What is an RF modulator? How it works, advantages and disadvantages, applications
As a key electronic component, RF modulators are widely used in a variety of communication and broadcasting systems. Their main function is to convert baseband audio and video signals into radio frequency (RF) signals. This conversion enables the signals to be captured and displayed by televisions and other receiving devices through various transmission media, such as coaxial cables or radio waves. This article will explore in depth the working principle, application advantages, and wide application of RF modulators in the field of modern electronic communications.Catalog
1. Concept and application of RF modulators
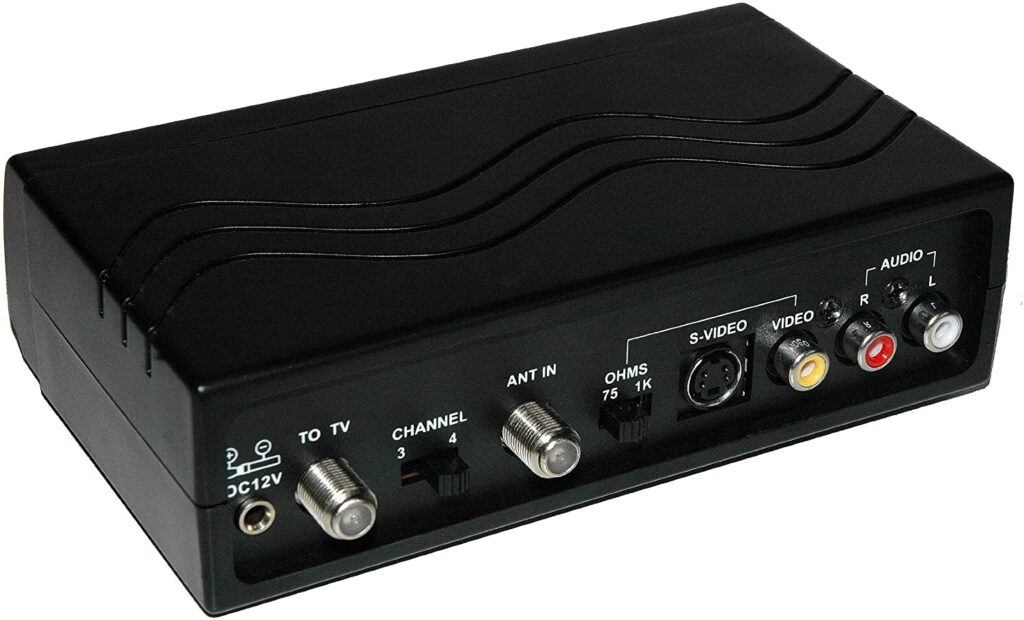

RF modulators convert audio and video signals from their original baseband form into radio frequency (RF) signals. This conversion enables various receiving devices, such as televisions, to receive these signals through coaxial cables or radio waves. For old TV sets lacking modern interfaces, RF modulators provide a solution to display content from contemporary digital devices.
Although digital broadcasting and HDMI have reduced the use of RF modulators in new devices, they remain essential for upgrading old equipment to receive modern signals. For instance, to connect an old TV with only RF input to a modern digital device, an RF modulator is used to convert the digital signal into an RF signal that the TV can receive. This involves not only matching the technology but also adjusting the signal transmission path precisely.
2. Working mechanism of RF modulator
How does the RF modulator convert the baseband signal into an RF signal and ensure that these signals are suitable for long-distance transmission? The working mechanism is roughly as follows.
Baseband signal input
First, the baseband signal is the starting point of the entire modulation process. These signals usually come from DVD players, game consoles, cameras, or other audio and video devices. In actual operation, the operator must select a suitable signal source and connect it to ensure the quality of the input audio and video signals. Baseband signals usually represent audio and video information by voltage changes, so the quality of the signal directly affects the final output effect.
Modulation process
Modulation is the core function of the RF modulator, which is responsible for converting baseband signals into RF signals. The modulation process involves the following technologies:
Amplitude modulation (AM): During operation, adjusting amplitude modulation involves monitoring the amplitude changes of the carrier signal to ensure that it accurately reflects the changes in the baseband signal. The operator needs to adjust the equipment settings to match the increase or decrease in the signal, which is usually achieved through a knob or software control.
Frequency Modulation (FM): FM involves changing the frequency of the carrier to match the level changes of the baseband signal. The operator must carefully adjust the frequency control to ensure stable transmission of the signal at higher or lower levels.
Phase Modulation (PM): In phase modulation, the phase of the carrier signal is adjusted according to the amplitude or frequency changes of the baseband signal. This requires precise control of the phase change to ensure that the phase of the signal correctly reflects the characteristics of the baseband signal.
When choosing a modulation technique, the operator needs to make decisions based on the signal quality requirements, bandwidth limitations, and specific applications. These decisions are based on an understanding of the advantages and limitations of different modulation techniques.
Frequency Upconversion
After modulation, the RF modulator also needs to perform a frequency upconversion operation to increase the modulated signal to a higher transmission frequency. At this stage, it is necessary to ensure that the signal frequency is properly increased and the entire process is monitored to avoid any possible signal loss.
Output and Additional Functions
The modulated and frequency-upgraded RF signal is finally output from the RF modulator and can be transmitted through a cable or antenna. This step requires ensuring that all connections are correct, and may involve additional functions such as amplification, filtering, and impedance matching to optimize signal quality and compatibility with the transmission system.
3. Advantages and limitations of RF modulators
Advantages
High Compatibility: RF modulators are highly compatible with a variety of older devices. Many older TVs only have RF interfaces and lack modern HDMI or other video inputs. RF modulators convert modern digital signals into RF signals, allowing these old TVs to display current audio and video content. Users can simply connect the modulator's output to the TV's RF input, making it easy to use.
Easy Setup: Setting up RF modulators is typically straightforward. Users don't need a deep technical background for installation. Generally, it involves connecting cables and adjusting a few settings based on clear instructions. This simplicity is ideal for those with limited technical skills, enabling them to achieve complex signal conversions with minimal effort.
Limitations
Degraded Signal Quality: A major drawback of RF modulators is the potential introduction of noise and distortion during the modulation process, which can degrade signal quality. Small setting errors or device limitations can lead to poor picture or sound quality. Careful adjustment of amplitude, frequency, and phase settings is necessary to minimize this loss.
Resolution and Compatibility Limits: RF modulators generally support limited resolutions, which is noticeable when converting high-definition video signals. Users expecting high-definition content might find the image blurry or distorted. Additionally, some modern devices may not support video formats received via RF signals, limiting the scenarios where RF modulators can be used.
Interference Issues: RF signals can be interfered with by other electronic devices or strong electrical signals, especially in crowded channel environments. This interference can cause intermittent or lost video and audio signals. Operators might need to adjust the signal frequency or add shielding to reduce or avoid interference when using RF modulators.
4. What does the RF modulator do?
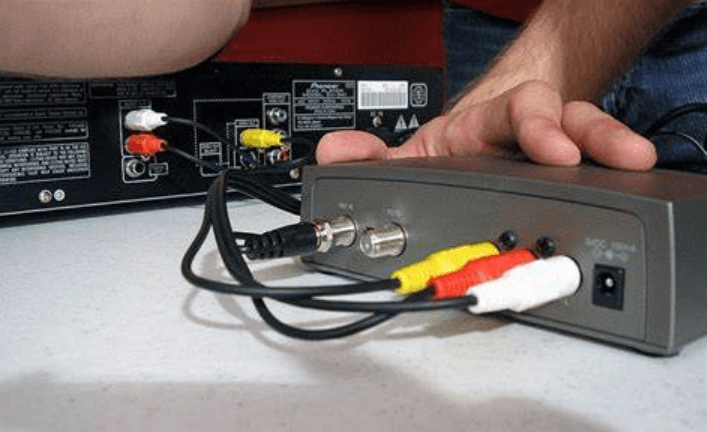

RF modulators play a key role in connecting and converting audio and video signals, especially when it comes to older TVs and other devices. These devices often only support radio frequency (RF) interfaces, while modern multimedia devices such as DVD players and game consoles output baseband signals.
The main function of an RF modulator is to convert baseband audio and video signals to RF signals for transmission over coaxial cable or radio waves. This conversion process is not only critical but also complex, involving multiple delicate operational steps and technical decisions.
Signal Conversion
In TVs that do not have modern HDMI or other advanced input jacks, RF modulators are able to convert signals from older devices (such as VCRs, DVD players, and game consoles) into a format that the TV can receive. This conversion process can preserve the life of older devices.
Modulation Techniques
Next, RF modulators use modulation techniques to adjust the characteristics of audio and video signals for RF transmission. This involves:
Frequency adjustment: The operator changes the frequency of the signal to match the requirements of RF transmission. This step requires careful adjustment to ensure that the signal can be effectively transmitted over the radio channel or coaxial cable.
Amplitude adjustment: Modifying the amplitude of the signal to reflect the strength of the baseband signal. Fine-tuning the amplitude helps maintain the integrity of the audio and video signals during transmission.
Phase Adjustment: The phase of the signal is also adjusted to ensure an accurate representation of the baseband signal characteristics. This precise control is necessary to avoid distortion and ensure clear signal reception.
5. Wide Application of RF Modulators
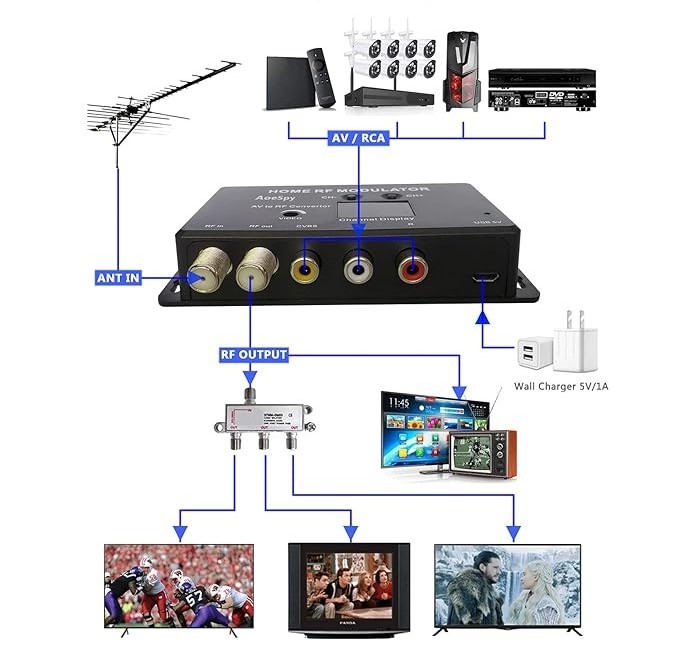
RF modulators convert baseband signals into RF (radio frequency) signals suitable for transmission by converting baseband signals into RF (radio frequency) signals. RF modulators convert baseband signals into RF (radio frequency) signals suitable for transmission by converting baseband signals into RF (radio frequency) signals. RF modulators are commonly used in the following applications:
TV broadcasting: In TV broadcasting, RF modulators are responsible for converting the audio and video signals from the studio into RF signals, ensuring that these signals can be transmitted to the home TV via radio waves or cable systems.
Cable TV distribution: In cable TV systems, RF modulators are used to distribute multi-channel audio and video signals to many subscribers via coaxial cables.
CCTV systems: In closed-circuit television (CCTV) systems, RF modulators enable video signals to be transmitted via RF to a monitoring center or recording device.
Home entertainment systems: In home entertainment systems, RF modulators allow older audio and video equipment, such as VCRs and DVD players, to be connected to modern TVs that do not have corresponding input ports.
Industrial control systems: In industrial control systems, RF modulators are used to wirelessly transmit critical sensor data and control signals, allowing engineers to remotely monitor and control complex machinery and production processes.
Test and measurement equipment: In telecommunications, aerospace, and research laboratories, RF modulators are used to drive measurement equipment such as spectrum analyzers and signal generators to provide precise test signals.
6. Conclusion
By converting baseband signals into RF signals, RF modulators enable various devices to adapt to complex and changing transmission requirements, ensuring effective signal transmission and high-quality output. The process of operating an RF modulator involves precise control of signal type, modulation technology, and transmission frequency, reflecting a high degree of technical expertise and operational complexity. Despite some limitations, such as possible signal quality loss and resolution limitations, RF modulators are still an important bridge between old equipment and modern technology.
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
1. What does an RF modulator do?
The core function of a radio frequency (RF) modulator is to convert the original audio or video signal into a radio frequency signal suitable for transmission over the air or cable. The key to this process is that the modulator encodes information onto high-frequency waves, allowing it to be transmitted over long distances and be recognized by the receiving device.
2. What is basic RF modulation?
Basic RF modulation involves combining information (such as sound or image data) with a high-frequency carrier signal. In this process, the original low-frequency information changes certain properties of the carrier (such as amplitude, frequency, or phase) in a specific way, so that the carrier can carry the information for effective transmission.
3. What are the different types of RF modulators?
- Amplitude modulator (AM modulator): transmits information by changing the amplitude (signal strength) of the carrier, suitable for simple broadcast transmission.
- Frequency modulator (FM modulator): encodes information by changing the frequency of the carrier, which is more stable to environmental noise and widely used in audio services.
- Phase modulator (PM modulator): information is encoded by changing the phase of the carrier, which is used in some professional communication systems.