2N6488 Transistor: Specifications and Datasheet
This article explores the 2N6488 transistor, a robust and versatile NPN silicon epitaxial-base device renowned for its durability and optimal performance in power and low-frequency switching scenarios. Renowned for its efficiency and reliability, this transistor is integral to numerous electronic circuits, garnering appreciation. Its adaptability makes it an important component in innovative electronic design, ensuring it remains a staple in technological advancements.Catalog
Overview of the 2N6488
The 2N6488 transistor, held within a TO-220 plastic case, is recognized for its dependable use in power linear and low-frequency settings. This package is favored in the industry, merging practicality and efficiency, suitable for diverse situations. The design supports efficient heat dissipation, influencing the durability and function of transistors. The 2N6488 thrives in power linear applications due to its robust build and thermal capabilities. It ensures consistent current and voltage management for stability in circuits. This reliability shines in audio amplifiers and regulated power supplies, where handling varying loads without losing performance is needed.
In the low-frequency tasks, the 2N6488 demonstrates impressive adaptability and performance. Its capacity to handle signals with minimal distortion highlights its strength. Thermal output management is central when working with the 2N6488. Using effective heat sinks and thermal compounds aids in optimizing heat transfer. These are need to prevent overheating, which can impair functionality and lessen the component’s lifespan. An emerging view in the field is adapting traditional components like the 2N6488 for innovative uses. As technology advances, incorporating these into hybrid, energy-efficient systems is trending. This method leverages the 2N6488’s established reliability while addressing modern needs for sustainability and energy efficiency.
2N6488 Equivalents
• 2N60
• 2N600
• 2N6000
• 2N6001
• 2N6002
• 2N6491
2N6488 Pin Configuration
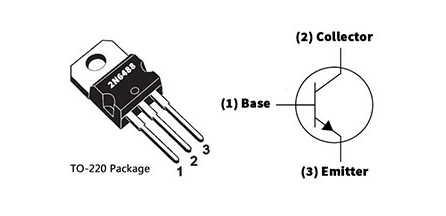
2N6488 Symbol, Footprint, and CAD Model

Features of the 2N6488
Enhancing Signal Precision
The 2N6488 transistor boasts a notable DC current gain alongside impressive bandwidth. These qualities elevate its effectiveness in scenarios demanding high-fidelity audio amplification and smooth switching operations. Many often delight in leveraging these attributes to minimize signal distortion in complex systems, ensuring clarity and precision.
Efficient Thermal Design
Encased in a streamlined TO-220 package, the 2N6488 promotes thermal efficiency and straightforward installation. Its structure adeptly facilitates heat dissipation for averting overheating in high-power applications. Many prefer this package for its adept handling of heat and compact form.
Commitment to Sustainability
The 2N6488 conforms to RoHS standards, highlighting a design considerate of environmental well-being by minimizing harmful substances. With growing importance in contemporary product innovation, this alignment complements global ecological goals.
Resilience in Voltage Management
Offering a collector-emitter breakdown voltage of 80V, the 2N6488 stands resilient in high-voltage settings. This characteristic earns appreciation when dependable performance under pressure is imperative. Industry frequently select such components for their capacity to endure substantial voltage variations.
Applications of the 2N6488 Transistor
Power Amplification in Audio Systems
The 2N6488 transistor stands out in audio systems where it plays a role in power amplification. It provides remarkable performance while driving speakers and audio components by efficiently managing current and voltage levels. This ensures a sound output that is both clear and free from distortion. Audio often favor transistors like the 2N6488 for crafting Class AB amplifier circuits. They appreciate its ability to deliver consistent thermal stability and efficiently dissipate heat, enhancing audio quality.
Low-Frequency Switching Operations
Exhibiting robustness in low-frequency switching tasks, the 2N6488’s versatility becomes evident. It is often utilized in circuits requiring precise control, such as in motor drivers and other electromechanical systems. Many opting for transistors like the 2N6488 can achieve steady performance in environments where long-term reliability is a primary consideration.
2N6488 Specifications
|
Type |
Parameter |
|
Lifecycle Status |
OBSOLETE (Last Updated: 3 days ago) |
|
Package / Case |
TO-220AB |
|
Supplier Device Package |
TO-220AB |
|
Current-Collector (Ic) (Max) |
15A |
|
Operating Temperature |
-65°C to 150°C TJ |
|
Published |
2007 |
|
Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL) |
1 (Unlimited) |
|
Min Operating Temperature |
-65°C |
|
Max Power Dissipation |
1.8W |
|
Base Part Number |
2N6488 |
|
Element Configuration |
Single |
|
Gain Bandwidth Product |
5MHz |
|
Collector Emitter Voltage (VCEO) |
3.5V |
|
DC Current Gain (hFE) (Min) @ Ic, Vce |
20 @ 5A 4V |
|
Vce Saturation (Max) @ Ib, Ic |
3.5V @ 5A, 15A |
|
Frequency - Transition |
5MHz |
|
Emitter Base Voltage (VEBO) |
5V |
|
Lead Free |
Contains Lead |
|
Mounting Type |
Through Hole |
|
Number of Pins |
3 |
|
Collector-Emitter Breakdown Voltage |
80V |
|
hFE/Min |
20 |
|
Packaging |
Tube |
|
Part Status |
Obsolete |
|
Max Operating Temperature |
150°C |
|
Voltage - Rated DC |
80V |
|
Current Rating |
15A |
|
Polarity |
NPN |
|
Power - Max |
1.8W |
|
Transistor Type |
NPN |
|
Max Collector Current |
15A |
|
Current - Collector Cutoff (Max) |
1mA |
|
Voltage - Collector Emitter Breakdown (Max) |
80V |
|
Collector Base Voltage (VCBO) |
90V |
|
RoHS Status |
Non-RoHS Compliant |
2N6488 Alternatives
|
Part
Number |
Manufacturer |
Package |
Polarity |
Collector Emitter Breakdown
Voltage |
Voltage - Collector Emitter
Breakdown (Max) |
Max Collector Current |
Frequency Transition |
Collector Emitter Saturation
Voltage |
hFE Min |
|
2N6488 |
ON Semiconductor |
TO-220-3 |
NPN |
80 V |
80V |
15 A |
5MHz |
3.5 V |
20 |
|
BD243B |
ON Semiconductor |
TO-220-3 |
NPN |
80 V |
80V |
3 A |
3MHz |
1.2 V |
25 |
|
TIP31B |
ON Semiconductor |
TO-220-3 |
NPN |
80 V |
80V |
6 A |
- |
1.5 V |
15 |
|
BDW42 |
ON Semiconductor |
TO-220-3 |
NPN |
100 V |
- |
15 A |
4MHz |
- |
- |
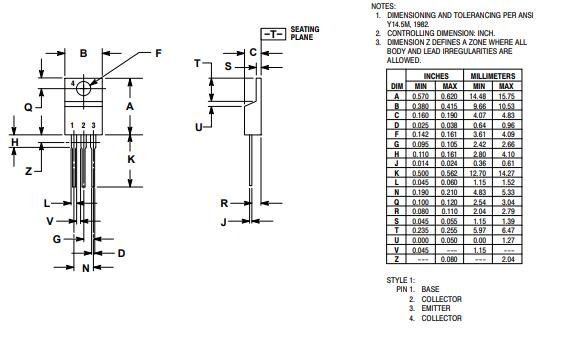
2N6488 Packaging
2N6488 Manufacturer Information
ON Semiconductor delivers solutions that are both innovative and mindful of energy use, carving out a leading position in electronics. Its extensive reach across the globe supports diverse applications including automotive, industrial, and consumer electronics. This wide influence keeps the company at the helm of tech progress. As we look ahead, pondering how ON Semiconductor can balance ongoing innovation with sustainability is intriguing. This interplay of rapid tech growth and environmental stewardship poses both hurdles and new paths. The firm's prowess in forecasting and adapting to future industry trends will shape its long-term success.
Datasheet PDF
2N6488 Datasheets:
Multiple Devices 19/Jun/2009.pdf
BD243B Datasheets:
Lead Frame Dimensions 29/Nov/2007.pdf
Tape and Box/Reel Barcode Update 07/Aug/2014.pdf
Mult Device EOL 19/May/2017.pdf
TIP31B Datasheets:
TIP31(A,B,C), TIP32(A,B,C).pdf
Lead Frame Dimensions 29/Nov/2007.pdf
