that the internal components still receive a steady 5V, protecting the device from damage caused by sudden changes in power. Low-power circuits, such as those in small electronic projects or gadgets, also rely on the 7805 to deliver consistent voltage. These circuits may contain sensitive parts like microcontrollers and sensors, which could malfunction or get damaged if the power isn't stable. The 7805 makes sure the output stays at 5V, regardless of what happens with the input power.
In some cases, the 7805 can be used in circuits that need to control the flow of current. Though it's mainly designed to regulate voltage, when combined with other parts like resistors or transistors, it can also help regulate current. It’s often used in infrared remote controls to provide the stable power needed for sending signals. Timing devices, such as stopwatches, also benefit from the 7805. It keeps the internal clock components working correctly, ensuring that the device measures time accurately by providing consistent voltage.
Role of Capacitors in 7805 Circuits
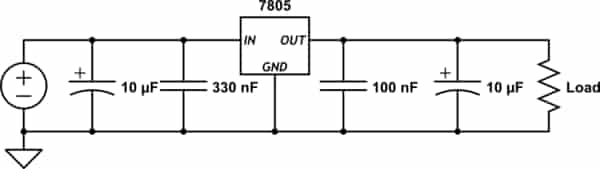
Figure 8: Voltage Regulation Circuit with Capacitors
Capacitors are small electronic components that are often added to circuits with the 7805 voltage regulator. They help make the voltage smoother and reduce unwanted electrical noise. Without these capacitors, the output from the regulator could have small changes in voltage, which could affect the performance of the connected parts.
At the input side of the 7805, a capacitor with a value of 0.33µF is typically used to filter out any noise coming from the power source. This becomes especially helpful if the regulator is placed more than 10 inches away from the power supply, as electrical noise or spikes can be more common over longer distances. The capacitor absorbs these fluctuations, ensuring a more steady voltage is delivered to the input of the 7805.
On the output side, a smaller capacitor, usually around 0.1µF, is added to further smooth the regulated voltage. Even though the 7805 does a good job of stabilizing the voltage, some minor changes can still occur. These changes could be caused by external factors or other parts in the circuit. The output capacitor helps filter out these small variations, ensuring that the voltage stays as steady as possible at 5V. This provides a more reliable power supply for devices that are sensitive to voltage changes, such as microcontrollers or other digital components that require consistent power to work correctly.
Conclusion
The 7805 voltage regulator helps keep the power supply steady at 5V, which makes it useful for many different electronics projects. It’s easy to use, has built-in protections, and can be found in a variety of devices, from small gadgets to more complex systems. By using the 7805, you can help ensure that your devices work properly without power problems.
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
1. How much voltage can 7805 handle?
The 7805 voltage regulator can handle an input voltage of up to 35V, but it’s safer and works better if the input stays between 7V and 25V. If the input voltage is too high, it may overheat or get damaged.
2. What is the voltage of AC in 7805?
The 7805 is designed to regulate DC voltage, not AC. You need to convert AC to DC first using something like a rectifier before connecting it to the 7805.
3. Can I use 7805 without a capacitor?
Yes, you can technically use the 7805 without capacitors, but it won’t work as well. Capacitors help smooth out the voltage and make sure the output stays stable. Usually, a small capacitor is placed on the input (0.33µF) and another on the output (0.1µF) for better performance.
4. How to reduce 12V to 5V using 7805?
To bring 12V down to 5V, you connect the 12V input to the 7805’s input pin, connect the ground pin to the ground, and the 7805 will give you 5V from its output pin. Don’t forget to use capacitors to help keep the voltage steady.
5. What is the internal work of 7805?
Inside the 7805, there are small electronic parts like transistors, resistors, and reference diodes that work together to keep the output voltage at 5V. It does this by turning the extra voltage into heat, so the output stays steady even if the input voltage or load changes.
About us
ALLELCO LIMITED
Read more
Quick inquiry
Please send an inquiry, we will respond immediately.

IRFZ44N MOSFET
on September 19th
Discovering Ring Counters: An In-Depth Guide to Their Functionality, Classifications, and Uses
on September 18th
Popular Posts
-
What is GND in the circuit?
on January 1th 2933
-

RJ-45 Connector Guide: RJ-45 Connector Color Codes, Wiring Schemes, R-J45 Applications, RJ-45 Datasheets
on January 1th 2493
-

Fiber Connector Types: SC Vs LC And LC Vs MTP
on January 1th 2081
-
Understanding Power Supply Voltages in Electronics VCC, VDD, VEE, VSS, and GND
on November 8th 1883
-

Comparison Between DB9 and RS232
on January 1th 1759
-

What Is An LR44 Battery?
Electricity, that ubiquitous force, quietly permeates every aspect of our daily lives, from trivial gadgets to life-threatening medical equipment, it plays a silent role. However, truly grasping this energy, especially how to store and efficiently output it, is no easy task. It is against this background that this article will focus on a type of coin cell battery that may seem insignificant on the...on January 1th 1710
-
Understanding the Fundamentals:Inductance Resistance, andCapacitance
In the intricate dance of electrical engineering, a trio of fundamental elements takes center stage: inductance, resistance, and capacitance. Each bears unique traits that dictate the dynamic rhythms of electronic circuits. Here, we embark on a journey to decipher the complexities of these components, to uncover their distinct roles and practical uses within the vast electrical orchestra. Inductan...on January 1th 1651
-

CR2430 Battery Comprehensive Guide: Specifications, Applications and Comparison to CR2032 Batteries
What is CR2430 battery ?Benefits of CR2430 BatteriesNormCR2430 Battery ApplicationsCR2430 EquivalentCR2430 VS CR2032Battery CR2430 SizeWhat to look for when buying the CR2430 and equivalentsData Sheet PDFFrequently Asked Questions Batteries are the heart of small electronic devices. Among the many types available, coin cells play a crucial role, commonly found in calculators, remote controls, and ...on January 1th 1541
-
What Is RF and Why Do We Use It?
Radio Frequency (RF) technology is a key part of modern wireless communication, enabling data transmission over long distances without physical connections. This article delves into the basics of RF, explaining how electromagnetic radiation (EMR) makes RF communication possible. We will explore the principles of EMR, the creation and control of RF signals, and their wide-ranging uses. The article ...on January 1th 1537
-

CR2450 vs CR2032: Can The Battery Be Used Instead?
Lithium manganese batteries do have some similarities with other lithium batteries. High energy density and long service life are the characteristics they have in common. This kind of battery has won the trust and favor of many consumers because of its unique safety. Expensive tech gadgets? Small appliances in our homes? Look around and you'll see them everywhere. Among these many lithium-manganes...on January 1th 1504














































