Comprehensive Guide to Wrist Watch Battery Replacement
In the intricate world of wristwatches, the choice of battery is not just a matter of power but of precision, longevity, and reliability. As watches evolve from traditional mechanical to high-tech digital models, the demand for batteries that can deliver consistent, long-lasting power without frequent replacements has significantly increased. This article explores the spectrum of battery technologies used in wristwatches, focusing on the characteristics and advantages of various types such as silver-oxide, alkaline, lithium, and newer innovations like Cobalt Titanium Lithium (CTL) and Lithium Titanium (MT) batteries. Each battery type is assessed for its voltage stability, energy density, environmental impact, and suitability for different watch designs and functionalities.
Catalog
Figure 1: Batteries for Wristwatches
Exploring Silver-Oxide Vs. Alkaline Button and Coin Cell Batteries
In the watch industry, batteries perform consistently. Long-lasting and reliable batteries are noteworthy for manufacturers and users alike. Non-rechargeable batteries for wristwatches primarily include button and coin cell types, with alkaline and silver oxide being the most common due to their availability and cost-effectiveness.
Alkaline batteries start with a voltage of 1.5V, which gradually decreases over their lifespan. Their declining voltage makes them less suitable for devices needing stable power. Silver-oxide batteries provide a steady output of 1.55V. This stable voltage is used for wristwatches, ensuring accurate timekeeping. Due to their consistent voltage, they are preferred over alkaline batteries in the watchmaking industry.
Best Battery for Your Wristwatch
Choosing the right battery for a wristwatch is chief for its performance and longevity. Various brands stand out for their reliability and consistent performance, offering distinct benefits.

Figure 2: Renata Batteries
Renata, known for its Swiss manufacturing, is highly regarded in the luxury watch community. These batteries provide a stable voltage output, ensuring precise timekeeping.

Figure 3: Energizer Batteries
Energizer is a well-known name in the battery industry, offering solutions perfect for high-drain devices like wristwatches. Their batteries prevent leakage and maintain a consistent charge, making them reliable for daily use.

Figure 4: Panasonic Batteries
Panasonic batteries are noted for their advanced technology and eco-friendly design. They are ideal for consumers seeking high performance without compromising environmental responsibility.

Figure 5: Varta Batteries
Varta, known for its German engineering, offers powerful and reliable batteries suitable for a wide range of watch types, from modern digital to classic analog styles.

Figure 6: Sony Batteries
Sony batteries are praised for their excellent energy retention and operational efficiency. They are the best choice for watch repair experts and enthusiasts, providing dependable performance for complex watch mechanisms.
Different Types of Batteries Used in Watches

Figure 7: Silver Oxide Batteries
Silver oxide batteries are preferred for analog watches due to their long lifespan and stable voltage output. They provide a steady discharge rate, ensuring consistent timekeeping.

Figure 8: Lithium Batteries
Lithium batteries are favored for digital watches that require higher voltage for functions like backlights and alarms. They offer high energy density and are lightweight, making them suitable for modern digital watches' intricate electronics.

Figure 9: Mercury Batteries
Though mostly phased out due to environmental concerns, mercury batteries are sometimes found in older or vintage watches. They were known for stable voltage and long shelf life but posed significant environmental hazards.

Figure 10: Solar-Powered Batteries
Solar-powered batteries convert light into energy, reducing the need for frequent replacements and supporting sustainable usage. These are ideal for low-maintenance, eco-friendly timepieces, as they continuously recharge under light exposure.

Figure 11: SR920SW Watch Battery
SR920SW Watch Battery: Performance and Durability
The SR920SW watch battery is known for its ideal balance between small size and strong performance. Measuring 9.5 mm in diameter and 2.1 mm in height, it delivers a steady nominal voltage of 1.55 volts. With a capacity ranging from 35 to 55 mAh, it meets various operational needs, from steady low currents in analog watches to higher pulse currents in digital displays.
The SR920SW outperforms its alkaline counterpart, the LR920, in both capacity and cutoff voltage. This results in longer intervals between battery replacements, making it more cost-effective and convenient for users. Recognizing the SR920SW's advantages, Energizer offers the 370/371 variant to cater to different discharge requirements, showcasing the battery's versatility.
The SR920SW's enhanced capacity and stable voltage output have made it a preferred choice in the watch industry. Its reliability and consistent performance ensure long-term accuracy with minimal maintenance, which makes it particularly popular among high-quality watches.
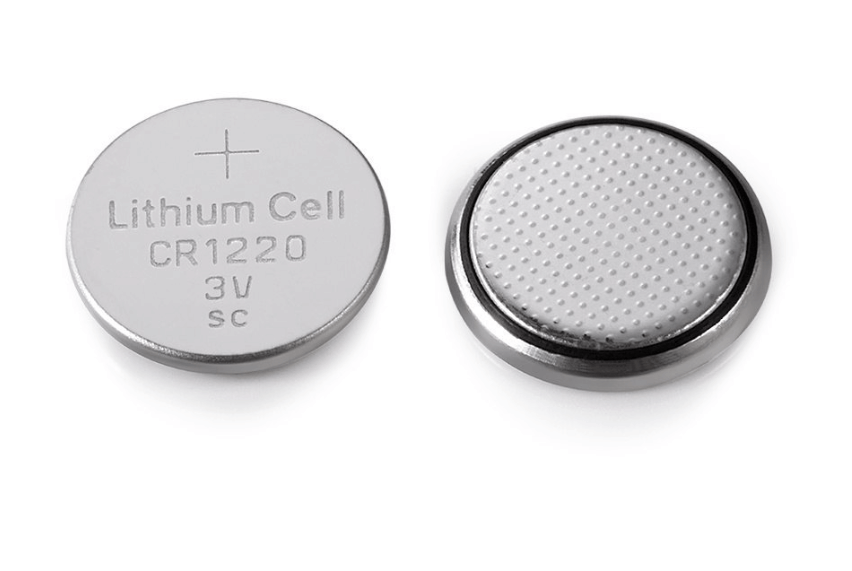
Figure 12: Lithium Button/Coin Cell Batteries
The Role of Lithium Button and Coin Cell Batteries in Watches
Lithium button/coin cell batteries, known for their 3V output, are useful in high-performance battery technology. A popular model, the CR2032, uses manganese-dioxide chemistry to achieve a capacity of about 225 mAh. This makes it ideal for various applications, including watches and medical devices, where consistent operation in different temperatures is dynamic.
For extreme environments, the BR2032 variant outputs 2.8V. Although slightly lower in voltage, it excels in harsh conditions, making it suitable for outdoor or specialized equipment. On the rechargeable front, the LiR2032 offers the benefit of recharging. It provides fewer total cycles than primary cells but is beneficial for applications where frequent battery replacements are inconvenient.

Figure 13: CR1216 Watch Battery
Inside the CR1216 Watch Battery
The CR1216 battery is designed for watches and small electronic devices, offering a capacity of about 25 mAh and a standard output of 3.0 volts. It is ideal for devices that need reliable, long-term power without high energy demands.
For applications requiring more consistent performance under various load conditions, the BR1216 variant provides enhanced voltage stability. However, it has a slightly lower discharge rate, making it less suitable for high-power devices. Although less common, the rechargeable LiR1216 offers the benefit of multiple recharge cycles. This is useful for devices that can handle occasional higher voltages.

Figure 14: CR2016 Watch Battery
CR2016 Watch Batteries: Efficiency and Longevity
The CR2016 lithium battery is used for both analog and digital watches. It provides a stable nominal voltage of 3.0V and a capacity of about 90 mAh. This makes it suitable for handling various watch features, such as alarms and backlighting, which require a stable power supply.
Handles varying power demands effectively, offering a maximum pulse current capacity for features like alarms and backlights. For more demanding environments, the BR2016 is preferable. It has a lower discharge rate and performs well across a wide range of temperatures. The rechargeable LiR2016 can deliver higher voltage output, which is beneficial for advanced technological applications. However, it may not be suitable for conventional watch designs due to its different energy requirements.

Figure 15: Cobalt Titanium Lithium (CTL) Watch Batteries
The Impact of Cobalt Titanium Lithium (CTL) Watch Batteries
Cobalt Titanium Lithium (CTL) batteries are designed for watches with rechargeable systems, such as those powered by solar or kinetic energy. These batteries operate at a lower voltage of 2.3 volts, making them basic for watches with integrated recharging capabilities.
These models are ideal for continuous low-drain operations, perfectly suited for watches that use kinetic or solar energy. Their design minimizes the need for frequent battery replacements, enhancing the watch’s operational lifespan and user satisfaction.
CTL batteries are optimized for longevity and stability. This makes them particularly suitable for modern, eco-friendly watches that use renewable energy sources. They provide reliable power while reducing environmental impact, aligning with the needs of contemporary, sustainability-focused timepieces.

Figure 16: Lithium Titanium (MT) Watch Batteries
Transfiguring Watch Technology with Lithium Titanium (MT) Batteries
Lithium Titanium (MT) batteries are designed to offer a perfect balance between capacity and voltage, making them ideal for devices that need reliable performance at a nominal voltage of 1.5 volts. These batteries prioritize durability and long battery life over peak energy output.
These models are crafted for niche applications requiring consistent power across various discharge scenarios. They provide steady performance, suitable for devices needing a lower voltage but higher capacity.
MT batteries are distinguished by their ability to deliver stable and long-lasting power. This makes them particularly suitable for environments where stability and longevity are insistent, setting them apart from conventional battery types.
Watch Battery Vs. Capacitor: The Differences
Grasping the differences between watch batteries and capacitors is noteworthy for optimal energy storage and power management in mechanical, solar, and kinetic watches.
Store energy chemically, providing sustained power over long periods. Ideal for extended use without frequent recharging. Store energy electrostatically, allowing for rapid charging but offering lower energy densities. They recharge quickly but may not sustain long-term energy needs as effectively.
The choice between a battery and a capacitor significantly affects a watch’s performance and maintenance. Better for devices that need consistent, long-lasting power. Suited for watches requiring quick recharge cycles, but not ideal for prolonged energy supply.
When to Repair or Replace Your Watch Battery?
Identifying when a watch battery needs repair or replacement is deciding to maintain the timepiece's accuracy and functionality.
• Complete Watch Cessation
If your watch stops working entirely, the battery is likely depleted. However, check for mechanical issues or environmental damage, such as moisture, which can also cause the watch to stop.
• Erratic Second-Hand Movement
If the second-hand skips or jumps, the battery's voltage is likely unstable and decreasing. This irregular movement affects the watch's accuracy. Replacing the battery promptly can prevent further timekeeping issues.
• Consistently Losing Time
A watch that consistently loses time indicates a battery nearing the end of its life. This pattern shows the battery is struggling to maintain the needed power output for normal operations.
Extending Your Watch Battery's Life
To extend your watch battery's life and maintain its accuracy, follow these practical steps:
Regulate Temperature Exposure: High temperatures can overwork the battery, while extreme cold can reduce its efficiency. Keep your watch in a temperature-controlled environment to prevent quicker battery depletion.
Store in Moderately Lit Areas: For quartz watches, store them in a moderately lit area. Extended darkness can drain the battery faster since it powers the timekeeping circuitry continuously. Light exposure helps maintain battery life, especially in solar-powered watches.
Protect from Water Exposure: Water can corrode internal components, straining the battery as it works harder to function. Ensure your watch's seals are intact, especially after battery replacement or any case opening.
Avoid Overwinding Mechanical Watches: For mechanical watches with a battery backup, avoid overwinding. This stresses mechanical parts, causing premature wear and potentially affecting the battery system indirectly.
Conclusion
The meticulous selection of the appropriate battery for a wristwatch transcends basic considerations of size and capacity; it is a decision that impacts the watch's operational efficiency, environmental footprint, and user convenience. From the stable voltage supply of silver-oxide batteries to the high energy density of lithium variants and the eco-friendly attributes of CTL batteries, the choice embodies a trade-off among various desirable qualities. As highlighted through different models and brands like Renata, Energizer, and Sony, the optimal battery must align with the specific needs of the watch's mechanism and the user's lifestyle.
In addition, considering the nuanced differences between battery and capacitor applications in watches helps refine energy management strategies, ensuring that the watch not only functions accurately but also aligns with broader sustainability goals. This article underscores the grave nature of informed battery selection and offers practical guidance on maintenance and replacement, which are the main for maximizing the lifespan and functionality of wristwatches in an era where precision and durability are dominant.
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
1. How do I know what size battery for my watch?
To find the correct battery size for your watch, remove the back cover of the watch and locate the existing battery. The battery size is usually printed directly on the battery. It will be a combination of letters and numbers, such as "CR2032" or "SR626SW."
2. How do I choose a wristwatch battery?
When selecting a watch battery, consider the type (silver oxide or lithium), voltage, and size that match your watch’s specifications. Silver oxide batteries are common for analog watches and provide steady voltage, while lithium batteries, generally for digital watches, offer longer life.
3. How do I find my exact battery?
The exact battery for your watch can be found by noting the battery code on the current battery and purchasing the same model. If the watch does not have a battery installed, consult the user manual or look up the watch model online to find the compatible battery type.
4. How do I find my battery model?
The battery model is usually identified by the code printed on the battery. This code indicates the battery's chemistry, size, and shape. If you cannot find a code, measure the battery’s diameter and height, and use these dimensions to find a matching battery.
5. What is a battery code?
A battery code is a standardized label printed on batteries to indicate their specific type and size. For example, "CR2032" means it is a lithium battery, 20 mm in diameter, and 3.2 mm thick. Codes help ensure you purchase the right battery for your device.
About us
ALLELCO LIMITED
Read more
Quick inquiry
Please send an inquiry, we will respond immediately.

Pulse Rate Monitoring Sensor
on July 29th
Exploring Piezoelectric Materials: Types, Properties, and Technological Impact
on July 26th
Popular Posts
-
What is GND in the circuit?
on January 1th 2814
-

RJ-45 Connector Guide: RJ-45 Connector Color Codes, Wiring Schemes, R-J45 Applications, RJ-45 Datasheets
on January 1th 2398
-

Fiber Connector Types: SC Vs LC And LC Vs MTP
on January 1th 2008
-
Understanding Power Supply Voltages in Electronics VCC, VDD, VEE, VSS, and GND
on November 5th 1751
-

Comparison Between DB9 and RS232
on January 1th 1723
-

What Is An LR44 Battery?
Electricity, that ubiquitous force, quietly permeates every aspect of our daily lives, from trivial gadgets to life-threatening medical equipment, it plays a silent role. However, truly grasping this energy, especially how to store and efficiently output it, is no easy task. It is against this background that this article will focus on a type of coin cell battery that may seem insignificant on the...on January 1th 1673
-
Understanding the Fundamentals:Inductance Resistance, andCapacitance
In the intricate dance of electrical engineering, a trio of fundamental elements takes center stage: inductance, resistance, and capacitance. Each bears unique traits that dictate the dynamic rhythms of electronic circuits. Here, we embark on a journey to decipher the complexities of these components, to uncover their distinct roles and practical uses within the vast electrical orchestra. Inductan...on January 1th 1611
-

CR2430 Battery Comprehensive Guide: Specifications, Applications and Comparison to CR2032 Batteries
What is CR2430 battery ?Benefits of CR2430 BatteriesNormCR2430 Battery ApplicationsCR2430 EquivalentCR2430 VS CR2032Battery CR2430 SizeWhat to look for when buying the CR2430 and equivalentsData Sheet PDFFrequently Asked Questions Batteries are the heart of small electronic devices. Among the many types available, coin cells play a crucial role, commonly found in calculators, remote controls, and ...on January 1th 1483
-

CR2450 vs CR2032: Can The Battery Be Used Instead?
Lithium manganese batteries do have some similarities with other lithium batteries. High energy density and long service life are the characteristics they have in common. This kind of battery has won the trust and favor of many consumers because of its unique safety. Expensive tech gadgets? Small appliances in our homes? Look around and you'll see them everywhere. Among these many lithium-manganes...on January 1th 1466
-
What Is RF and Why Do We Use It?
Radio Frequency (RF) technology is a key part of modern wireless communication, enabling data transmission over long distances without physical connections. This article delves into the basics of RF, explaining how electromagnetic radiation (EMR) makes RF communication possible. We will explore the principles of EMR, the creation and control of RF signals, and their wide-ranging uses. The article ...on January 1th 1433