on April 22th
466
Popular BCI Battery Pack Introduction Guide
There are so many types of automotive batteries that it can be difficult to choose, and there are many types of BCI battery packs alone. But with the BCI Battery Pack Size Chart, car owners and technicians can make informed decisions with confidence. The chart carefully categorizes batteries not only by physical size but also by capacity and intended application, tailoring selections to the specific needs of various vehicles. The BCI chart significantly eases the process of battery selection by delineating which battery types are best suited for different vehicle categories—from family cars to commercial fleets. Understanding these distinctions helps vehicle owners ensure that their choice aligns with their vehicle's power requirements and installation constraints. This article will mainly introduce the most popular battery packs and provide some suggestions for everyone to buy batteries.
Catalog
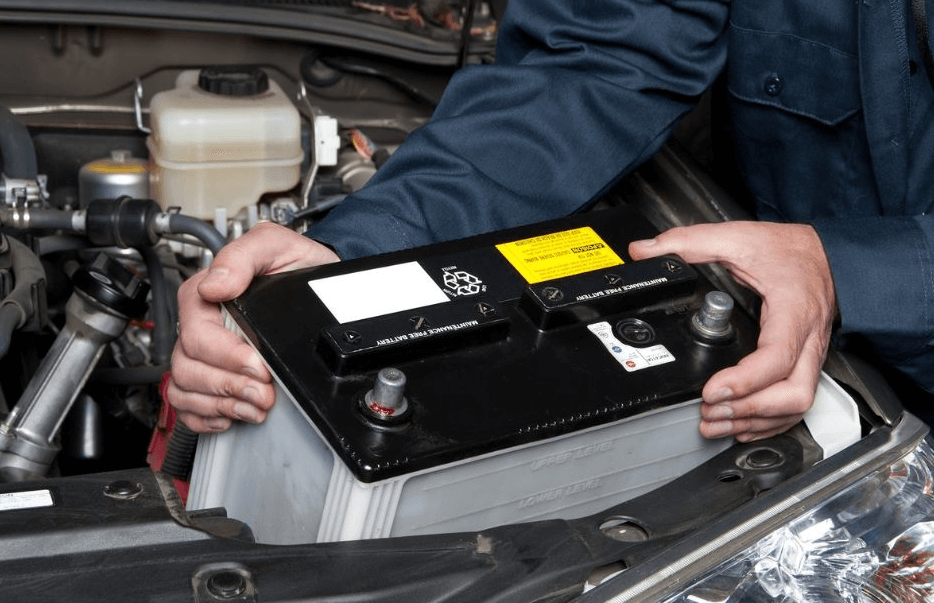
Figure 1: BCI Battery
The BCI Battery Pack Size Chart is a vital tool for identifying the right automotive battery. It categorizes batteries by size, capacity, and intended use, making it easier for users to make informed choices. Each category, like Group 27 and Group 31, targets specific vehicle needs. Group 31 batteries stand out for their use in heavy-duty applications. These are ideal for large vehicles and equipment that consume a lot of power. Their large size and high capacity are tailored for prolonged, intensive use. Users should closely examine their amp-hour (AH) ratings and endurance to ensure they meet the demands of their high-powered vehicles.
On the other hand, Group 24 and Group 27 are perfect for medium-sized vehicles. They strike a balance between size and power capacity, ensuring they provide enough energy for starting and running the vehicle without being too heavy. This makes them a smart choice for everyday vehicle use.
For smaller vehicles with cramped engine spaces, the compact Group 51R battery is a perfect fit. Despite its size, it delivers sufficient power for basic vehicle operations, making it an efficient option for smaller cars.
Larger vehicles like SUVs and trucks benefit from Group 35 batteries. These batteries offer more capacity and stronger current output, crucial for supporting sophisticated electronics and big starter motors. Their design prioritizes durability and a stable power supply. The chart also includes various other groups like Groups 47, 34, 48, 41, 65, 94R, and 78, catering to a broad spectrum of vehicles from family cars to commercial fleets. The physical dimensions and amp-hour ratings of these batteries significantly influence their performance characteristics like starting power, longevity, and temperature resistance.
Choosing the correct battery size and capacity goes hand in hand with achieving optimal performance and safety. A mismatch can cause power failure and potential damage to the vehicle's electrical system. When it's time to replace the battery, consulting your vehicle's manual or a trusted online resource can help ensure that the new battery is not only installed correctly but also operates safely and efficiently. Understanding the specifics of each battery type and selecting the right one according to the vehicle’s needs are essential steps every car owner should take to maintain their vehicle’s efficiency and safety.
In the automotive industry, choosing the right type of battery affects how reliably a vehicle will operate over its lifetime, and automakers are constantly developing different battery options suitable for specific types of vehicles. The three main types of batteries on the market today are lead-acid, AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat), and lithium-ion, each serving unique roles depending on their technological attributes.
Lead-acid batteries, known for their cost-effectiveness and reliability, are a traditional choice, particularly in conventional fuel vehicles. They provide the essential power needed to start engines and maintain stable voltage output. Despite their heavier weight, the maturity of lead-acid technology makes these batteries relatively simple to maintain, making them a budget-friendly option.
AGM batteries build on the traditional lead-acid design by incorporating special glass mats that absorb electrolytes. This structure prevents leakage and makes AGM batteries more stable in vibrating environments, with lower discharge rates. They're ideal for vehicles with higher energy needs, such as luxury cars and high-performance vehicles that have extensive electronic setups and demanding starter systems.
Lithium-ion batteries stand out due to their high energy density and lighter weight, making them the preferred choice for electric and hybrid vehicles. They offer longer lifespans and the ability to charge quickly. Although they come at a higher initial cost, their operational efficiency and environmental benefits make them increasingly popular in modern vehicles.
|
Group Size
|
LxWxH (inches)
|
LxWxH (cm)
|
|
Group 24 Batteries
|
10.25 x 6.8125 x 8.875
|
26 x 17.3 x 22.5
|
|
Group 27 Batteries
|
12.0625 x 6.8125 x 8.875
|
30.6 x 17.3 x 22.5
|
|
Group 31 Batteries
|
13 x 6.8125 x 9.4375
|
33 x 17.3 x 24
|
|
Group 34 Batteries
|
10.25 x 6.8125 x 7.875
|
26 x 17.3 x 20
|
|
Group 35 Batteries
|
9.0625 x 6.875 x 8.875
|
23 x 17.5 x 22.5
|
|
Group 51 and 51R Batteries
|
9.374 x 5.0625 x 8.8125
|
23.8 x 12.9 x 22.3
|
|
Group 65 Batteries
|
12.0625 x 7.5 x 7.5625
|
30.6 x 19 x 19.2
|
|
Group 78 Batteries
|
10.25 x 7.0625 x 7.3125
|
26 x 17.9 x 18.6
|
Chart 1: Comparison Chart of the Main Battery Pack Sizes in
this Article
Figure 2: BCI Group 24 Battery
BCI Group 24 batteries are versatile units often utilized in various applications including large Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) systems, medical equipment, security systems, electric wheelchairs, different types of vehicles, and industrial uses. These batteries are specifically designed for deep cycle applications that require extended standby or float charging, rather than primarily for starting engines. Their medium size comes with slight variations among subgroups, which necessitates careful selection to ensure each battery fits properly into its specific housing or battery box.
The most common chemical compositions found in BCI Group 24 batteries are AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) and SLA (Sealed Lead Acid). Both types offer excellent durability and stable performance. Additionally, there are Group 24 batteries made from gel, flooded lead acid, and lithium-ion materials available on the market. Each type of battery comes with its unique charging and maintenance requirements as well as lifespan characteristics due to its specific chemical properties.
In terms of size, the standard dimensions for BCI Group 24 batteries are 10.25 inches (260 mm) in length, 6.8125 inches (173 mm) in width, and 8.875 inches (225 mm) in height. However, within this group, there are subgroups with slight differences in size which must be carefully checked against the specifications required to ensure the battery will precisely fit the intended device or battery compartment. For instance, the BCI Group 24F battery is slightly longer and wider than other subgroups, while the Group 24T battery stands taller at 9.75 inches (about 248 mm), which is 0.875 inches (about 22 mm) taller than the standard Group 24 battery. This means if a battery compartment is designed to house a standard Group 24 battery at 8.875 inches in height, it can generally accommodate a Group 24T battery as well.
It's important to note that Group 34 batteries share the same length and width as the Group 24 batteries but are an inch shorter in height. This gives users who might need to choose between batteries of the same length and width but different heights additional flexibility.
Figure 3: BCI Group 27 Battery
BCI Group 27 batteries are recognized for their large size and robust capabilities, making them a preferred choice for demanding applications such as automotive, marine, off-grid systems, RVs, and similar setups. With a capacity range typically spanning 66 to 110 amp-hours (Ah) over 20 hours, these batteries are designed to deliver substantial power, supporting 600 to 1000 cold cranking amps (CCA) and providing reserve capacities (RC) of 140 to 220 minutes. This combination of high capacity and power output ensures that they can handle higher energy demands, which is critical for vehicles and systems requiring reliable startup and operational power under various conditions.
The weight of Group 27 batteries varies significantly, generally falling between 54 and 70 pounds (24.5 to 32 kilograms), influenced primarily by their internal construction. This variance in weight is reflective of the different types of technologies employed within this group, such as flat plates or spiral-wound plates, each contributing differently to the battery's overall performance and durability. Physically, the dimensions of a standard Group 27 battery are typically 12.0625 inches in length, 6.8125 inches in width, and 8.875 inches in height (about 306 x 173 x 225 millimeters). This size makes Group 27 batteries slightly smaller than those in Group 31, allowing them to fit in a variety of settings where space may be slightly constrained but substantial power is still needed.
Group 27 includes several closely related but distinct subcategories, namely Group 27, 27F, and 27H, each tailored to slightly different specifications and applications but generally categorized under the Group 27 umbrella. While these batteries are most commonly constructed using sealed lead-acid (SLA) technology with absorbent glass mat (AGM) components, which is particularly suited for deep cycle applications, there are also dual-purpose AGM options available that are designed to provide both excellent starting power and deep cycle capabilities to accommodate a broader range of applications.
In terms of lithium-based options, Group 27 lithium batteries are less common than those in Group 31. For users specifically seeking a 12V 100Ah or similar lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) battery, it may be beneficial to consider options within Group 31, which are more prevalent and specifically tailored for such needs. When selecting a Group 27 battery, it is important to consider the specific requirements of your application. This includes not only the physical dimensions and weight but also the type of battery technology—whether AGM for deep cycling or dual-purpose or perhaps lithium if higher efficiency and lower weight are priorities.
Figure 4: BCI Group 31 Battery
BCI Group 31 batteries are designed for high-demand applications, including marine, automotive, and off-grid systems. These robust units boast a capacity range of 75 to 125 amp-hours (Ah) over a 20-hour discharge period, capable of delivering 750 to 1250 cold cranking amps (CCA) and providing reserve capacities (RC) between 150 to 250 minutes. These characteristics make them well-suited to power systems that require a dependable, sustained energy supply.
The physical dimensions of these batteries, typically around 13 inches long, 6.8 inches wide, and 9.44 inches high (330 x 173 x 240 millimeters), allow them to fit into various spaces, from the compact to the expansive. The weight of these batteries can vary significantly—lithium models are lighter, often less than 30 pounds, while lead-acid versions can weigh close to 80 pounds. This variation primarily stems from the differences in their internal chemistry and construction.
Group 31's traditional lead-acid batteries include varieties such as AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat), gel, and flooded types. AGM batteries, in particular, are favored for their low maintenance needs and vibration resistance, thanks to the electrolyte being absorbed between specially designed glass mats that are snug between the lead plates. Advancements in technology have propelled lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries into popularity within this group. These batteries are equipped with a Battery Management System (BMS) that vigilantly monitors key metrics such as voltage, charging and discharging rates, and temperature. This monitoring helps prevent issues like overcharging, deep discharging, and overheating, which are crucial for batteries used in safety-critical settings. LiFePO4 batteries are considerably lighter than their lead-acid counterparts—often two to three times so—and can endure significantly more charge/discharge cycles with minimal performance degradation.
When it comes to charging these units, it is imperative to use dedicated lithium battery chargers or advanced AGM chargers equipped with a lithium-specific charging mode. This ensures both the safety and the longevity of the battery. Group 31 now offers higher voltage models, such as 24V (actually 25.6V) and 36V (actually 38.4V), perfect for systems requiring more substantial power, like trolling motors and RV setups. These higher voltage options help reduce the overall number of batteries needed in these configurations.
Figure 5: BCI Group 34 Battery
BCI Group 34 batteries are well-known for their mid-sized build and powerful performance, making them ideal for diverse applications, including vehicles, boats, industrial settings, and off-grid systems. With an energy capacity ranging from 50 to 75 amp-hours (Ah) over a 20-hour discharge cycle, these batteries also offer cold cranking amps (CCA) between 750 to 900 and reserve capacities (RC) from 100 to 145 minutes. These capabilities make Group 34 batteries reliable for both routine starts and rigorous usage that involves frequent and deep discharges.
In terms of physical dimensions, Group 34 batteries measure approximately 10.25 inches in length, 6.8125 inches in width, and 7.875 inches in height. This size is somewhat similar to the Group 24 batteries, although the Group 34 models are about an inch shorter, an important factor to consider for fitting them in specific compartments or tight spaces. The weight of these batteries can vary a lot, typically from 37 to 51 pounds (16.8 to 23.1 kilograms), influenced by their internal structure and the materials used. Batteries might employ Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) technology, gel, or traditional flooded lead-acid configurations. To facilitate easier handling and transportation, most Group 34 batteries include built-in handles. However, even though they aren't excessively heavy, carrying them over substantial distances can be challenging and might lead to muscle fatigue or strain if not handled carefully.
An interesting variant is the 34/78 battery which includes the standard terminals typical of Group 34 and also features additional side terminals suitable for 3/8-inch sockets. These dual-terminal batteries are generally a bit larger than the standard Group 34 models, necessitating careful measurement before purchase to ensure they fit the designated battery boxes.
It's also crucial to note the difference between Group 34 and Group 34R batteries, which lies in the orientation of the terminal posts. The standard Group 34 battery has its positive terminal on the left, while the Group 34R version places the positive terminal on the right, a minor but vital distinction for ensuring correct installation and proper alignment with vehicle or equipment wiring.
Most leading brands offer both Group 34 and Group 34R batteries, widely available in both physical stores and online. Predominantly, these batteries are crafted using AGM technology, appreciated for their maintenance-free operation and enhanced safety due to their sealed design. Nevertheless, there are exceptions like the Banshee 34M battery, which uses enhanced flooded battery (EFB) technology, claimed to be maintenance-free but still retaining characteristics of traditional flooded lead-acid batteries.
Figure 6: BCI Group 35 Battery
BCI Group 35 batteries fall into the mid-sized category with a 20-hour capacity that generally spans from 42 to 65 amp-hours (Ah). They deliver cold cranking amps (CCA) in the range of 430 to 850 and have reserve capacities (RC) stretching from 90 to 130 minutes. These specifications showcase their capacity to manage both intensive power requirements and prolonged usage. With physical dimensions of roughly 9 1/16 inches by 6 7/8 inches by 8 7/8 inches (230 mm by 175 mm by 225 mm), these batteries fit comfortably in varied installation settings while still providing substantial power output.
The AGM design within Group 35 batteries is specifically engineered to prevent leaks and eliminate maintenance hassles, making them particularly suitable for starting and dual-purpose roles. Modern vehicles often rely on these batteries not only for substantial starting currents necessary for both gasoline and diesel engines but also to supply power to various electrical and electronic systems when the engine is off—ranging from audio systems and ventilation to lighting and security setups. AGM Group 35 batteries are excellent for providing strong starting currents and due to recent technological advancements in AGM technology, they are also effective in handling frequent charge and discharge cycles, often outperforming traditional wet/flooded lead-acid batteries. They remain reliable even in extremely low temperatures, a condition that can challenge standard lithium batteries.
The growing preference for Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries in this group is largely due to their equipped Battery Management Systems (BMS). The BMS meticulously monitors and controls battery parameters, protecting the battery by disconnecting it from the circuit when necessary to prevent over-voltage, over-charging, over-current, and over-discharging, and to manage temperature fluctuations. It also ensures individual cells are balanced, making LiFePO4 batteries a direct replacement for traditional AGM SLA batteries in many scenarios. Weight-wise, lithium-ion batteries significantly outshine AGM batteries as starter batteries due to their lighter weight and higher efficiency. However, it’s important to recognize that lithium batteries are sensitive to low temperatures, which might trigger their BMS to disconnect them from the vehicle's power system, an issue not faced with AGM lead-acid batteries.
Figure 7: BCI Group 51 Battery
BCI Group 51 and 51R batteries are meticulously engineered to conform to the specific dimensions typically required for automotive battery boxes, each measuring about 9.375 inches long, 5.0625 inches wide, and 8.75 inches high. This compact size allows for mounting into designated battery spaces within most vehicles.
These batteries employ Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) technology within a Sealed Lead Acid (SLA) structure, making them highly resistant to vibrations and robust enough to withstand demanding automotive environments. AGM technology is preferred in these applications because it encapsulates the electrolyte within glass mats, enhancing the battery's efficiency and lifespan by preventing leakage and outperforming traditional flooded lead-acid batteries in terms of reliability and maintenance requirements. Occasionally, you'll find variations like those in the U1 group, which, despite being labeled as Group 51, are slightly smaller. This adjustment typically reduces their weight and marginally lowers their capacity, starting power, and reserve capacity. However, these batteries are strategically optimized for specific scenarios where a smaller size and lighter weight are advantageous, ensuring that these adjustments don't detract from the battery’s performance in its primary role.
The distinction between Group 51 and 51R batteries primarily involves the placement of the terminals, which is vital for seamless installation. Group 51 batteries feature the positive terminal on the left, while the 51R version has it on the right. This difference is crucial for vehicles that require a specific terminal arrangement to accommodate the layout of cable connections in the battery compartment, ensuring a secure and clean setup without the need for re-routing cables or additional adjustments. When selecting a Group 51 or 51R battery, it's essential to match not only the physical size and terminal configuration to your vehicle's specifications but also to consider the battery's performance capabilities. AGM batteries in these groups are known for their excellent cold-cranking amps and their ability to maintain a charge efficiently, making them highly suitable for various automotive applications that demand dependable and long-lasting power sources. By understanding these detailed attributes, you can ensure that the battery you choose not only fits perfectly but also robustly meets the operational demands of your vehicle, ensuring reliability and extending the battery’s service life.
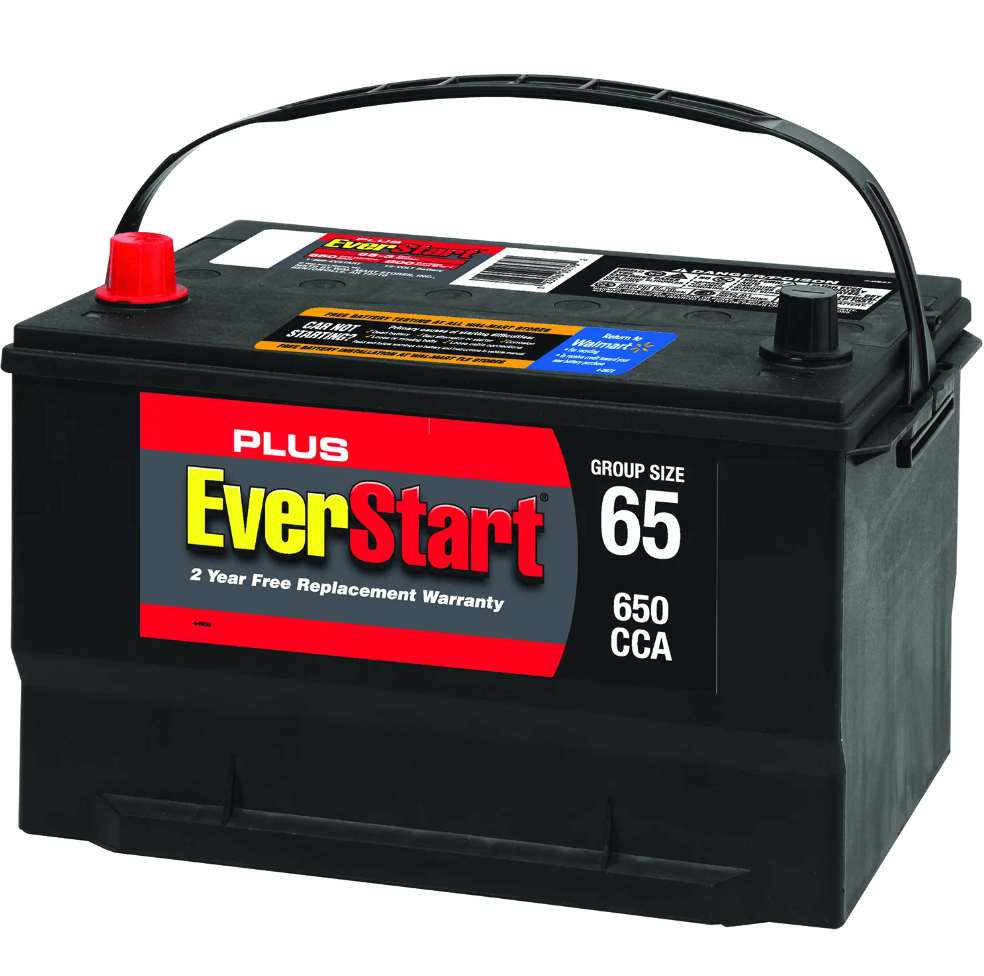

Figure 8: BCI Group 65 Battery
BCI Group 65 batteries boast substantial physical dimensions, typically 12.1 inches long, 7.5 inches wide, and 7.6 inches tall, or approximately 306 mm x 192 mm x 192 mm. These dimensions make it a common choice for modern vehicles, ships, and various industrial machinery.
Primarily, Group 65 batteries incorporate Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) technology within a Sealed Lead Acid (SLA) framework. The AGM design is highly sought after for its exceptional vibration resistance and leak-proof qualities, ideal for demanding environments that require durable and low-maintenance power solutions. For applications that demand even more safety and stability, some Group 65 batteries utilize Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) chemistry with cells like the IFR-26650. These cells generally operate at a nominal voltage of 3.2 to 3.3 volts, with a maximum recommended charging voltage of 3.5 to 3.6 volts. Recognized for their robustness, these batteries provide reliable energy even under stringent conditions.
The newer LiFePO4 batteries in the Group 65 range are increasingly adopting prismatic or flat cells to boost their capacity and the efficiency of their charge/discharge cycles. However, these lithium-ion batteries are less frequently used for applications that need starting power or dual-purpose solutions since LiFePO4 is better suited for high-capacity, deep-cycle demands. This makes them particularly beneficial for long-duration energy delivery required in renewable energy setups or backup power systems. Automotive, marine, and industrial sectors that utilize lithium-ion batteries generally equip them with a sophisticated Battery Management System (BMS). This system diligently monitors crucial battery parameters like voltage, current, and temperature. It also actively intervenes to disconnect the battery from the circuit to prevent risks like overcharging, deep discharging, and overheating, thereby safeguarding the battery's operational integrity and prolonging its service life.

Figure 9: BCI Group 78 Battery
BCI Group 78 batteries are mid-sized lead-acid units that predominantly use Sealed Lead Acid (SLA) technology with an Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) design. This construction is highly regarded for its durability and maintenance-free operation, making it ideal for various automotive applications. AGM technology is particularly beneficial because it encases the battery's electrolyte within glass mats, effectively preventing any leakage and enhancing both charging and discharging efficiency. Although AGM batteries are standard for Group 78, alternatives like gel, wet/flooded, and Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries are available but less prevalent. LiFePO4, known for its stability and extended lifecycle, is typically not chosen for Group 78 applications due to the specific power and design requirements of vehicles that usually employ these batteries.
Group 78 batteries measure about 10.25 inches long, 7.0625 inches wide, and 7.3125 inches high (26 x 17.9 x 18.6 centimeters), sizes that are similar to those of Groups 34 and 24. This similarity allows for high interchangeability among these batteries in diverse applications.
What needs special attention is that manufacturers sometimes offer batteries labeled as "34/78" which are equipped with both top SAE terminals typical of Group 34 and side 3/8" terminals typical of Group 78. These dual-terminal batteries, often marked with "DT" for Dual Terminal, offer greater versatility across various vehicle makes and models, accommodating different terminal configurations required by different vehicle designs.
When it's time to replace a battery, especially models labeled as 34, 34/78, or 78, it's crucial to double-check the battery box dimensions against the actual dimensions of the new battery. Always take accurate measurements to ensure the new battery fits securely in the compartment and aligns with the specific power needs and operational demands of your application, thus preventing any issues related to improper fit or battery displacement during use.
Maintaining your car's battery ensures it runs efficiently and lasts as long as possible. Here's a simple guide to help you keep your battery in top condition:
Regular Inspections: Start by checking your battery for signs of corrosion, loose connections, and any potential leaks. These issues can lead to poor performance and decreased battery life.
Clean the Terminals: Over time, battery terminals may accumulate deposits that can disrupt the connection. Clean these terminals with a mixture of baking soda and water. Apply the mixture gently with a brush, scrubbing away any corrosion or residue to ensure a solid connection.
Manage Electrical Usage: When the engine is off, minimize the use of electrical accessories like the radio, lights, or air conditioning. Excessive use without the engine running can drain the battery faster than usual.
Drive Regularly: Battery charge is maintained through regular use of the vehicle. Try to drive your car at least once a week for a sufficient distance to keep the battery properly charged and prevent the battery from losing charge over time.
Protect from Extreme Temperatures: Batteries are sensitive to temperature extremes. During hot weather, try to park in the shade to prevent overheating. In cold weather, consider using an insulation blanket to keep the battery warm and efficient.
Check the Charging System: Occasionally test your car’s charging system to catch any issues early. This can prevent battery-related problems and ensure the system is charging the battery as it should.
Keep an eye on other vehicle components, such as belts and alternators, that can affect battery life. Maintaining these parts can help keep the whole vehicle running smoothly and extend the life of your battery.
Whether you're replacing an old battery or choosing one for a new vehicle, the BCI Battery Pack Size Chart is an invaluable resource that simplifies this crucial decision. By consulting the chart, vehicle owners can avoid the pitfalls of battery mismatch, which can lead to power failures and potential damage to the vehicle’s electrical system. Moreover, regular checks and maintenance, such as ensuring terminals are clean and connections are tight, can extend the life of the battery. Ultimately, understanding and using the BCI Battery Pack Size Chart empowers car owners to make choices that enhance their vehicle's performance and longevity, ensuring safe and efficient operation across various driving conditions.
|
BCI Group Size
|
L x W x H (mm)
|
L x W x H (inches)
|
|
21
|
208 x 173 x 222
|
8 3/16 x 6 13/16 x 8 3/4
|
|
21R
|
208 x 173 x 222
|
8 3/16 x 6 13/16 x 8 3/4
|
|
22F
|
241 x 175 x 211
|
9 1/2 x 6 7/8 x 8 5/16
|
|
22HF
|
241 x 175 x 229
|
9 1/2 x 6 7/8 x 9
|
|
Group 22NF Batteries
|
240 x 140 x 227
|
9 7/16 x 5 1/2 x 8 15/16
|
|
22R
|
229 x 175 x 211
|
9 x 6 7/8 x 8 5/16
|
|
Group 24 Batteries
|
260 x 173 x 225
|
10 1/4 x 6 13/16 x 8 7/8
|
|
24F
|
273 x 173 x 229
|
10 3/4 x 6 13/16 x 9
|
|
24H
|
260 x 173 x 238
|
10 1/4 x 6 13/16 x 9 3/8
|
|
24R
|
260 x 173 x 229
|
10 1/4 x 6 13/16 x 9
|
|
24T
|
260 x 173 x 248
|
10 1/4 x 6 13/16 x 9 3/4
|
|
25
|
230 x 175 x 225
|
9 1/16 x 6 7/8 x 8 7/8
|
|
Group 26 Battery
|
208 x 173 x 197
|
8 3/16 x 6 13/16 x 7 3/4
|
|
Group 26R Battery
|
208 x 173 x 197
|
8 3/16 x 6 13/16 x 7 3/4
|
|
Group 27 Battery
|
306 x 173 x 225
|
12 1/16 x 6 13/16 x 8 7/8
|
|
27F
|
318 x 173 x 227
|
12 1/2 x 6 13/16 x 8 15/16
|
|
27H
|
298 x 173 x 235
|
11 3/4 x 6 13/16 x 9 1/4
|
|
29NF
|
330 x 140 x 227
|
13 x 5 1/2 x 8 15/16
|
|
33
|
338 x 173 x 238
|
13 5/16 x 6 13/16 x 9 3/8
|
|
Group 34 Battery
|
260 x 173 x 200
|
10 1/4 x 6 13/16 x 7 7/8
|
|
Group 34R Battery
|
260 x 173 x 200
|
10 1/4 x 6 13/16 x 7 7/8
|
|
Group 35 Battery
|
230 x 175 x 225
|
9 1/16 x 6 7/8 x 8 7/8
|
|
36R
|
263 x 183 x 206
|
10 3/8 x 7 3/16 x 8 1/8
|
|
40R
|
278 x 175 x 175
|
11 x 6 15/16 x 6 15/16
|
|
41
|
293 x 175 x 175
|
11 9/16 x 6 15/16 x 6 15/16
|
|
42
|
242 x 175 x 175
|
9 9/16 x 6 15/16 x 6 15/16
|
|
43
|
334 x 175 x 205
|
13 1/8 x 6 7/8 x 8 1/16
|
|
45
|
240 x 140 x 227
|
9 7/16 x 5 1/2 x 8 15/16
|
|
46
|
273 x 173 x 229
|
10 3/4 x 6 13/16 x 9
|
|
Group 47 Batteries
|
242 x 175 x 190
|
9 9/16 x 6 7/8 x 7 1/2
|
|
Group 48 Batteries
|
278 x 175 x 190
|
11 x 6 7/8 x 7 1/2
|
|
Group 49 Batteries
|
354 x 175 x 190
|
13 15/16 x 6 7/8 x 7 1/2
|
|
50
|
343 x 127 x 254
|
13 1/2 x 5 x 10
|
|
Group 51 Batteries
|
238 x 129 x 223
|
9 3/8 x 5 1/16 x 8 3/4
|
|
Group 51R Batteries
|
238 x 129 x 223
|
9 3/8 x 5 1/16 x 8 3/4
|
|
52
|
186 x 147 x 210
|
7 5/16 x 5 13/16 x 8 1/4
|
|
53
|
330 x 119 x 210
|
13 x 4 11/16 x 8 1/4
|
|
54
|
186 x 154 x 212
|
7 5/16 x 6 1/16 x 8 3/8
|
|
55
|
218 x 154 x 212
|
8 9/16 x 6 1/16 x 8 3/8
|
|
56
|
254 x 154 x 212
|
10 x 6 1/16 x 8 3/8
|
|
57
|
205 x 183 x 177
|
8 1/16 x 7 3/16 x 6 15/16
|
|
Group 58 Batteries
|
255 x 183 x 177
|
10 1/16 x 7 3/16 x 6 15/16
|
|
Group 58R Batteries
|
255 x 183 x 177
|
10 1/16 x 7 3/16 x 6 15/16
|
|
Group 86 Batteries
|
230 x 173 x 203
|
9 1/16 x 6 13/16 x 8
|
|
90
|
243 x 175 x 175
|
9 9/16 x 6 7/8 x 6 7/8
|
|
91
|
280 x 175 x 175
|
11 x 6 7/8 x 6 7/8
|
|
92
|
316 x 175 x 175
|
12 7/16 x 6 7/8 x 6 7/8
|
|
93
|
354 x 175 x 175
|
13 15/16 x 6 7/8 x6 7/8
|
|
Group 94R Batteries
|
315 x 175 x 190
|
12 7/16 x 6 7/8 x 7 1/2
|
|
Group 95R Batteries
|
394 x 175 x 190
|
15 9/16 x 6 7/8 x 7 1/2
|
|
Group 96R Batteries
|
242 x 175 x 175
|
9 1/2 x 6 7/8 x 6 7/8
|
|
97R
|
252 x 175 x 190
|
9 15/16 x 6 7/8 x 7 1/2
|
|
98R
|
283 x 175 x 190
|
11 1/8 x 6 7/8 x 7 1/2
|
|
99
|
207 x 175 x 175
|
8 1/8 x 6 7/8 x 6 7/8
|
|
99R
|
210 x 175 x 175
|
8 1/4 x 6 7/8 x 6 7/8
|
|
100
|
260 x 179 x 188
|
10 1/4 x 7 1/16 x 7 3/8
|
|
101
|
260 x 179 x 170
|
10 1/4 x 7 1/16 x 6 11/16
|
|
121R
|
208 x 177 x 215
|
8 1/4 x 7 x 8 1/2
|
|
124
|
265 x 175 x 214
|
10 7/16 x 6 7/8 x 8 7/16
|
|
124R
|
262 x 177 x 218
|
10 3/8 x 7 x 8 5/8
|
|
151R
|
188 x 125 x 225
|
7 7/16 x 4 15/16 x 8 7/8
|
|
59
|
255 x 193 x 196
|
10 1/16 x 7 5/8 x 7 3/4
|
|
60
|
332 x 160 x 225
|
13 1/16 x 6 5/16 x 8 7/8
|
|
61
|
192 x 162 x 225
|
7 9/16 x 6 3/8 x 8 7/8
|
|
62
|
225 x 162 x 225
|
8 7/8 x 6 3/8 x 8 7/8
|
|
63
|
258 x 162 x 225
|
10 3/16 x 6 3/8 x 8 7/8
|
|
64
|
296 x 162 x 225
|
11 5/8 x 6 3/8 x 8 7/8
|
|
Group 65 Batteries
|
306 x 192 x 192
|
12 1/16 x 7 9/16 x 7 9/16
|
|
66
|
306 x 192 x 194
|
12 1/16 x 7 9/16 x 7 11/16
|
|
67R
|
231 x 175 x 176
|
9 1/8 x 6 7/8 x 6 15/16
|
|
70
|
208 x 179 x 186
|
8 3/16 x 7 1/16 x 7 5/16
|
|
71
|
208 x 179 x 216
|
8 3/16 x 7 1/16 x 8 1/2
|
|
72
|
230 x 179 x 210
|
9 1/16 x 7 1/16 x 8 1/4
|
|
73
|
230 x 179 x 216
|
9 1/16 x 7 1/16 x 8 1/2
|
|
74
|
260 x 184 x 222
|
10 1/4 x 7 1/4 x 8 3/4
|
|
Group 75 Batteries
|
230 x 179 x 186
|
9 1/16 x 7 1/16 x 7 5/16
|
|
76
|
334 x 179 x 216
|
13 1/8 x 7 1/16 x 8 1/2
|
|
77
|
306 x 184 x 222
|
12 1/16 x 7 1/4 x 8 3/4
|
|
Group 78 Batteries
|
260 x 179 x 186
|
10 1/4 x 7 1/16 x 7 5/16
|
|
79
|
307 x 179 x 188
|
12 1/16 x 7 1/16 x 7 3/8
|
|
Group 85 Batteries
|
230 x 173 x 203
|
9 1/16 x 6 13/16 x 8
|
|
Passenger Car and Light
Commercial 6V Batteries (3 Cells)
|
|
1
|
232 x 181 x 238
|
9 1/8 x 7 1/8 x 9 3/8
|
|
2
|
264 x 181 x 238
|
10 3/8 x 7 1/8 x 9 3/8
|
|
2E
|
492 x 105 x 232
|
19 3/8 x 4 1/8 x 9 1/8
|
|
2N
|
254 x 141 x 227
|
10 x 5 9/16 x 8 15/16
|
|
17HF
|
187 x 175 x 229
|
7 3/8 x 6 7/8 x 9
|
|
19L
|
216 x 178 x 191
|
8 1/2 x 7 x 7 1/2
|
|
Heavy Duty Commercial and
Special Tractor 12V Batteries (6 Cells)
|
|
3EE
|
491 x 111 x 225
|
19 5/16 x 4 3/8 x 8 7/8
|
|
3ET
|
491 x 111 x 249
|
19 5/16 x 4 3/8 x 9 13/16
|
|
Group 4D Batteries
|
527 x 222 x 250
|
20 3/4 x 8 3/4 x 9 7/8
|
|
4DLT
|
508 x 208 x 202
|
20 x 8 3/16 x 7 15/16
|
|
Group 6D Batteries
|
527 x 254 x 260
|
20 3/4 x 10 x 10 1/4
|
|
Group 8D Batteries
|
527 x 283 x 250
|
20 3/4 x 11 1/8 x 9 7/8
|
|
12T
|
179 x 177 x 202
|
7 1/16 x 6 15/16 x 7 15/16
|
|
28
|
261 x 173 x 240
|
10 1/4 x 6 13/16 x 9 7/16
|
|
29H
|
334 x 171 x 232
|
13 1/8 x 6 3/4 x 9 1/8
|
|
30H
|
343 x 173 x 235
|
13 1/2 x 6 13/16 x 9 1/4
|
|
Group 31 Batteries
|
330 x 173 x 240
|
13 x 6 13/16 x 9 7/16
|
|
Electric Vehicle 6V
Batteries (3 Cells)
|
|
Group GC2 Batteries
|
264 x 183 x 277
|
10 3/8 x 7 3/16 x 10 7/8
|
|
Group GC2H Batteries
|
264 x 183 x 295
|
10 3/8 x 7 3/16 x 11 5/8
|
|
Electric Vehicle 8V Batteries (4 Cells)
|
|
Group GC8 Batteries
|
264 x 183 x 277
|
10 3/8 x 7 3/16 x 10
7/8
|
|
Group GC8H Batteries
|
264 x 183 x 295
|
10 3/8 x 7 3/16 x 11
5/8
|
|
Electric Vehicle 12V Batteries (6 Cells)
|
|
Group GC12 Batteries
|
327 x 183 x 277
|
12 7/8 x 7 3/16 x 10
7/8
|
|
Commercial/Marine 8V Batteries (4 Cells)
|
|
981
|
527 x 191 x 273
|
20 3/4 x 7 1/2 x 10
3/4
|
|
982
|
546 x 191 x 267
|
21 1/2 x 7 1/2 x 10
1/2
|
|
983
|
622 x 191 x 267
|
24 1/2 x 7 1/2 x 10
1/2
|
|
984
|
699 x 191 x 267
|
27 1/2 x 7 1/2 x 10
1/2
|
|
985
|
683 x 216 x 273
|
26 7/8 x 8 1/2 x 11
3/4
|
|
General Purpose 12V Batteries (6 Cells)
|
|
Group U1 Batteries
|
197 x 132 x 186
|
7 3/4 x 5 3/16 x 7
5/16
|
|
Group U1R Batteries
|
197 x 132 x 186
|
7 3/4 x 5 3/16 x 7
5/16
|
|
U2
|
160 x 132 x 181
|
6 5/16 x 5 3/16 x 7
1/8
|
|
Ordnance 12V Batteries (6 Cells)
|
|
2H
|
260 x 135 x 227
|
10 1/4 x 5 5/16 x 8
15/16
|
|
6T
|
286 x 267 x 230
|
11 1/4 x 10 1/2 x 9
1/16
|
|
Ordnance 24V Batteries (12 Cells)
|
|
4H
|
273 x 262 x 229
|
10 3/4 x 10 5/16 x 9
|
|
Floor Scrubber 6V Commercial Batteries (3 Cells)
|
|
901
|
298 x 181 x 302
|
11 3/4 x 7 1/8 x 11
7/8
|
|
902
|
302 x 181 x 371
|
12 x 7 1/8 x 14 5/8
|
|
903
|
302 x 181 x 432
|
12 x 7 1/8 x 17
|
|
Floor Scrubber 12V Commercial Batteries (6 Cells)
|
|
920
|
356 x 171 x 311
|
14 x 6 3/4 x 12 1/2
|
|
921
|
397 x 181 x 378
|
15 3/4 x 7 1/8 x 14 7/8
|
Chart 2: Popular Battery Group Size Chart
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
1. What type of battery do I need for my car?
The type of battery you need for your car depends on several factors including the vehicle’s make, model, engine size, and the electrical demands of the vehicle. Generally, most cars use a standard lead-acid battery or more advanced types such as Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) or even Lithium-ion for newer models.
2. Are AGM batteries better?
AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries have several advantages over traditional lead-acid batteries. They are designed to better handle repeated charging and discharging cycles and are more resistant to vibration, making them ideal for vehicles with start-stop technology and high electronic demand.
3. What is the disadvantage of AGM batteries?
While AGM batteries offer numerous advantages, they do come with some disadvantages. The primary drawback is cost; AGM batteries are significantly more expensive than traditional flooded lead-acid batteries. They also require a specific type of charger and careful charging to avoid overcharging. Lastly, if they are deeply discharged (below 50% capacity), they may have a shorter lifespan compared to when they are regularly topped up.
4. How many volts is a car battery?
A standard car battery is a 12-volt battery.
5. What does BCI Group 24 mean?
BCI Group 24 refers to a classification standard set by the Battery Council International, which categorizes batteries not only based on their physical dimensions but also by their terminal placement and type.
Share: