Electronics Challenge: Male or Female Connectors
Connectors are not just about making physical links but it helps how well a system works, how reliable it is and how safe it is. High-quality connectors help keep signals clear and save power while poorly made ones can lead to system failures, data loss, and even safety hazards. One important idea in connectors is the difference between male and female connectors.This article focuses on the roles and features of male and female connectors in electronics. It explains how they fit together, where they’re used, and gives examples of each type. By looking at how the "gender" of these connectors influences their design and function, the article highlights their impact on the strength, reliability, and safety of electronic systems.
Catalog
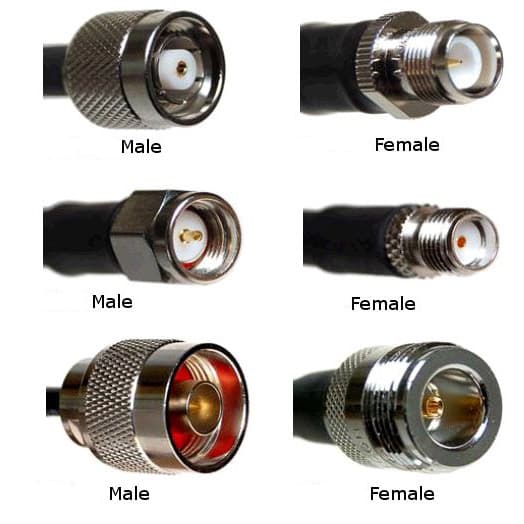

Figure 1: Male and Female Connectors
Differences Between Male and Female Connectors
Identifying Male and Female Connectors
Male and female connectors are distinct in their design, with each type playing a specific role in forming a stable connection.
Male Connectors: Commonly called "plugs," these connectors feature pins or protruding elements that extend outward. Their primary function is to be inserted into a compatible female connector.
Female Connectors: Also known as "sockets" or "jacks," these connectors have recessed areas or cavities designed to receive the male connector's protrusions.
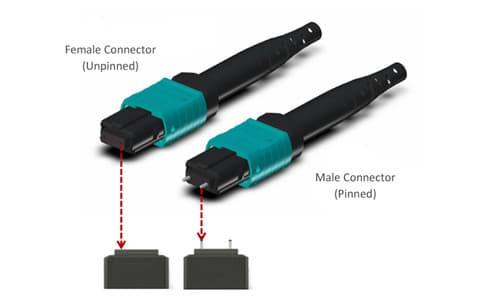
Figure 2: Male and Female Connector
Physical Features
The primary difference between male and female connectors lies in their structural design:
Male Connectors: The protruding parts, metallic pins or blades, extend from the connector body. These components fit snugly into the matching slots of a female connector, ensuring a tight connection that supports the flow of electricity or data.
Female Connectors: These have indentations or slots that are shaped to receive the male connector’s protrusions. Inside these indentations, conductive materials ensure proper contact with the male connector's pins or blades, completing the circuit.
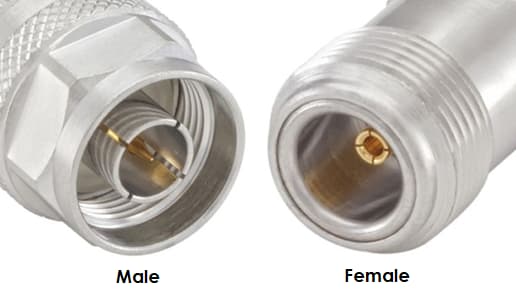
Figure 3: Male and Female Connector
How Male and Female Connectors Join?
The process of connecting these two types of connectors is often called "mating." This term, borrowed from biological reproduction, simply describes the joining of two electronic components to form a functional electrical connection. The mating process involves aligning the male connector with the female connector and inserting it until a secure connection is made. To prevent accidental disconnections, many connectors include a locking mechanism like a latch or clip.
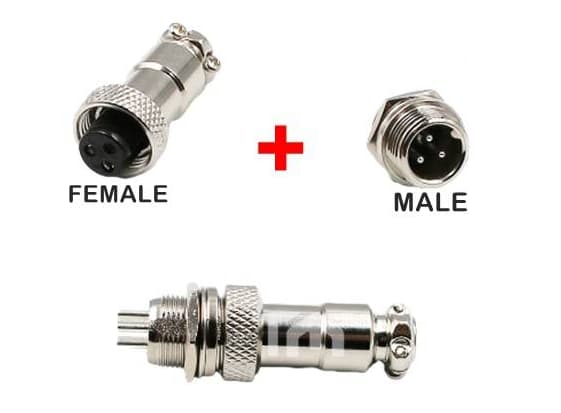

Figure 4: Male and Female Connectors Join
Uses of Male and Female Connectors
Male connectors serve as the starting point in an electrical system, channeling signals or power from a source to another device. They are found most at the ends of power cables, where they connect directly to the power source, such as in standard power cords used to plug devices into wall outlets. In data transmission, male connectors on USB or HDMI cables link computers, media players, or other electronic devices to output screens or peripherals. In audio and video setups, male connectors are good for connecting components like microphones, speakers, and mixers, often using cables with XLR or TRS male ends.
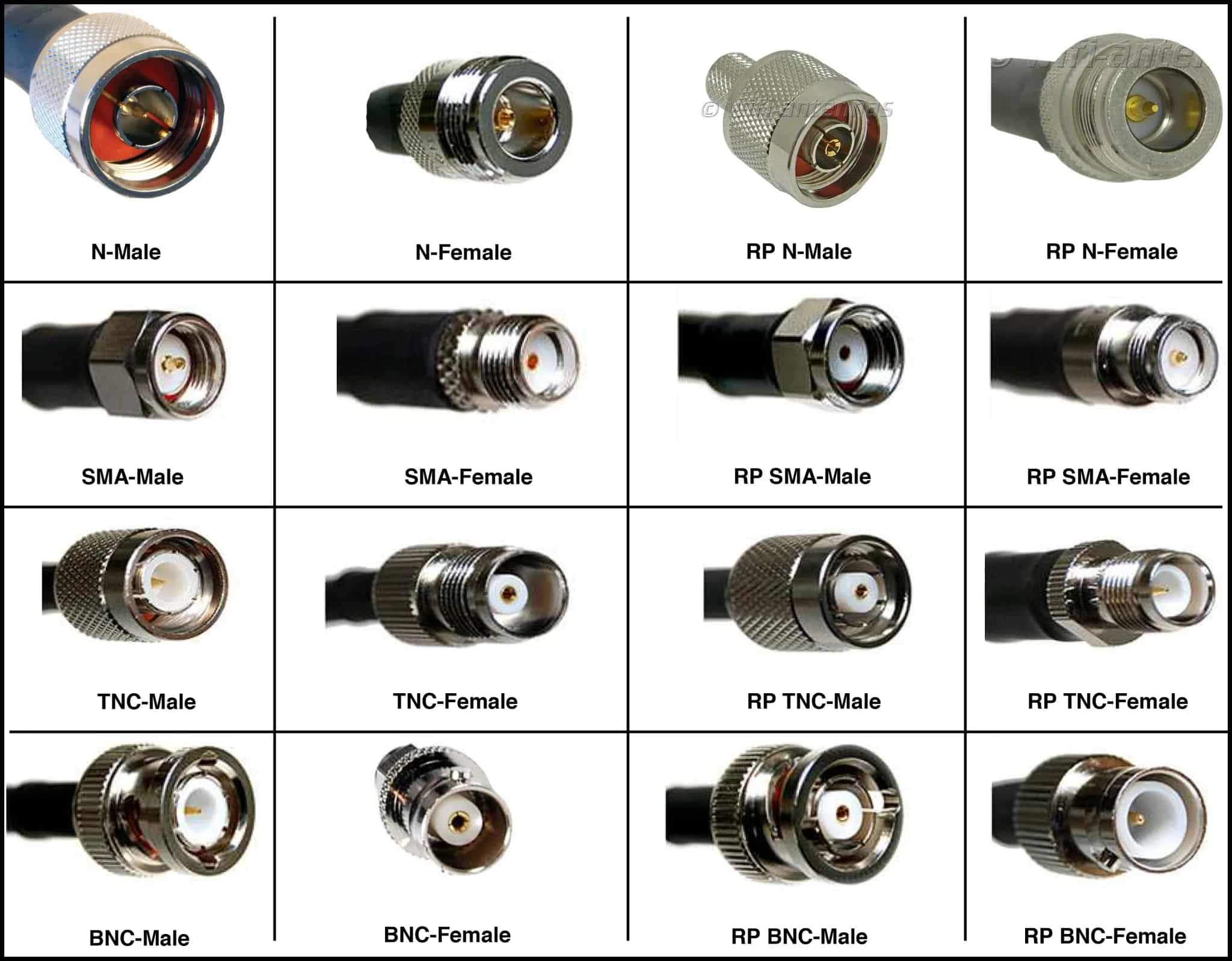

Figure 5: Male and Female Connectors
Female connectors are integrated into fixed installations within devices or systems, providing a stable docking point for male plugs. The conductive material inside these connectors completes the electrical circuit initiated by the male connector. They are standard in devices that require power from external sources, such as computers, televisions, and household appliances, where they interface with the male plugs of power cords. In networking and telecommunications, female connectors are used in routers, modems and servers for receiving data lines from male-ended cables. In complex systems like audiovisual setups or manufacturing equipment, female connectors are the receiving ends for multiple connections, ensuring seamless communication between different system components.
Examples of Male and Female Connectors
DC Barrel Power Jack and Plug
The DC barrel power jack and plug used to connect power. The plug, or male connector, has a central metal pin surrounded by an insulating ring. This lets it fit securely into the matching jack, or female connector, which is a hollow cylinder that holds the plug snugly. These connectors are categorized by exact measurements, like the outer diameter of the barrel and the size of the central pin. Getting these measurements right is need to making sure the connection is strong and reliable.
The plug is considered male, and the jack is seen as female. However, this can get confusing when different manufacturing standards or unusual designs are involved. For example, some jacks might have a male pin inside a female casing, flipping the usual roles. Similarly, some plugs might look female but actually work as male. This variation can make it tricky to identify the right connector without knowing the specific internal structure.
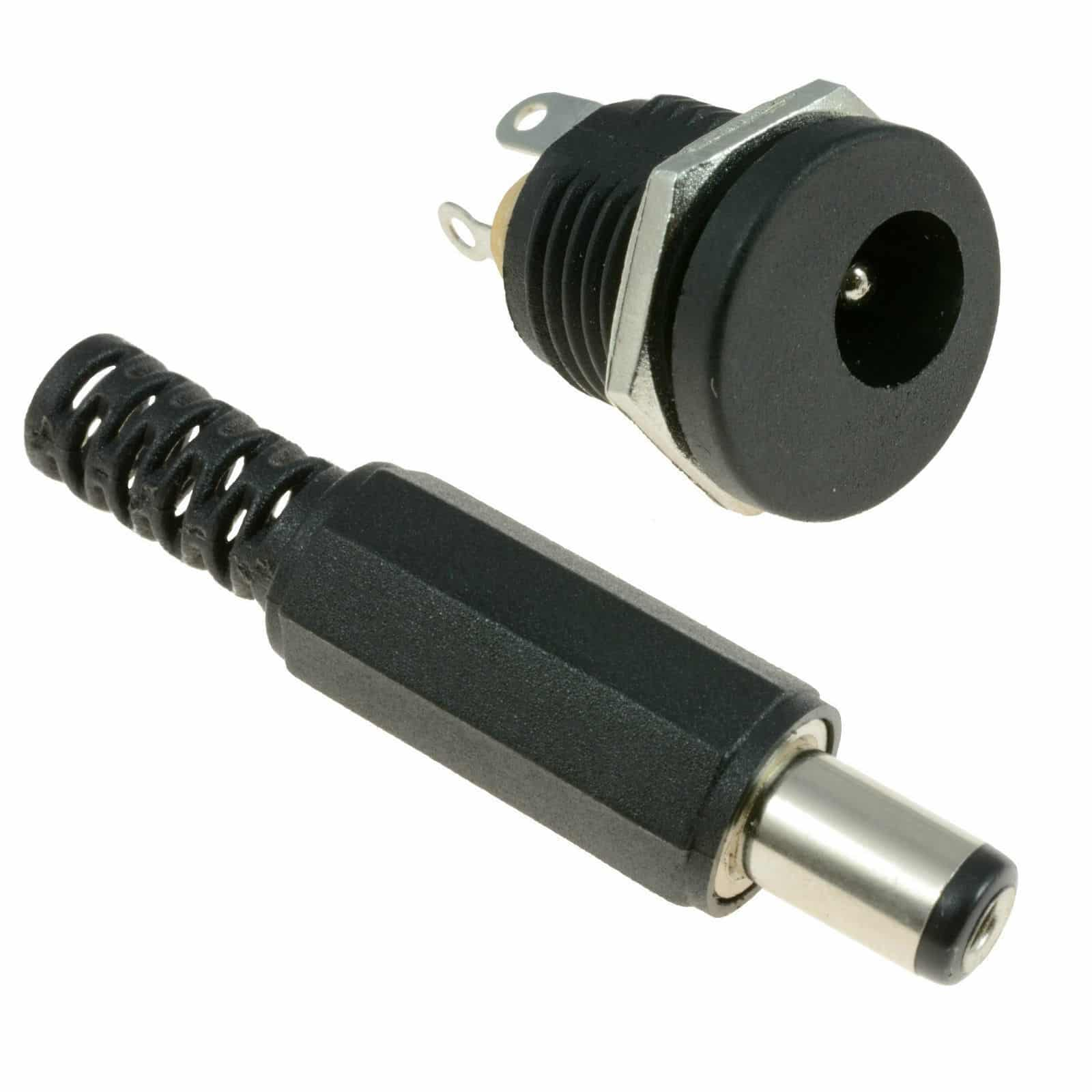

Figure 6: Male and Female DC Barrel Power
D-Sub Connectors
D-Sub connectors are used for sending signals and data in computers and telecommunications. They are easy to recognize by their D-shaped metal casing. The male D-Sub connector has pins that stick out, while the female one has sockets that match the pins. To connect them, you need to carefully line up the pins with the sockets for a secure connection. However, it can be tricky to tell whether a connector is male or female because metal covers often hide the pins and sockets, or the design might make it hard to see them.
A male D-Sub connector on a cable plugs into a female port on a computer. But identifying the right type can be difficult if the connectors are covered or if non-standard designs are used. This isn't just a small issue, plugging the wrong types together can cause signal problems, data loss, or even damage the connectors.
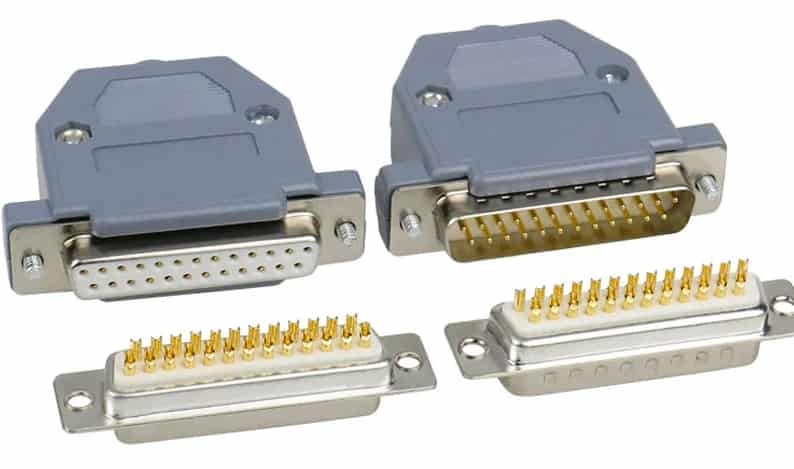

Figure 7: Female and Male D-Sub Connectors
When Gender is a Factor in Design
Sometimes, gender is important in designing products, as it can impact how well components work and how long they last.
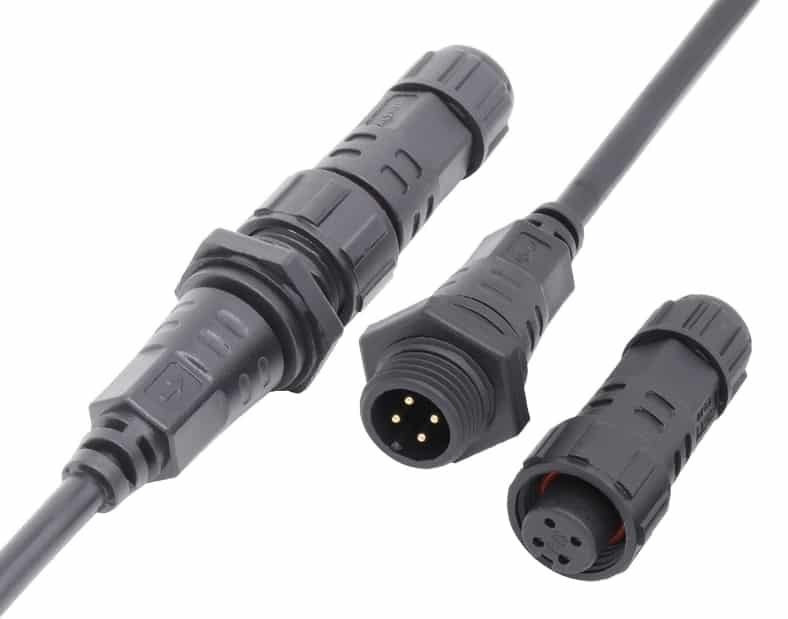

Figure 8: Male and Female Connector
Mounting Choices
In electronics, female connectors are often better for fixed setups because they last longer and stay cleaner. Their design hides the contact points, offering better protection against damage than male connectors, which have exposed parts that can wear out more easily. This is true for sensitive parts like motherboards, where broken connectors can be costly to fix. Female connectors, like those in RS232 serial ports are chosen for their strength, even though male connectors are more common. However, opinions differ on whether male coaxial connectors are less durable.
Reliability Concerns
When reliability is important, female connectors are often preferred for computers and other devices. This can sometimes clash with standard designs, leading to confusion when technicians find unexpected port types. Choosing female connectors in serial ports is a deliberate decision to move away from traditional male-dominated designs, aiming to boost reliability and reduce maintenance needs.
Power Connections
In power setups, design rules ensure that gender specifications aren't reversed, as doing so could expose live AC lines through male connectors, and illegal in many places for safety reasons. Devices needing strong mechanical support, like those linked to the power grid, often use male IEC connectors recessed into the mounting panel. This design meets safety standards and provides physical protection.
Safety Concerns
Safety is a major factor in deciding the gender of connectors. In places where electrical discharge is a concern, female connectors are used to cover male connectors, reducing the risk of accidental contact with live wires. This not only improves safety but also keeps the connection secure by shielding it from environmental damage.
Conclusion
This article offers a detailed look at male and female connectors, explaining how their design impacts the way electronic devices work. It covers everything from simple power plugs to more complex setups like those used in telecommunications. The choice between male and female connectors affects how efficient, reliable and safe a device is. It also points out the physical and functional differences between these connectors, as well as why female connectors are often chosen for fixed installations because they are more durable and offer better protection. It highlights the importance of considering the connector type when thinking about safety standards to prevent electrical accidents. As technology advances, understanding these details becomes important for engineers and designers who want to create the best electronic systems while following safety rules. This guide provide insights into how the type of connector used can influence the performance and safety of modern devices.
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
1. Is female connector positive or negative?
Female connectors are characterized as the receptacle or socket into which the male connector plugs. In terms of electrical polarity (positive or negative), female connectors can be either, depending on the circuit design. It is best to consult specific product documentation to determine the polarity of a particular connector.
2. What is the new name for male and female connectors?
In recent efforts to adopt more inclusive and neutral terminology, male and female connectors are increasingly referred to as "pins" and "sockets." The term "pin" refers to the protruding part that inserts into another component, while "socket" describes the receptacle that receives the pin.
3. Are battery connectors male or female?
Battery connectors can be either male or female. The design depends on the battery and the device it connects to. For instance, a battery may have a male connector that fits into a female socket on the device, or vice versa. This setup ensures proper alignment and polarity matching, good for safety and function.
4. What is the difference between male and female coupling?
The primary difference between male and female coupling lies in their design and function in a mechanical system. Male couplings have protruding elements designed to fit into another component. In contrast, female couplings consist of a cavity designed to accept and hold the male part. This distinction ensures secure and effective connections in various applications, from plumbing to electrical systems.
5. Is ESC male or female connector?
The type of connector on an Electronic Speed Controller (ESC) can be either male or female, depending on its design and the requirements of the device it connects to. An ESC will have a male connector to link with a female connector on a motor or battery. However, configurations might vary, so you may refer to the specific ESC model's specifications.