Understanding the PCF8574A Expander: Datasheet, Pin Configuration, and Alternatives
The PCF8574A I/O expander is a basic tool for you aiming to broaden the GPIO capacity of microcontroller systems via I2C communication. As a versatile 8-bit I/O expander, the PCF8574A integrates seamlessly with I2C interfaces, allowing it to support both digital input and output functionalities without requiring additional pins. This article explores the PCF8574A's key features, design considerations, and practical applications, highlighting its role in streamlining system designs by reducing wiring complexity and improving operational reliability.Catalog

Pinout of PCF8574A
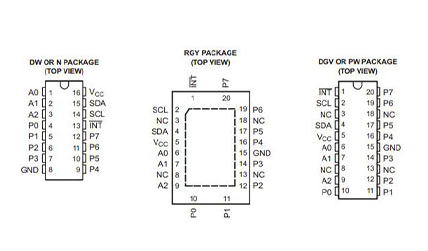
|
NAME |
PIN |
TYPE |
DESCRIPTION |
|
A[0..2] |
RGY: 6, 7, 9 |
I |
Address inputs 0 through 2. Connect directly to Vcc or
ground. Pullup resistors are not needed. |
|
DGVR or PW: 6, 7, 9 |
|||
|
DW or N: 1, 2, 3 |
|||
|
GND |
RGY: 15 |
— |
Ground |
|
DGVR or PW: 15 |
|||
|
DW or N: 8 |
|||
|
INT |
RGY: 1 |
O |
Interrupt output. Connect to Vcc through a pullup
resistor. |
|
DW or N: 13 |
|||
|
NC |
RGY: 3, 8, 13, 18 |
— |
Do not connect |
|
DGVR or PW: 3, 8, 13, 18 |
|||
|
P[0..7] |
RGY: 10, 11, 12, 14, 16, 17, 19, 20 |
I/O |
P-port input/output. Push-pull design structure. |
|
DGVR or PW: 10, 11, 12, 14, 16, 17, 19, 20 |
|||
|
DW or N: 9, 10, 11, 12 |
|||
|
SCL |
RGY: 2 |
I |
Serial clock line. Connect to Vcc through a pullup
resistor. |
|
DGVR or PW: 2 |
|||
|
DW or N: 14 |
|||
|
SDA |
RGY: 4 |
I/O |
Serial data line. Connect to Vcc through a pullup
resistor. |
|
DGVR or PW: 4 |
|||
|
DW or N: 15 |
|||
|
Vcc |
RGY: 5 |
— |
Voltage supply |
|
DGVR or PW: 5 |
|||
|
DW or N: 16 |
PCF8574A Design Documentation
Schematic Symbol
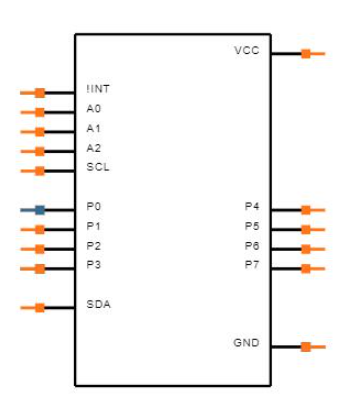
PCB Footprint
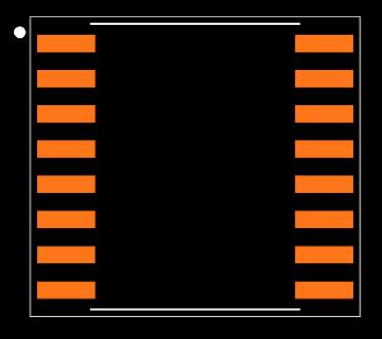
Exploring the PCF8574A I/O Expander
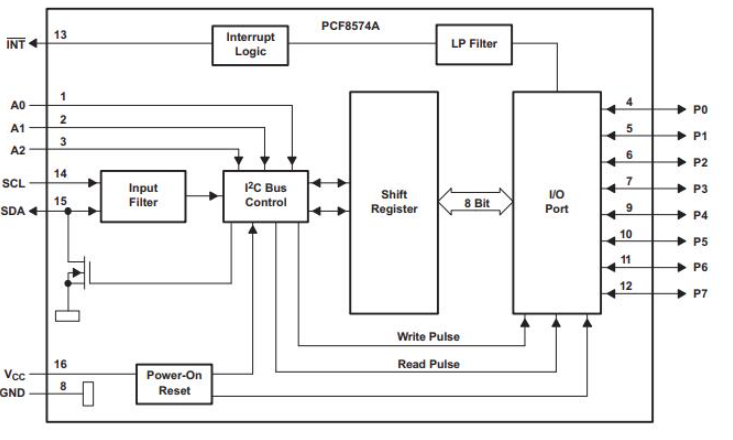
The PCF8574A is an 8-bit I/O expander for the I2C bus, known for its versatility in integrating with different microcontroller families. Employing I2C lines (SCL and SDA), broadens input/output options, especially beneficial when microcontroller GPIO pins are sparse.
The I2C interface uses a two-wire communication protocol, allowing multiple devices on the same bus. The PCF8574A manages this by utilizing SCL (Serial Clock Line) and SDA (Serial Data Line) for synchronized data transfer. Each device on the bus has a unique address, ensuring flexibility and scalability. Configuration of the PCF8574A is achieved through distinct addressing, enabling the coexistence of several devices on one bus. This feature is advantageous in diverse settings, such as industrial automation systems or multiplexed signal arrays, where numerous I/O expanders are needed.
When applying the PCF8574A, careful consideration of I2C bus speed and pull-up resistors supports reliable functionality. In home automation systems, it simplifies wiring and enhances functionality, proving its adaptability. This expander shines in complex interface projects, such as control panels handling multiple buttons and indicators. It elevates microcontroller capabilities, fostering advanced designs without increasing expenses, and showcasing its role in inventive applications.
Technical Specifications
Here's a table summarizing the technical specifications, attributes, and parameters of the Texas Instruments PCF8574ADW, along with similar parts.
|
Type |
Parameter |
|
Lifecycle Status |
ACTIVE (Last Updated: 6 days ago) |
|
Factory Lead Time |
6 Weeks |
|
Mount |
Surface Mount |
|
Mounting Type |
Surface Mount |
|
Package / Case |
16-SOIC (0.295", 7.50mm Width) |
|
Number of Pins |
16 |
|
Weight |
420.395078 mg |
|
Number of I/Os |
8 |
|
Operating Temperature |
-40°C to 85°C |
|
Packaging |
Tube |
|
JESD-609 Code |
e4 |
|
Pbfree Code |
Yes |
|
Part Status |
Active |
|
Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL) |
1 (Unlimited) |
|
Number of Terminations |
16 |
|
ECCN Code |
EAR99 |
|
Terminal Finish |
Nickel/Palladium/Gold (Ni/Pd/Au) |
|
Voltage - Supply |
2.5V to 6V |
|
Terminal Position |
Dual |
|
Terminal Form |
Gull Wing |
|
Peak Reflow Temperature |
260°C |
|
Supply Voltage |
5V |
|
Terminal Pitch |
1.27mm |
|
Base Part Number |
PCF8574 |
|
Pin Count |
16 |
|
Output Type |
Push-Pull |
|
Power Supplies |
3V, 5V |
|
Interface |
I2C |
|
Number of Ports |
1 |
|
Number of Bits |
8 |
|
Clock Frequency |
100kHz |
|
Supply Current - Max |
0.1mA |
|
Interrupt Output |
Yes |
|
Current - Output Source/Sink |
1mA / 25mA |
|
Features |
POR (Power-On Reset) |
|
Height |
2.65mm |
|
Length |
10.3mm |
|
Width |
7.5mm |
|
Thickness |
2.35mm |
|
REACH SVHC |
No SVHC |
|
Radiation Hardening |
No |
|
RoHS Status |
ROHS3 Compliant |
|
Lead Free |
Yes |
Features
|
Feature |
Description |
|
Low Standby-Current Consumption |
10 μA Max, IC to Parallel-Port Expander |
|
Open-Drain Interrupt Output |
Allows the device to trigger an interrupt on a low signal |
|
Microcontroller Compatibility |
Compatible with most microcontrollers |
|
Latched Outputs with High-Current Drive |
Capable of directly driving LEDs with latched output
states |
|
Latch-Up Performance |
Exceeds 100 mA per JESD 78, Class II standards for
reliability and durability |
Functional Block Diagram
Areas of Application
The PCF8574A is widely used across various fields, primarily owing to its ability to enhance GPIO in systems where digital pin resources are scarce. Incorporating this component can elevate both system performance and capabilities.
Telecom Shelters
Within telecom shelters, the PCF8574A enhances communication equipment's efficiency by easily managing multiple indicators and relays. This occurs without the need for major modifications to existing setups, allowing for better monitoring and management, which can boost overall reliability.
Servers and Data Centers
In server settings, optimizing cooling systems and power distribution is a constant demand. The PCF8574A offers precise control over fan speeds and status LEDs, which aids in lowering energy usage and extending the lifespan of the equipment.
Networking Equipment
Routers and similar networking devices gain from the PCF8574A's superior I/O capabilities. It manages indicators, system resets, and network traffic lights, thus supporting strong network performance management. This ensures service continuity, which contributes to client satisfaction.
Personal Computers and Consumer Electronics
PCs frequently need additional GPIO for peripherals. The PCF8574A facilitates connecting additional sensors or input devices without necessitating more intricate motherboard designs, thereby streamlining upgrades and expansions.
Industrial Automation
Precision in control and machinery monitoring is vital for industrial automation. The PCF8574A enriches I/O expansion for PLC systems, enhancing the regulation of production operations. By boosting signal accuracy and response times, it aids in sustaining superior production quality and safety.
Devices with Limited GPIO
For devices like single-board computers that possess limited GPIO, this component offers a viable solution. It supports the addition of numerous control interfaces without the need for expensive hardware upgrades, which can significantly reduce costs and encourage innovation in prototyping and development.
Typical Use
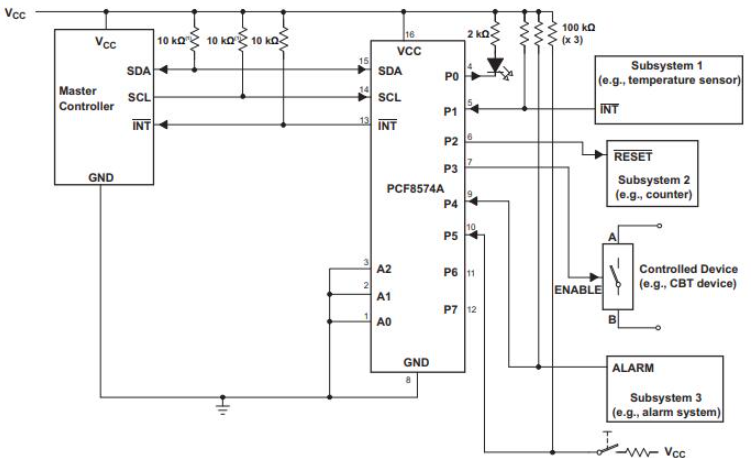
Comparing PCF8574A and PCF8574
The PCF8574A and PCF8574 serve as I2C-bus I/O expanders, and they share common features but diverge in the fixed segment of their slave addresses. This variation enables the connection of up to eight devices for each expander on a single I2C-bus, allowing for 16 expanders in total. This setup supports up to 128 possible input/output connections.
Package
Manufacturer
Texas Instruments (TI) plays a remarkable role in the global semiconductor scene. It specializes in crafting analog and embedded processing chips, initial to numerous technological innovations. TI offers creative solutions across a wide array of sectors automotive. industrial, and consumer electronics. The company employs an experienced team of over 30,000 individuals, cultivating a lively and inventive workforce. TI's focus on a supportive and collaborative atmosphere nurtures creativity, encouraging a flow of new ideas and skills. TI frequently share their insights, promoting ongoing learning and growth.
Datasheet PDF
PCF8574ADW Datasheets:
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
1. What is PCF8574A?
The PCF8574A functions as an 8-bit I/O expander for the I2C bus, offering remote I/O extension with operational voltages from 2.5 V to 6 V. It combines eight quasi-bidirectional ports with a 100 kHz I2C interface and includes interrupt abilities. This device finds its place in projects where integrating peripheral components into a microcontroller feels like an art of necessity, sidestepping the need for numerous pins. Efficiently expanding systems is a dance of creativity and control, balancing multiple peripherals with a few communication lines. This streamlines the design process, elegantly reducing complexity.
2. What is an I2C device?
I2C, known as Inter-Integrated Circuit, is a versatile serial communication protocol that makes use of two lines a clock line and a data line. This framework enables multiple devices to talk in a master-slave setup, simplifying both design and wiring. The charm of I2C lies in its flexibility, allowing up to 127 devices on a single bus, each with unique addresses. Its allure comes from low power usage and straightforward implementation.
3. What is I/O Expander?
An I/O expander subtly yet powerfully broadens the input/output capacity of a microcontroller system while keeping reduced I/O needs. Harmonizing with the primary controller helps to conserve kernel resources and thoughtfully control development costs. In countless practical scenarios, you can encounter the hurdle of limited GPIO pins on microcontrollers. I/O expanders offer a graceful solution by providing extra functionality without extensive redesigns, fostering adaptable, scalable circuitry in embedded systems.