Comparing 2N3904 and BC547 Transistors: What Sets Them Apart?
In this article, we dig into the detailed comparison between two popular NPN transistors, the 2N3904 and BC547. While both serve as staples in the electronics world, their subtle differences in electrical properties and performance characteristics influence their optimal applications within circuits. By understanding these distinctions, you can make informed decisions that improve circuit functionality and resilience. Join us as we break down the unique aspects of each transistor, guiding you through the intricacies of component selection to elevate your design's efficiency and reliability.Catalog

Exploring the 2N3904 vs. BC547
Understanding how two components stack up against each other offers valuable insights into their characteristics and potential interchangeability. Both the 2N3904 and BC547 are popular transistors, widely recognized in the electronic community. Here's a closer look at their unique features and potential applications.
2N3904 Features
|
Feature |
Specification |
|
Type |
Bi-Polar NPN Transistor |
|
DC Current Gain (hFE) |
300 (max) |
|
Continuous Collector Current (IC) |
200 mA |
|
Base-Emitter Voltage (VBE) |
6 V |
|
Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCE) |
40 V |
|
Collector-Base Voltage (VCB) |
60 V |
|
Package |
TO-92 |
BC547 Features
|
Feature |
Description |
|
Type |
Bi-Polar NPN Transistor |
|
DC Current Gain (hFE) |
Up to 800 |
|
Continuous Collector Current (IC) |
100 mA |
|
Emitter-Base Voltage (VBE) |
6 V |
|
Base Current (IB) |
5 mA (maximum) |
|
Package |
TO-92 |
Comparing the Pinouts of 2N3904 and BC547
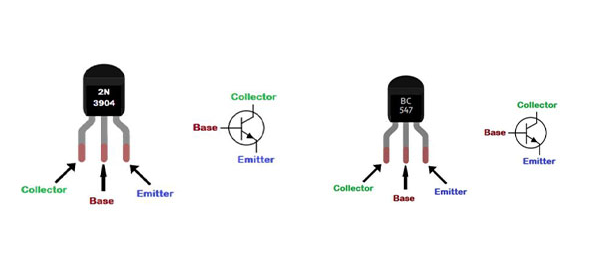
|
Transistor |
Package |
Pin 1 |
Pin 2 |
Pin 3 |
|
2N3904 |
TO-92 |
Emitter |
Base |
Collector |
|
BC547 |
TO-92 |
Collector |
Base |
Emitter |
Comparison of Ratings & Characteristics
|
Ratings &
Characteristics |
2N3904 |
BC547 |
|
Collector-Emitter Voltage (Vceo) |
40V |
50V |
|
Collector Current (Ic) |
200mA |
100mA |
|
Total Device Dissipation (PD) |
625mW |
500mW |
|
DC Current Gain (hFE) |
30 to 300 |
110 to 800 |
|
Frequency (fT) |
300 MHz |
300 MHz |
2N3904 and BC547 Substitutes
Alternatives for 2N3904
- BC548
- BC547
- BC636
- BC639
- 2N2222A
- 2N2222
- 2N2369
- 2N3055
- 2N3906
- 2SC5200
Alternatives for BC547
- BC548
- BC549
- 2N2222
- 2N3904
- 2N4401
- BC337
Replacing BC547 with 2N3904
Switching out a BC547 transistor with a 2N3904 is feasible under specific conditions, mostly when the load voltage remains below 40V. A major aspect here is acknowledging their distinct current handling capabilities. The BC547 generally manages up to 100mA, and ensuring the load stays within this limit is ultimate for maintaining circuit stability.
Transistors such as BC547 and 2N3904 are basic to electronic circuits, serving roles in switching and amplification. When selecting a substitute, consider aspects like current gain (Hfe), collector-emitter voltage (Vce), and power dissipation. These attributes directly affect performance and compatibility. You can frequently engage in diverse testing scenarios to confirm reliable functioning.
When integrating a 2N3904, it's wise to reassess circuit conditions to prevent overheating issues through effective thermal management. Testing under practical conditions, involving different load scenarios and environmental variables, yields insights that purely notional calculations may overlook. The choice between these transistors can also be swayed by factors like availability and cost. Both BC547 and 2N3904 are common, yet project-specific budgets and supply chain dynamics often influence the selection. Conducting step-by-step testing and examining circuit performance after replacement can provide a deeper understanding of the effects during the transition.
Replacing 2N3904 with BC547
Substituting the 2N3904 with the BC547 can be practical when the load stays under 100mA. Both are general-purpose NPN transistors, yet subtle distinctions in their features influence their use in various situations. Careful consideration of collector current variations is active, as these affect circuit performance.
•Collector Current: The 2N3904 supports up to 200mA of collector current. The BC547 accommodates up to 100mA. When load demands are consistently below this threshold, the BC547 can be effective. Monitoring the load to ensure it remains under this limit helps maintain circuit integrity and avoid failures.
•Collector-Emitter Voltage: Both models work within a collector-emitter voltage range of approximately 45-60V. Confirming that specific application voltage needs align with these parameters enhances durability and long-term reliability.
•Thermal Management: Handling thermal aspects is remarkable, especially in prolonged operations or tight spaces. Proper heat dissipation through heatsinks or cooling methods can mitigate overheating risks encountered when components operate near their limits.
•Amplification Considerations: The current gain (beta) differs between these transistors. The BC547 typically offers higher gain, which may be advantageous or challenging depending on amplification needs. Insights gleaned from practical experience reveal how this factor influences signal amplification for optimal results.
Conclusion
In sum, the 2N3904 and BC547 each hold distinct advantages, determined by their specific current, voltage capacities, and amplification properties. Selecting the right transistor is more than just matching technical specifications; it requires a comprehensive understanding of each component's distinctions to meet a circuit’s precise demands. Through thoughtful evaluation and practical insights, this article has highlighted key considerations that will support your journey in optimizing electronic designs. Whether for switching or amplification, these transistors offer versatile solutions tailored to your engineering goals.
Datasheet PDF
2N3904 Datasheets:
2N3904 Preliminary Datasheet.pdf
2N2222A Datasheets:
2N2222 Datasheets:
2N3055 Datasheets:
2N3906 Datasheets:
2N3906 Preliminary Datasheet.pdf
2SC5200 Datasheets:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Is there a 2N3904 equivalent transistor?
Transistors like the 2N2222, 2N4401, 2N2907, and BC547 offer comparable functionality to the 2N3904. These components cater to a spectrum of electronic needs. Factors influencing selection may include frequency response, current handling, and gain characteristics. Experimentation is often part of the process to align with the circuit's unique demands.
2. What does a BC547 do?
The BC547, an NPN transistor, finds use in both switching and amplification. Positioned strategically after the load, it serves various educational and commercial applications. Its prowess in switching emphasizes the art of load placement in circuit design, reflecting a blend of theory and practicality.
3. What is the equivalent of a BC547 transistor?
Several transistors equate to the BC547, such as BC548, BC549, BC636, BC639, and 2N2222 (available in TO-92 and TO-18 packages), along with 2N2369, 2N3055, and 2N3904. Choosing the right one necessitates an appreciation of distinct electrical characteristics and mechanical dimensions. This aids in ensuring circuit compatibility and integrity.
4. How do you know if a transistor is working?
To assess a transistor's condition, attach a multimeter's positive lead to the BASE and the negative to the EMITTER. For an operational NPN transistor, anticipate a voltage drop between 0.45V and 0.9V. A PNP transistor should display "OL" for "Over Limit." This practice highlights the significance of regular checks in maintaining electronic efficiency and reliability.