How Much Do you Know about Car Battery Weight?
Catalog
How Much Does a Car Battery Weigh?
How Do I Know the Weight of My Car Battery?
Types of Car Batteries


Ten Car Battery Pack Recommendations
|
Model |
Battery Type |
Capacity(Ah) |
CCA |
Weight (lbs/kg) |
|
ACDelco M24AGM |
Deep Cycle |
80 |
500 |
43.0 lbs; ~19.5 kg |
|
Battle Born BB1250 |
Deep Cycle |
50 |
60A const. |
22 lbs; 9.96 kg |
|
Battle Born BB1275 |
Deep Cycle |
75 |
100A const. |
27 lbs; 12.23 kg |
|
Exide Edge FP-AGM24DP |
Dual Purpose |
75 |
775 |
50 lbs; ~22.7 kg |
|
Lifeline GPL-24T |
Deep Cycle |
80 |
550 |
56 lbs; 25.5 kg |
|
LiTime 12V 100Ah Mini |
Deep Cycle |
100 |
100A cont. |
19 lbs; 8.6 kg |
|
Mighty Max ML75-12 |
Deep Cycle |
77 |
- |
50.71 lbs; ~22.97 kg |
|
Mighty Max ML75-12 Gel |
Deep Cycle |
75 |
- |
50.55 lbs; 22.9 kg |
|
NorthStar NSB-AGM24F |
Dual Purpose |
76 |
840 |
57 lbs; ~25.8 kg |
|
Power Sonic PS-12750 |
Deep Cycle |
78 |
900A 5s |
50.6 lbs; 22.9 kg |
|
UPG UB12750 |
Deep Cycle |
75 |
- |
49.1 lbs; ~22.3 kg |
|
VMAXTANKS FLP24-1265 |
Deep Cycle |
65 |
65A const. |
15.5 lbs, 7.0 kg |
|
VMAXTANKS MB107-85 |
Deep Cycle |
85 |
- |
55 lbs; ~24.9 kg |
|
VMAXTANKS MR107-85 |
Deep Cycle |
85 |
- |
55 lbs; ~24.9 kg |
|
VMAXTANKS SLR-85 |
Deep Cycle |
85 |
- |
55 lbs; ~24.9 kg |
|
Weize FP12750/TL1275 |
Deep Cycle |
77 |
- |
46 lbs; 20.9 kg |
Chart 1: The Specifications of the Most Popular BCI Group 24 Batteries
|
Model |
Battery Type |
Capacity (Ah) |
CCA |
Weight (lbs/kg) |
|
ACDelco 78AGM |
Starting |
60 |
740 |
37.8 lbs; 17.2 kg |
|
Bosch Group 78 Platinum |
Dual Purpose |
60 |
770 |
43 lbs; 19.5 kg |
|
Delphi BU9078 MaxStart |
Starting |
55 |
775 |
43 lbs; 19.5 kg |
|
Northstar NSB-AGM34/78 |
Dual Purpose |
65 |
880 |
51 lbs; 23.1 kg |
|
Northstar NSB-AGM78 |
Dual Purpose |
65 |
880 |
51 lbs; 23.1 kg |
|
Odyssey 34/78-PC1500DT |
Dual Purpose |
68 |
850 |
49.5 lbs; 22.4 kg |
|
Odyssey 78 PC1500 |
Dual Purpose |
68 |
850 |
49.5 lbs; 22.4 kg |
|
Odyssey 78-790 |
Dual Purpose |
61 |
792 |
47.1 lbs; 21.4 kg |
|
Optima 8004-003 34/78 RedTop |
Starting |
50 |
800 |
38.8 lbs; 17.6 kg |
|
Optima 8014-045 D34/78 YellowTop |
Dual Purpose |
55 |
750 |
43.5 lbs; 19.7 kg |
|
Optima 8078-109 78 RedTop |
Starting |
50 |
800 |
39.5 lbs; 17.9 kg |
Chart 2: The Specifications of the Most Popular BCI Group 34/78 Batteries
|
Model |
Battery Type Battery Chemistry |
Ah RC |
CCA MCA |
Weight (lbs/kg) |
|
Arc-Angel Group 35 |
Starting |
40 |
900 |
16
lbs; 7.3 kg |
|
Bosch S6523B |
Dual
Purpose |
53 |
650 |
40
lbs; 18.1 kg |
|
Delphi BU9035 |
Dual
Purpose |
50 |
680 |
40
lbs; 18.1 kg |
|
DieHard 38275 |
Dual
Purpose |
50 |
650 |
42
lbs; 19.0 kg |
|
NorthStar NSB-AGM35 |
Dual
Purpose |
60 |
740 |
49
lbs; 22.2 kg |
|
Optima 8020-164 35 RedTop |
Starting |
44 |
720 |
31.7 lbs; 14.4 kg |
|
Optima 8040-218 D35 YellowTop |
Dual
Purpose |
48 |
620 |
36.4
lbs; 16.5 kg |
|
Odyssey 35-PC1400T |
Dual
Purpose |
65 |
850 |
50
lbs; 22.7 kg |
|
Odyssey ODP-AGM35 |
Dual
Purpose |
59 |
675 |
45.9
lbs; 20.8 kg |
|
PowerTex PTLG35 |
Dual
Purpose |
48 |
430 |
13.5
lbs; 6.1 kg |
|
XING CELL Group 35 |
Dual
Purpose |
42 |
500 |
13.6
lbs; 6.2 kg |
Chart 3: The Specifications of the Most Popular BCI Group 35 Batteries
|
Model |
Battery Type |
Capacity (Ah) |
CCA |
Weight (lbs/kg) |
|
ACDelco 47AGM Professional |
Starting |
60 |
630 |
39.2 lbs; 17.8 kg |
|
ACDelco 47AGMA Gold |
Starting |
60 |
660 |
39.24 lbs; 17.8 kg |
|
Bosch S6-47 AGM Battery |
Starting |
60 |
600 |
39 lbs; 17.7 kg |
|
Deka 9A47 Intimidator |
Dual Purpose |
60 |
600 |
39 lbs; 17.7 kg |
|
Delphi BU9047 MaxStart |
Starting |
60 |
600 |
38.5 lbs; 17.5 kg |
|
Interstate Group 47/H5 Battery |
Starting |
54 |
650 |
32.9 lbs; 14.9 kg |
|
Interstate Group 47/H5 AGM Battery |
Starting |
60 |
650 |
39.2 lbs; 17.8 kg |
|
Marxon AGM-L60-MX Battery |
Starting |
60 |
660 |
40.97 lbs; 18.6 kg |
|
Optima DH5 YellowTop |
Dual Purpose |
64 |
700 |
44 lbs; 20 kg |
|
UPLUS AGM-L60-UP Battery |
Starting |
60 |
660 |
40 lbs; 18.1 kg |
|
Weize Group 47 Battery |
Dual Purpose |
60 |
680 |
41.6 lbs; 18.9 kg |
Chart 4: The Specifications of the Most Popular BCI Group 47 Batteries
|
Model |
Battery Type |
Capacity (Ah) |
CCA |
Weight (lbs/kg) |
|
ACDelco 48AGM Professional |
Starting |
70 |
760 |
45.5 lbs; 20.6 kg |
|
Deka 9A48 Intimidator |
Dual Purpose |
70 |
760 |
45 lbs; 20.4 kg |
|
Delphi BU9048 MaxStart |
Starting |
70 |
760 |
45.5 lbs; 20.6 kg |
|
Interstate MTX-48/H6 AGM |
Starting |
70 |
760 |
45.4 lbs; 20.6 kg |
|
MARXON Group 48 H6 L3 |
Starting |
70 |
760 |
46.53 lbs; 21.1 kg |
|
NorthStar NSB-AGM48 |
Dual Purpose |
69 |
775 |
48 lbs; 21.8 kg |
|
Odyssey Battery 48-720 Battery |
Dual Purpose |
69 |
723 |
48 lbs; 21.8 kg |
|
Optima Batteries DH6 YellowTop |
Dual Purpose |
72 |
800 |
54 lbs; 24.5 kg |
|
UPLUS Group 48 Battery |
Starting |
70 |
760 |
46.53 lbs; 21.1 kg |
|
Weize Group 48 Battery |
Dual Purpose |
70 |
760 |
47.5 lbs; 21.5 kg |
|
XS Power D4800 |
Dual Purpose |
60 |
- |
47.6 lbs; 21.6 kg |
Chart 5: The Specifications of the Most Popular BCI Group 48 Batteries
|
Model |
Battery Type Cell Type |
Capacity (Ah) RC (min) |
CCA MCA |
Weight (lbs/kg) |
|
ACDelco 49AGM Professional |
Starting |
95 |
900 |
58.6 lbs; 26.6 kg |
|
Bosch S6588B S6 Flat Plate AGM Battery |
Starting |
92 |
850 |
61.9 lbs; 28.1 kg |
|
Deka 9AGM49 AGM Intimidator Battery |
Starting |
92 |
850 |
58.5 lbs; 26.5 kg |
|
Delphi BU9049 MaxStart |
Starting |
92 |
850 |
58 lbs; 26.3 kg |
|
Duracell AGM49 Battery |
Starting |
92 |
850 |
57.8 lbs; 26.2 kg |
|
Exide Edge FP-AGML5/49 Flat Plate AGM |
Dual Purpose |
92 |
850 |
59.8 lbs; 27.1 kg |
|
Full River FT890-49 |
Dual Purpose |
80 |
890 |
61.1 lbs; 27.7 kg |
|
Interstate MTX-49/H8 |
Starting |
95 |
900 |
59 lbs; 26.7 kg |
|
Odyssey 49-950 Performance |
Dual Purpose |
94 |
950 |
62.8 lbs; 28.5 kg |
|
Weize Group 49 Battery |
Dual Purpose |
95 |
900 |
56.43 lbs; 25.56 kg |
|
XS Power D4900 |
Dual Purpose |
80 |
- |
59 lbs; 26.8 kg |
Chart 6: The Specifications of the Most Popular BCI Group 49 Batteries
|
Model |
Battery Type |
Capacity (Ah) |
CCA |
Weight (lbs/kg) |
|
ACDelco ACDB24R |
Dual Purpose |
45 |
325 |
29.11 lbs; 13.2 kg |
|
Deka/East Penn 8AMU1R |
Starting |
- |
320 |
25 lbs; 11.3 kg |
|
Delphi BU9051P MaxStart |
Dual Purpose |
46 |
325 |
29.5 lbs; 13.4 kg |
|
Optima 8071-167 D51 |
Dual Purpose |
38 |
450 |
26 lbs; 11.8 kg |
|
Optima 8073-167 D51R |
Dual Purpose |
38 |
450 |
26 lbs; 11.8 kg |
|
VMAXTANKS SLR60 |
Deep Cycle |
60 |
- |
43 lbs; 19.5 kg |
Chart 7: The Specifications of the Most Popular BCI Group 51&51R Batteries
|
Model |
Battery Type |
Capacity (Ah) |
CCA |
Weight (lbs/kg) |
|
ACDelco 65AGM |
Dual Purpose |
- |
750 |
42.5 lbs; 19.3 kg |
|
ACDelco 65AGMHRC |
Dual Purpose |
70 |
775 |
45.8 lbs; 20.75 kg |
|
ACDelco 65XAGM |
Dual Purpose |
74 |
950 |
58 lbs; 26.3 kg |
|
Bosch S6551B S6 |
Dual Purpose |
70 |
760 |
54.9 lbs; 24.9 kg |
|
Deka 9A65 |
Dual Purpose |
75 |
775 |
46 lbs; 20.85 kg |
|
Delphi BU9065 65 |
Dual Purpose |
75 |
750 |
47.5 lbs; 21.5 kg |
|
Full Throttle FT930-65 |
Dual Purpose |
75 |
930 |
57.5 lbs; 26.1 kg |
|
NORTHSTAR NSB-AGM65 |
Dual Purpose |
69 |
930 |
55 lbs; 24.9 kg |
|
Odyssey 65-760 |
Dual Purpose |
64 |
762 |
49.8 lbs; 22.6 kg |
|
Odyssey 65-PC1750T |
Dual Purpose |
74 |
950 |
54 lbs; 24.5 kg |
|
Renogy RBT100LFP12S-G1 |
Deep Cycle |
100 |
100A max. cont. |
26 lbs; 11.8 kg |
|
XS Power D6500 |
Dual Purpose |
75 |
- |
58.3 lbs; 26.4 kg |
Chart 8: The Specifications of the Most Popular BCI Group 65 Batteries
|
Model |
Battery Type |
Capacity (Ah) |
CCA |
Weight (lbs/kg) |
|
Delphi BU9075DT MaxStart |
Starting |
60 |
680 |
41.0 lbs; 18.6 kg |
|
Odyssey 75-PC1230 |
Dual Purpose |
55 |
760 |
45.5 lbs; 20.6 kg |
|
Odyssey 75/86-PC1230DT |
Dual Purpose |
55 |
760 |
45.5 lbs; 20.6 kg |
|
Odyssey ODP-AGM7586 |
Dual Purpose |
49 |
708 |
43.4 lbs; 19.7 kg |
|
Optima 8022-091 75/25 RedTop |
Starting |
44 |
720 |
33.1 lbs; 15.0 kg |
|
Optima 8042-218 D75/25 YellowTop |
Dual Purpose |
48 |
620 |
37.8 lbs; 17.2 kg |
Chart 9: The Specifications of the Most Popular BCI Group 75 Batteries
Weight of Different Brands of Car Batteries
Bosch

Optima

EverStart

DieHard

Odyssey

AC Delco

How to Find the Best Car Battery Weight?
Pros and Cons of Lightweight Batteries
Advantages of Lightweight Batteries
Disadvantages of Lightweight Batteries
Conclusion
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
1. How long can a car battery last?
2. How heavy is a 12-volt car battery?
3. How much does a 12V car battery weigh in kg?
4. Do larger, heavier batteries always provide more power?
About us
ALLELCO LIMITED
Read more
Quick inquiry
Please send an inquiry, we will respond immediately.

CR2430 VS CR2450 Battery: Size, Battery Characteristics, Applications
on April 29th

AG1 Battery Equivalent Replacements
on April 27th
Popular Posts
-
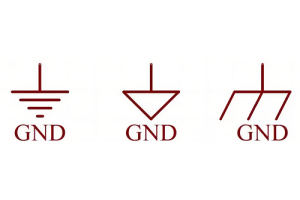
What is GND in the circuit?
on January 1th 2946
-

RJ-45 Connector Guide: RJ-45 Connector Color Codes, Wiring Schemes, R-J45 Applications, RJ-45 Datasheets
on January 1th 2502
-

Fiber Connector Types: SC Vs LC And LC Vs MTP
on January 1th 2091
-
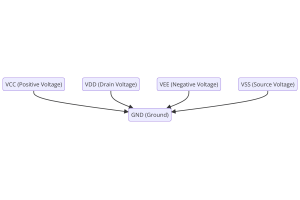
Understanding Power Supply Voltages in Electronics VCC, VDD, VEE, VSS, and GND
on November 9th 1898
-

Comparison Between DB9 and RS232
on January 1th 1765
-

What Is An LR44 Battery?
Electricity, that ubiquitous force, quietly permeates every aspect of our daily lives, from trivial gadgets to life-threatening medical equipment, it plays a silent role. However, truly grasping this energy, especially how to store and efficiently output it, is no easy task. It is against this background that this article will focus on a type of coin cell battery that may seem insignificant on the...on January 1th 1714
-
Understanding the Fundamentals:Inductance Resistance, andCapacitance
In the intricate dance of electrical engineering, a trio of fundamental elements takes center stage: inductance, resistance, and capacitance. Each bears unique traits that dictate the dynamic rhythms of electronic circuits. Here, we embark on a journey to decipher the complexities of these components, to uncover their distinct roles and practical uses within the vast electrical orchestra. Inductan...on January 1th 1662
-

CR2430 Battery Comprehensive Guide: Specifications, Applications and Comparison to CR2032 Batteries
What is CR2430 battery ?Benefits of CR2430 BatteriesNormCR2430 Battery ApplicationsCR2430 EquivalentCR2430 VS CR2032Battery CR2430 SizeWhat to look for when buying the CR2430 and equivalentsData Sheet PDFFrequently Asked Questions Batteries are the heart of small electronic devices. Among the many types available, coin cells play a crucial role, commonly found in calculators, remote controls, and ...on January 1th 1567
-
What Is RF and Why Do We Use It?
Radio Frequency (RF) technology is a key part of modern wireless communication, enabling data transmission over long distances without physical connections. This article delves into the basics of RF, explaining how electromagnetic radiation (EMR) makes RF communication possible. We will explore the principles of EMR, the creation and control of RF signals, and their wide-ranging uses. The article ...on January 1th 1550
-

CR2450 vs CR2032: Can The Battery Be Used Instead?
Lithium manganese batteries do have some similarities with other lithium batteries. High energy density and long service life are the characteristics they have in common. This kind of battery has won the trust and favor of many consumers because of its unique safety. Expensive tech gadgets? Small appliances in our homes? Look around and you'll see them everywhere. Among these many lithium-manganes...on January 1th 1519















































