Choosing the Right Motor Driver: The Differences Between L293D and L298N Motor Drivers
In this article we will explore the main differences between the L293D and L298N motor drivers. Both motor drives have their own unique features and applications. Understanding the difference between the two can help us better choose the appropriate motor control product. Let's take a look at the differences between the L293D and L298N motor drivers.
Catalog
What Is L293D?
L293D is a dual H-bridge DC motor driver chip, commonly used to control various DC motors, including stepper motors and DC motors. It was developed by STMicroelectronics. Due to its characteristics of high efficiency, low power consumption and high reliability, it is widely used in smart homes, robots, smart vehicles and other fields.
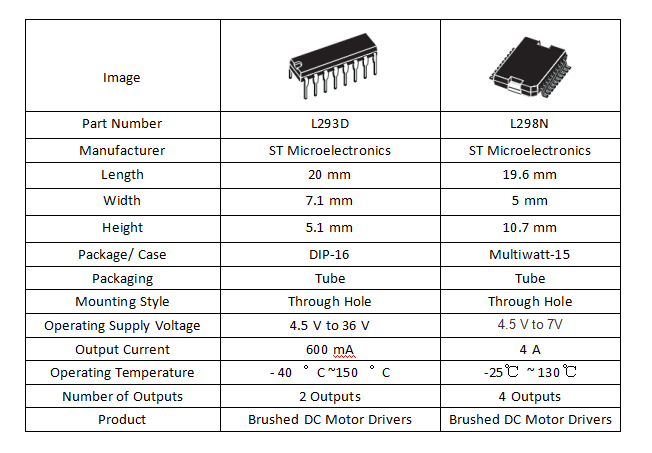
L293D is conveniently packaged in a tube, ensuring easy handling and storage. It boasts a through-hole mounting style, making it compatible with a wide range of applications. With an input voltage requirement of 7V and a versatile operating supply voltage range spanning from 4.5V to 36V, it offers flexibility and adaptability in various scenarios. Moreover, its robust design allows it to function reliably in extreme temperatures, ranging from -40°C to 150°C. With an impressively low operating supply current of just 2 mA, it remains energy-efficient while delivering a substantial output current of 600 mA, catering to a range of power needs. Additionally, it features the convenience of two outputs, enhancing its utility for diverse projects and systems.
Replacement and Equivalent
• L293DD
• L293E
What Is L298N?
L298N is a motor driver chip produced by ST Microelectronics. It can be used to control motor types such as DC motors and stepper motors, and has the advantages of high efficiency and low heat loss. The internal structure of L298N is complex, mainly including logic control part, power output part, temperature compensation circuit and overload protection circuit, etc. Its working principle is to realize functions such as forward and reverse rotation of the motor and PWM speed regulation by inputting different control signals.
Replacement and Equivalent
• L298P
• L293DD
• L6206N
• L6207QTR
• L6225N
• L6227DTR
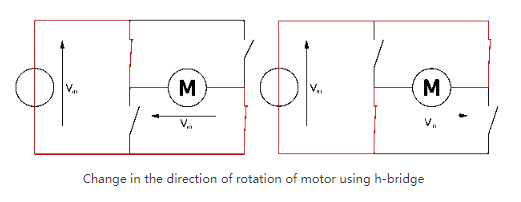
What Is an H-Bridge Configuration?
An H-bridge is an electronic circuit that switches the polarity of a voltage applied to a load. These circuits are commonly used in robotics and other applications to allow DC motors to run forward or backward. It can change the direction of rotation by changing the polarity of the DC motor power supply. In addition to changing the direction of rotation, the H-bridge can also provide additional operating modes such as "brake" and "free run until friction stops".
The H-bridge device is usually used to reverse the polarity of a motor, but it can also be used to "brake" the motor, meaning that the motor suddenly stops when its terminals are connected together. By connecting its terminals, the kinetic energy of the motor is rapidly consumed in the form of current, causing the motor to slow down. Another situation allows the motor to inertia stop because the motor is actually disconnected from the circuit. The schematic diagram of H-bridge is as follows:
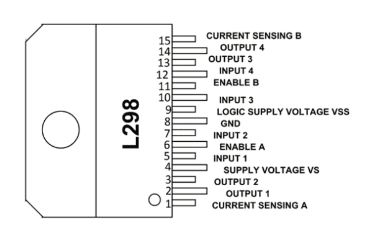
Pin Diagram of L293D and L298N
L293D
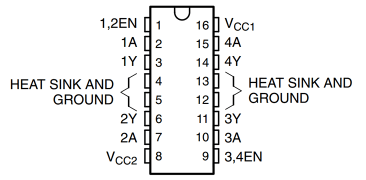
L298N
Specifications of L293D and L298N
Features of L293D and L298N
L293D adopts DIP and SOIC packaging methods, which can better adapt to various application requirements. Moreover, it also has over-temperature protection and over-current protection functions, which can effectively prevent chip damage and greatly improve the stability of the chip. In addition, it has strong driving capability and can control DC motors, stepper motors and other high-current devices. In addition, another feature of L293D is that it can realize the control of various motors such as forward, reverse, braking, etc., and has strong flexibility. Last but not least, it can deliver up to 1.2A. This is very beneficial for large motors and high current equipment, making them perform well in a variety of demanding situations.
L298N consists of two mutually separated H bridge circuits, which can control the direction and speed of two DC motors. This makes it an ideal choice for dual-motor driven applications such as robots, cars and other automatic control systems. In addition, L298N can also support 5V standard logic output. Therefore, L298N can be compatible with a variety of controllers (such as MCU, Arduino, etc.). Furthermore, L298N can also use pulse width modulation (PWM) signals to regulate the speed of the motor, allowing users to adjust the motor speed at will. In general, the L298N usually has easy-to-connect pins for interfacing with other electronic components and motors. It usually has pins for power, ground, motor output, and control input.
The Difference Between L293D and L298N
Package
In terms of packaging, L293D uses dual in-line packaging, while L298N usually uses multi-pin in-line packaging.
Current and Voltage
Each H-bridge of L293D can provide a maximum current of 600mA, and the peak output current can reach 1.2A. Each H-bridge of the L298N can provide a maximum current of 2A, and the power supply voltage range of the power part is 2.5-48v.
Different Chips
The chip of the L293D motor driver module is a stepper motor driver chip, while the chip of the L298N motor driver module is an H-bridge driver integrated circuit chip.
Heating Requirements
The L293D generally does not require much cooling due to its lower current capability. But under high load conditions, it may still require cooling. The L298N has a higher current capability and generally requires more heat dissipation, especially under high load or high voltage conditions.
Control Interface
L293D usually uses logic levels to control the direction and status of the motor, which is relatively simple. The L298N usually requires the use of PWM signals to control the speed of the motor, and logic levels to control the direction.
Different Optocouplers
The L293D motor drive module does not add an optocoupler, which will interfere with the microcontroller and make the system work more unstable. The L298N motor drive module adds an optocoupler for photoelectric isolation, so that the system can work stably and reliably.
Function
L293D is a dual-bridge motor driver chip that can drive two DC motors or one stepper motor at the same time. The L298N is a dual H-bridge motor driver chip, suitable for controlling two DC motors or a stepper motor.
Application Scenarios
The maximum output current of the L293D is 600mA, making it suitable for low-power applications such as motors in toys or educational projects. The maximum output current of L298N is as high as 4A, so it is suitable for high-power applications such as robots and model cars.
Although L293D and L298N have some differences, they can both realize forward and reverse control of DC motors and PWM speed regulation. Therefore, they can be used interchangeably in many application scenarios.
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
1. What Is a L293D?
The L293D is a 16-pin Motor Driver IC which can control a set of two DC motors simultaneously in any direction. The L293D is designed to provide bidirectional drive currents of up to 600 mA (per channel) at voltages from 4.5 V to 36 V (at pin 8!). You can use it to control small dc motors - toy motors.
2. What Does L293D Driver Do?
The L293D is designed to provide bidirectional drive currents of up to 600-mA at voltages from 4.5 V to 36 V. Both devices are designed to drive inductive loads such as relays, solenoids, DC and bipolar stepping motors, as well as other high-current/high-voltage loads in positive-supply applications.
3. How Much Power Does L298N Use?
It makes use of the well-known L298N Dual H-Bridge Motor Driver chip and is potent enough to drive motors at up to 2 Amps per channel at voltages between 5 and 35 volts.
4. How Many Motors Can Be Connected to L298N?
L298N Module can control up to 4 DC motors, or 2 DC motors with directional and speed control.
5. What Is the Difference Between L293D and L298N?
L293D drivers operate between 4.5 and 36 volts, while L298N drivers can operate up to 46 volts. The L293D Motor Driver can draw up to 600mA from both channels, whereas the L298N Motor Driver can draw up to 2A from both channels.
About us
ALLELCO LIMITED
Read more
Quick inquiry
Please send an inquiry, we will respond immediately.
→ Previous

2N2222 and BC547 are both NPN-type general-purpose low-power transistors, which are widely used in circuits such as audio amplifiers and frequency oscillators. In this article, we will compare both in terms of symbol, technical parameters, features, applications, and working principles. Catalog1. Wh...

Overview of 1N4148 1N4148 is a small, high-speed switching diode with rapid switching speed, so it is widely used in circuits with high signal frequency for single-lead isolation, such as computer boards, communications, television circuits and industrial control circuits. It is available in DO35, L...
→ Next

From Audio Amplifiers to Frequency Oscillators: Analyzing 2N2222 and BC547 Transistors
on April 29th

An In-Depth Look at the 1N4148 Diode for Industrial and Communication Uses
on April 29th
Popular Posts
-
What is GND in the circuit?
on January 1th 3270
-

RJ-45 Connector Guide: RJ-45 Connector Color Codes, Wiring Schemes, R-J45 Applications, RJ-45 Datasheets
on January 1th 2815
-
Understanding Power Supply Voltages in Electronics VCC, VDD, VEE, VSS, and GND
on November 20th 2632
-

Fiber Connector Types: SC Vs LC And LC Vs MTP
on January 1th 2265
-

Comparison Between DB9 and RS232
on January 1th 1881
-

What Is An LR44 Battery?
Electricity, that ubiquitous force, quietly permeates every aspect of our daily lives, from trivial gadgets to life-threatening medical equipment, it plays a silent role. However, truly grasping this energy, especially how to store and efficiently output it, is no easy task. It is against this background that this article will focus on a type of coin cell battery that may seem insignificant on the...on January 1th 1846
-
Understanding the Fundamentals:Inductance Resistance, andCapacitance
In the intricate dance of electrical engineering, a trio of fundamental elements takes center stage: inductance, resistance, and capacitance. Each bears unique traits that dictate the dynamic rhythms of electronic circuits. Here, we embark on a journey to decipher the complexities of these components, to uncover their distinct roles and practical uses within the vast electrical orchestra. Inductan...on January 1th 1805
-
What Is RF and Why Do We Use It?
Radio Frequency (RF) technology is a key part of modern wireless communication, enabling data transmission over long distances without physical connections. This article delves into the basics of RF, explaining how electromagnetic radiation (EMR) makes RF communication possible. We will explore the principles of EMR, the creation and control of RF signals, and their wide-ranging uses. The article ...on January 1th 1799
-

CR2430 Battery Comprehensive Guide: Specifications, Applications and Comparison to CR2032 Batteries
What is CR2430 battery ?Benefits of CR2430 BatteriesNormCR2430 Battery ApplicationsCR2430 EquivalentCR2430 VS CR2032Battery CR2430 SizeWhat to look for when buying the CR2430 and equivalentsData Sheet PDFFrequently Asked Questions Batteries are the heart of small electronic devices. Among the many types available, coin cells play a crucial role, commonly found in calculators, remote controls, and ...on January 1th 1796
-
Comprehensive guide to hFE in transistors
Transistors are crucial components in modern electronic devices, enabling signal amplification and control. This article delves into the knowledge surrounding hFE, including how to select a transistor's hFE value, how to find hFE, and the gain of different types of transistors. Through our exploration of hFE, we gain a deeper understanding of how transistors work and their role in electronic circu...on November 20th 1782















































